 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Green Hydrothermal Synthesis and Applications of Sorbus pohuashanensis/Aronia melanocarpa Extracts Functionalized-Au/Ag/AuAg Nanoparticles
1
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Resource Utilization, Key Laboratory of Forest Plant Ecology Ministry of
Education, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 150040, China
2
School of Forestry, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 150040, China
3
Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Ecological Utilization of Forestry-Based Active Substances, Harbin, 150040, China
4
National Engineering Laboratory of Bio-Resource Eco-Utilization, Harbin, 150040, China
* Corresponding Authors: Zhiguo Liu. Email: ; Liqiang Mu. Email:
# These Authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: New Insights on Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Agricultural Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(4), 1807-1821. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.023721
Received 17 June 2022; Accepted 11 August 2022; Issue published 01 December 2022
Abstract
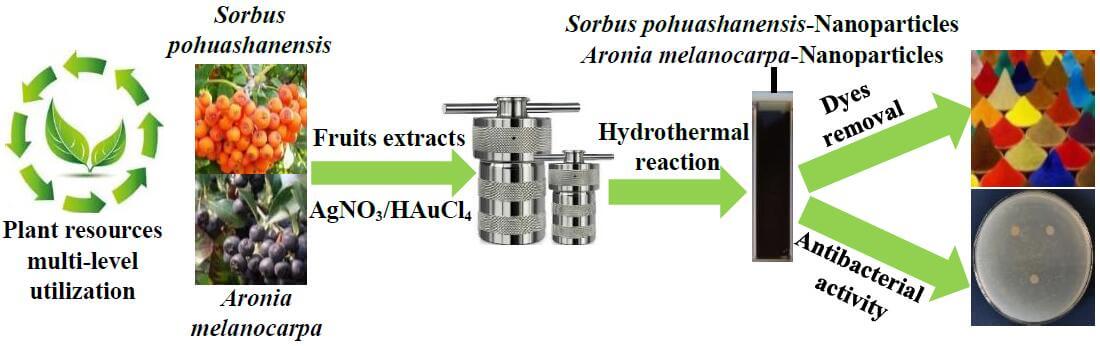
Nanoparticles (NPs) have already been widely used in catalysis, antibacterial and coating fields. Compared with the traditional toxic and harmful reducing reagents, green synthesis of NPs by using plant extracts is not only environmental-friendly and cost-effective but also conducive to the multi-level and efficient utilization of wild plant resources. In this study, the aqueous extracts from Sorbus pohuashanensis (SP) and Aronia melanocarpa (AM) fruits were used as the reducing and protective reagents for synthesizing Au/AgNPs, with the characteristics of originality operation and high repeatability. The SP/AM fruit extracts functionalized Au/AgNPs were characterized by UV-vis spectroscopy (UV-vis), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). UV-vis spectrums showed the NPs peaks verified by the presence between 400–550 nm; TEM and SEM demonstrated NPs displayed approximately spherical structures; EDS confirmed the existence of Au/Ag elements; XRD measurements confirmed that the obtained NPs showed highly crystalline structures; FTIR demonstrated the fruits extracts were adsorbed on the surface of NPs. Primary experiments indicated that SP/AM fruit extracts functionalized-NPs could be used as the reagents for removing the organic dyes efficiently; Zone of inhibition tests (ZOI) explained that NPs have slow-release antibacterial activity.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools