 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Passivation of PEA+ to CsPbI3 (110) Surface States: From the First Principles Calculations
1
School of Materials Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Nonferrous Metals,
Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, 730050, China
2
Department of Materials Engineering, Lanzhou Institute of Technology, Lanzhou, 730050, China
3
School of Peili Mechanical Engineering, Lanzhou City College, Lanzhou, 730070, China
4
School of Chemical Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an, 710069, China
* Corresponding Author: Fuling Tang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Perovskite Solar Cells)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(3), 1293-1301. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.023095
Received 09 April 2022; Accepted 10 May 2022; Issue published 31 October 2022
Abstract
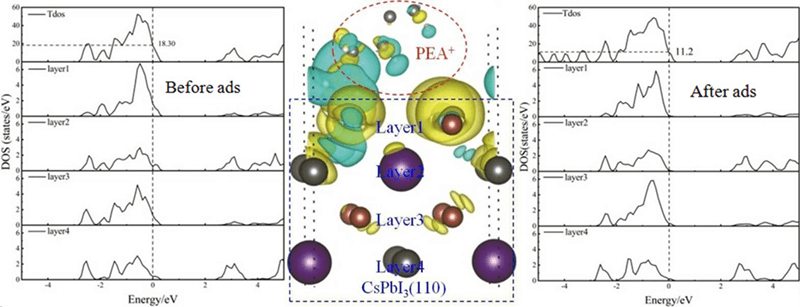
This work investigates the effect of passivation on the electronic properties of inorganic perovskite CsPbI3 materials by using first-principles calculations with density functional theory (DFT). The passivation effect after the addition of Phenylethylamine (PEA+ ) molecule to CsPbI3 (110) surface is studied. The results of density of states (DOS) calculations show that the CsPbI3 (110) surface model with I atom terminated reveals new electronic DOS peaks (surface states) near the Fermi level. These surface states are mainly due to the contribution of I-5p orbital and are harmful to the CsPbI3-based solar cells because they reduce the photoelectric conversion efficiency. The surface states near the Fermi level are significantly reduced, and the decline rate reaches 38.8% with the addition with PEA+ molecule to the CsPbI3 (110) surface.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools