 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Preparation and Properties of Chinese Lacquer Modified by Methylolureas
1
College of Forestry, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, 611130, China
2
Wood Industry and Furniture Engineering Key Laboratory of Sichuan Provinvial Department of Education, Sichuan Agricultural
University, Chengdu, 611130, China
* Corresponding Authors: Ming Chen. Email: ; Yuzhu Chen. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bio-Composite Materials and Structures-2021)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(2), 1003-1016. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.023621
Received 06 May 2022; Accepted 18 July 2022; Issue published 22 September 2022
Abstract
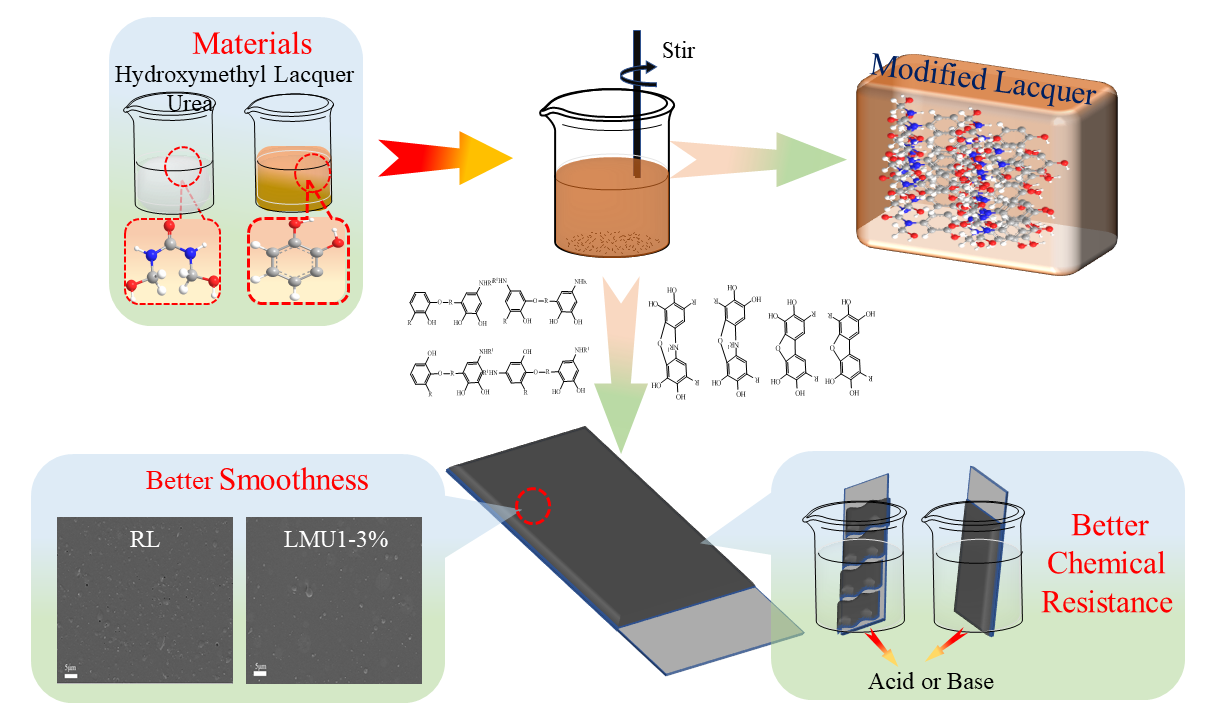
In this study, different molar of methylolureas (MMU) were used to improve the properties and drying speed of the raw lacquer (RL). The drying time, gloss, pencil hardness and impact resistance of the lacquer film were tested. The thermal behaviors and chemical structures of the lacquer membrane were also discussed by thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), fourier infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis, respectively. The results demonstrated that lower molar ratio MMU can significantly improve the properties of lacquer. The TGA analysis showed that the modified lacquer had high thermal stability than that of the control. The FT-IR and 13C NMR analysis revealed that the structures of the modified lacquer were significantly improved by cross-linking with the hydroxymethyl groups and methylene methyl ethers of MMU. In addition, through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) characterization, it was found that the introduction of MMU can effectively improve the surface smoothness of the lacquer film.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools