 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
MALDI ToF Investigation of the Reaction of Soy Protein Isolate with Glutaraldehyde for Wood Adhesives
1 Yunnan key Laboratory of Wood Adhesives and Glue Products, College of Material Science and Engineering, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, 650224, China
2 International Joint Research Center for Biomass Materials, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, 650224, China
3 Université de Lorraine LERMAB-ENSTIB, 27 rue Philippe Seguin, Epinal, 88000, France
* Corresponding Authors: Hong Lei. Email: ; Xuedong Xi. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(3), 1439-1450. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.023535
Received 05 May 2022; Accepted 28 May 2022; Issue published 31 October 2022
Abstract
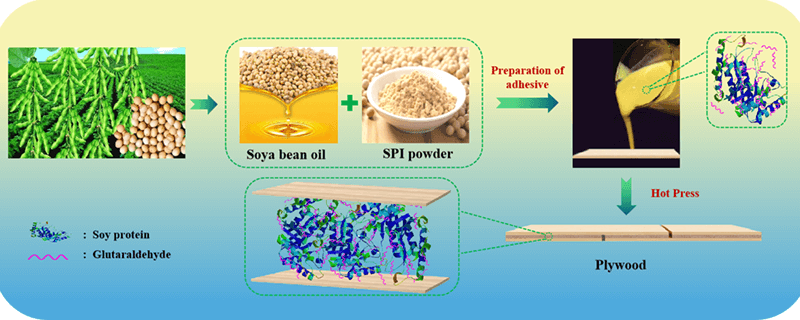
Soy protein adhesives are currently a hot research topic in the wood panels industry for the abundant raw material reserves, reasonable price and outstanding environmental features. But their poor water resistance, low bonding strength and intolerance to mold are major drawbacks, so that proper modification before use is essential. Glutaraldehyde is one of the more apt cross-linking agents for soybean protein adhesives, which can effectively improve the bonding strength and water resistance of the adhesive. Equally, glutaraldehyde is also an efficient and broad-spectrum fungicide that can significantly improve the anti-fungal properties of a soy protein adhesive. In the work presented here, matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI-ToF) mass spectrometry and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy techniques were used to analyze the reaction mechanism of glutaraldehyde cross-linking soybean protein. The results confirmed the reaction of the aldehyde group with amino groups of the side chains and the amide groups of the peptide linkages constituting the skeletal chain of the protein. The laboratory plywood and particleboard bonded with glutaraldehyde-soy bean protein adhesives were prepared to determine the adhesive bonding properties, the dry strength, 24 h cold water soaking wet strength and 3 h hot water (63°C) wet strength of plywood were 2.03, 1.13 and 0.75 MPa, respectively, which satisfied the requirements of industrial production.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools