 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effect of Polypropylene Fiber on the Unconfined Compressive Strength of Loess with Different Water Content
1
College of Geological Engineering and Geomatics, Chang’an University, Xi’an, 710054, China
2
Ningxia Institute of Survey and Monitoring of Land and Resources, Yinchuan, 750002, China
* Corresponding Author: Haiman Wang. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(4), 1699-1814. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.023805
Received 16 May 2022; Accepted 18 July 2022; Issue published 01 December 2022
Abstract
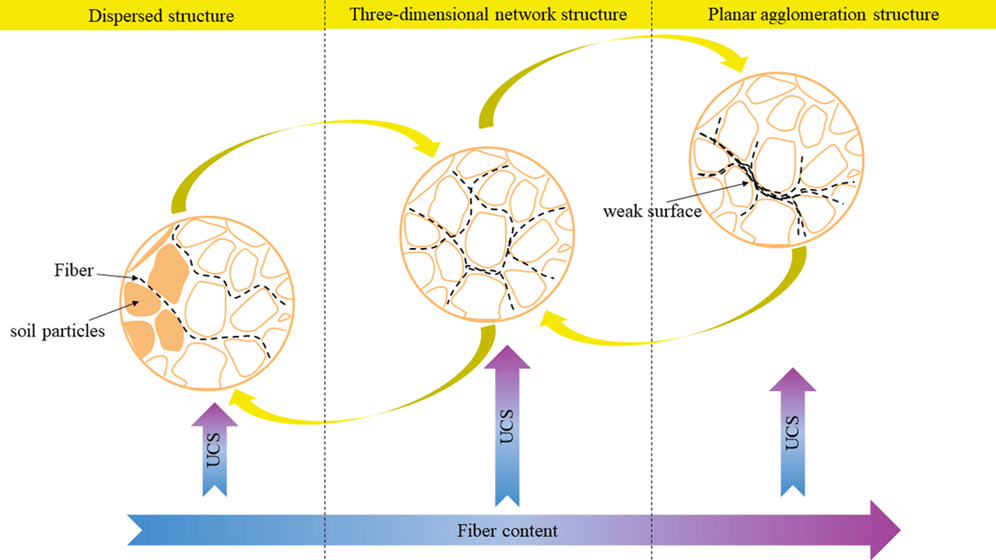
Fiber-reinforced soils have been of great interest to experimenters for building foundations’strength performance, time, and economy. This paper investigates the effects of water content and polypropylene fiber dosage and length on loess’s unconfined compressive strength (UCS) according to the central composite response surface design test procedure. The water content is 11%–25%, the mass ratio of fiber to soil is 0.1%–0.9%, and the fiber length ranges from 6–18 mm. The response surface method (RSM) developed full quadratic models of different variables with response values. After analysis of variance (ANOVA), the mathematical model developed in this study was statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05) and applicable to the optimization process. The optimization results showed that the optimal water content values, fiber amount, and fiber length were 16.41%, 0.579%, and 14.90 mm, respectively. The unconfined compressive strength of the optimized specimens was increased by 288.017 kPa. The research results can reference the design and construction of fiber-reinforced soil in practical projects such as road base engineering and foundation engineering.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools