 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Experimental Study of Composite Columns Filled with Eucalyptus nitens Timber under Axial Compression
1
Faulty of Public Security and Emergency Management, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, 650093, China
2
School of Engineering, University of Tasmania, Hobart, TAS 7001, Australia
3
School of Civil Engineering, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Suzhou, 215011, China
4
College of water conservancy and Hydropower Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing, 210098, China
5
College of Automation & College of Artificial Intelligence, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, 210023,
China
* Corresponding Author: Huaming An. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bio-based Composite/Hybrid Structures and Components)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(2), 825-836. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.022599
Received 16 March 2022; Accepted 18 July 2022; Issue published 22 September 2022
Abstract
Eucalyptus nitens (E. nitens) has been much used for producing paper but also shows promise for structural applications. In this study, static compressive tests were undertaken to examine its suitability to be used in an innovative composite column. The composite column was comprised of a rectangular steel tube with E. nitens timber infill. The nonlinear compressive behaviour of the composite column filled with E. nitens wood for both dry and wet conditions was examined. The same tests on rectangular steel tubes and bare dry and wet E. nitens samples were also undertaken as a comparison. For samples with different conditions, the ultimate capacity was evaluated and the effect of each condition on the compressive behaviour of the composite column was clarified. The steel tubes showed greater ductile behaviour, and more ductility was found in the wet samples. The steel tubes with E. nitens timber infill samples exhibited a greater linear elastic range connected with higher maximum loads, while the bare timber samples could support only lower maximum loads. The results from this research were promising for the use of rectangular steel tubes with E. nitens timber infill in structural applications.Graphic Abstract
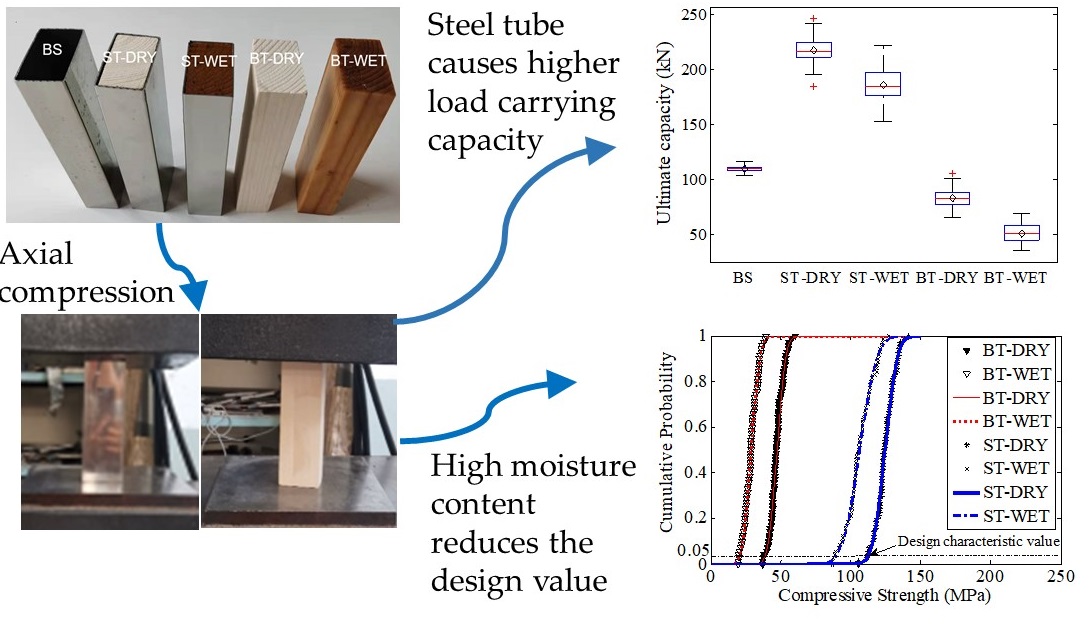
Keywords
Composite members are increasingly being used in the building industry [1–4]. Many studies have examined the compressive behaviour of composite columns with infilled timber, and the deformations, as well as the failure modes of such composites, have been assessed [2,5]. However, previous studies focused on coniferous species, such as P. radiata and Douglas fir [1,2,5]. Currently, there is a serious shortage of timber from softwood plantation resources due to the increasing demand for timber resources used in structural applications [6]. Fast-growing plantation hardwood species such as Eucalyptus nitens (E. nitens) are drawing attention with their potential for various structural building applications [7–11]. However, the available information on E. nitens to date is limited to its basic mechanical properties, such as bending strength, compressive stiffness, and so on [9,10,12]. To gather the missing information, it is, therefore, necessary to assess the compressive behaviour of composite columns with E. nitens wood infill.
The safety assessment of timber structures has been of much concern recently, especially in situations with moisture contents (MCs) above fibre saturation point (FSP) [11]. However, very few standards give the maximum load carrying allowances for such timber elements above FSP, especially for compressive failure, which is an important failure mechanism of columns or piles in buildings and bridges [7]. Only those design standards for soil and water immersed piles [13] and wet piles [14] address this issue. While the research above was for a limited number of species [15–17], several new studies show an increasing interest in Eucalypt but very few studies have examined the moisture/strength relationship in this timber [9,10,17]. Lack of design values for composite columns filled with E. nitens wood below and above FSP, may lead to unsafe use of this composite column when the E. nitens timber is exposed to water, for example in wood piling foundations near the coast for a long time [10].
The design values are usually determined based on the small clear sample or the full-size testing [10,18]. The test results from full-size testing are much closer to the actual situation as it takes the effect of size into consideration [18]. Small clear samples were used to develop design values for the composite columns filled with E. nitens wood below and above FSP because they were still used to determine the design values based on the design code of timber structures as well as timber members [19,20].
This study examines the comprehensive behaviours of composite columns filled with E. nitens timber for dry and wet conditions. Here, “low MC” or “dry” means the moisture content (MC) of the timber is about 12%, which is the standard condition below FSP, and “high MC” or “wet” means the MC is above fibre saturation point (FSP), with the assumption that FSP of E. nitens is 30% [10]. In this study, the specific objectives are listed as follows:
• Determine the load-deformation curves for the composite columns with E. nitens timber infill under axial compression for dry and wet conditions.
• Investigate the impact of the steel tube on the compressive behaviour of the composite columns with E. nitens timber infill for dry and wet conditions.
• Obtain the design values for composite columns filled with E. nitens timber for dry and wet conditions.
An experimental investigation of steel composite columns filled with E. nitens timber under axial compression was undertaken to obtain the load and deformation curves. The loads and deformations were measured by a Universal Testing Machine according to ASTM D143–09 [21]. The machine has a maximum loading capacity of 1000 kN. The ultimate capacity of the composite columns was obtained from these load-deformation curves. The test series and sample configurations used were summarised in Table 1 and Fig. 1.


Figure 1: The samples with different configurations
The samples were 150 mm (in length) × 50 mm (in width) × 35 mm (in depth) in accordance with ASTM D143-09 [21]. Steel tubes (cold-formed mild steel sections) were bought from local traders with detailed dimensions provided in Figs. 2b and 2c. The yield strength and modulus of elasticity of steel tubes were 415.00 MPa and 185.00 GPa, respectively. E. nitens timber samples were prepared according to the work of Cheng et al. [10]. The grain direction coincided with the longitude of the samples. Two kinds of moisture content (MC) conditions were considered. The first was the “dry condition”, which means with MC of around 12%, and the second was the “wet condition” with MC > FSP (FSP = 30% [10] assumed in this study). E. nitens timber samples were originally cut to be a larger size with dimensions 200 mm (in length) × 50 mm (in width) × 35 mm (in depth), then cut to the final size just before the testing. The cut pieces from the timber samples were used to determine the MCs and the basic densities according to the work of Cheng et al. [10].

Figure 2: Dimensions of the samples for testing
The bare steel (BS) and bare timber samples (BT) tests were measured directly from the prepared steel tubes and E. nitens samples, respectively. For the steel tube filled with E. nitens timber samples (ST), the timber blocks, both wet and dry, were machined using a planer to allow the dimension of a timber block to fit tightly into the inside of a steel tube (Fig. 2a). Then the timber block was placed at one end of the steel tube and the impact of a hammer was used to insert the block into the steel tube.
2.2 Methods for the Test and the Data Analysis
The tests were undertaken at roughly 18°C with relative humidity (RH) between 60% and 70%. The test for each sample was performed on a Universal Testing Machine with a loading rate of 0.3 mm/mins. The test photos were provided in Fig. 3.

Figure 3: Test photos for the samples in axial compression
The compressive strength (
where, A (mm2) is the area of the section applied the load. This equation was consistent with the previous studies [9,22] and the Standards [21,23]. The ultimate capacity was the peak value obtained directly from the experimental load-deformation curve for each sample, while the area of the section applied the load (A) for the sample with different configurations was A = D × W – (D − 2t) × (W − 2t) for BS samples and A = D × W for ST/BT samples, respectively.
The compressive strain was calculated from the relative deformation in relation to the original dimensions.
The ductility coefficient, μ, which is an important measure to show the elastic-plastic deformation capacity of structural members, was calculated as:
where,
Statistical analyses were used to determine the design characteristic values at 95% confidence via Matlab (version R2021a, Natick, Massachusetts: The MathWorks Inc.). MCs and basic densities for E. nitens timber samples were determined in accordance with the work of Cheng et al. [10].
This study shows the compressive properties of the composite columns, i.e., rectangular steel tubes filled with dry (MC = 12%) and wet (MC > FSP) E. nitens, under axial compression. It first assesses the experimental findings with the work of previous studies in Section 3.1 to give a rationale for the compressive behaviour of composite columns with E. nitens timber infill. In Sections 3.2–3.4, the effect of the steel tube and the E. nitens timber on the compressive behaviour of the composite columns are explored and the usage of such composite columns is considered.
3.1 Physical Properties of E. nitens Timber
Table 2 presented a statistical summary of the E. nitens samples. The mean values of the basic density were 511.7 kg/m3 and 528.2 kg/m3 for dry condition (MC = 12%) and 499.8 and 507.4 kg/m3 for wet condition (MC > FSP), respectively, which was lower than that from native forests (670 kg/m3) [26]. This was because the samples of this study were from an E. nitens plantation resource, which was younger than those from native forests and density increases with age [27,28]. Basic densities of the E. nitens in this study lay in the range of those obtained by Cheng et al. [9] and Derikvand et al. [12], respectively, showing that the data was reasonable for plantation E. nitens timber.

The MCs of E. nitens timber in ST samples were 11.8%–13.6% with a mean value of 12.8% for the dry condition and 45.0%–87.3% with an average of 65.1% for the wet condition, respectively. MC of BT samples varied between 11.3% to 13.3% for dry samples and between 44.5% to 84.3% for wet samples, with average (coefficient of variation, COV) values of 12.2% (3.3%) and 64.2% (13.1%), respectively. In the present study for E. nitens, ST samples had similar MCs compared to the corresponding BT samples (Table 2). Thus, the samples with different configurations were comparable.
Fig. 4 presented a boxplot of compressive strengths of BT samples and the data from other studies on plantation E. nitens [9,12]. The compressive strength for each sample was obtained using Eq. (1). In this figure, the red lines in the boxplots represented the median, while the red crosses represented possible outliers. Wet samples were linked with low values of failure strengths compared to the corresponding dry samples. High MC significantly reduced the compressive strength in this study, which agreed with the findings reported by other research on plantation E. nitens timber [9].

Figure 4: Boxplot of the compressive strength for bare E. nitens timber in this study compared with the work of Cheng et al. 2022 (C22 [9]) and Derikvand et al. 2019 (D19 [12])
A similar MC range between the bare E. nitens (BT) samples and other experimental work of compression on E. nitens was found, and the strengths of dry BT samples in this study lay in the range of those obtained by Cheng et al. [9] and Derikvand et al. [12] (Fig. 4), implying the repeatability of this study.
3.2 Load and Deformation Curves
In this section, the load and deformation curves for the samples with different configurations under axis compression were provided (Fig. 5). Generally, the compressive behaviour of the samples can be classified into three stages: (a) the elastic stage, (b) the inelastic stage with the yielding, and (c) the load drop. For both dry and wet conditions, an approximately linear relationship at the beginning of the load and deformation curve was found (Fig. 5), and the deformation increased when the load increased. At a certain level of loading, which is defined as yield load, the samples yielded, and permanent deformations occurred. Then, as the load continued to increase, loading reached its peak. At this stage, the deformation of the sample can be visibly detected. The gradually decreasing loads were observed after their peaks, which is called softening (load drop), and the samples were functionally unacceptable. Fig. 5 also explored the effect of the steel tubes on the compressive behaviour of composite columns filled with E. nitens timber. The compressive behaviours of ST samples were stiffer as well in higher strengths than the corresponding BS and BT samples (Figs. 5a and 5b). This is because E. niten timber in a steel tube acts as a stiffener, supporting the steel tube and results in a higher peak load.
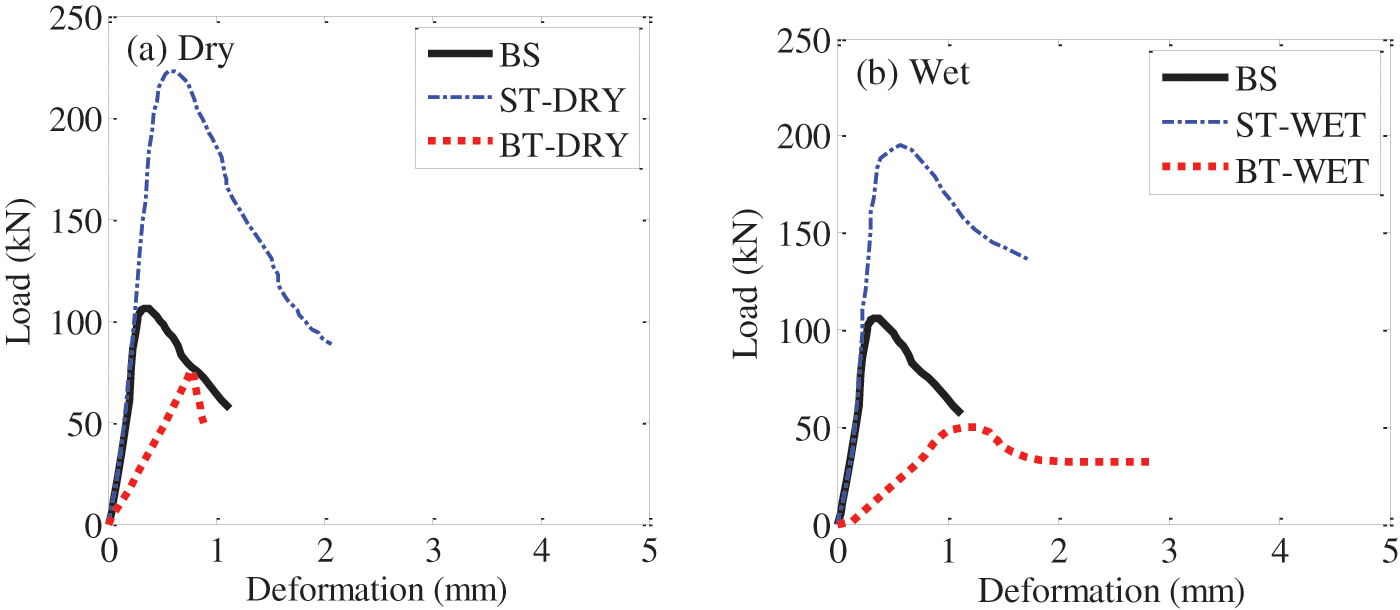
Figure 5: Load (kN) vs. Deformation (mm) for the samples with different configurations: Left plot, dry E. nitens timber; right plot, wet E. nitens timber
Fig. 6 presented the ductility coefficients (ductility indices) of each group of samples. In general, samples under compression exhibited relatively ductile behaviour. ST samples (steel tubes filled with E. nitens timber) tended to exhibit higher ductility compared with the bare timber samples. This behaviour was also reported by Ghanbari Ghazijahani et al. for composite columns filled with P. radiata timber [5], i.e., the steel tubes resulted in greater ductile behaviour for the samples filled with timber when compared with their bare counterparts. Results also indicated that increasing the moisture content in similar samples could increase the ductility, i.e., wet samples had higher ductility coefficients compared to the corresponding dry samples. The ductility in ST samples increased more than 100% compared with the corresponding bare timber samples, while an increase in ductility coefficients from dry to wet samples was round 30%. Thus, steel tubes had a stronger effect on the performance of composite columns compared with the effect of moisture content on the samples.

Figure 6: Ductility coefficients (μ) for the samples with different configurations
The boxplot of ultimate capacities for the samples with different configurations was provided in Fig. 7. The average values were 109.4 kN for BS, 217.8 kN for ST-DRY, 82.8 kN for BT-DRY, 186.2 kN for ST-WET and 50.7 kN for BT-WET, respectively.
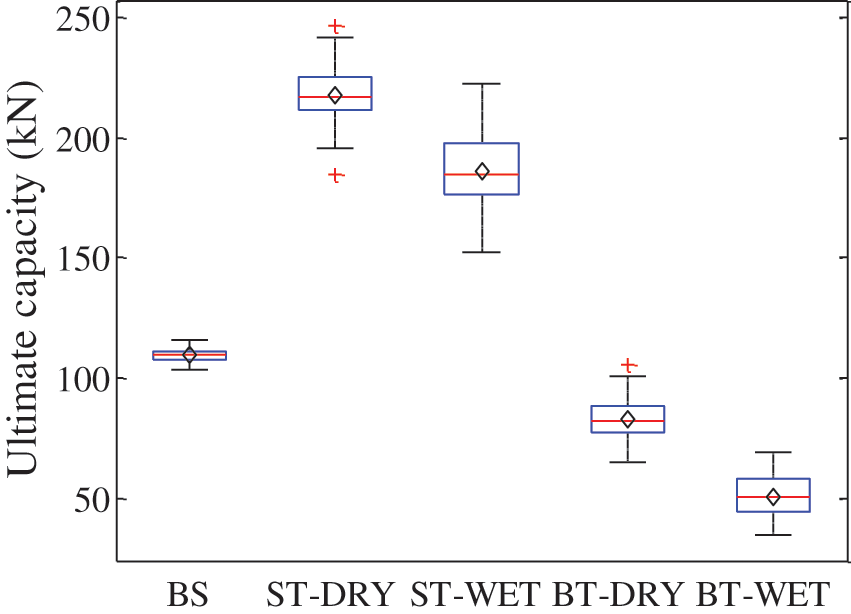
Figure 7: Boxplot of the ultimate capacities for the samples with different configurations
A remarkable difference in the value of ultimate capacities can be seen. The highest value was in the ST-DRY samples, implying that the composite columns filled with E. nitens timber have higher failure capacities than the BS and BT samples. The ultimate capacity decreased with the increases in moisture content for both ST samples and BT samples. But a greater decrease in the ratio of the ultimate capacity for BT samples than for ST samples when the cell walls of E. nitens timber were filled with water was found, ie., in the group of ST samples; only 14.5% reduction in the mean ultimate capacity was observed, while a 38.8% reduction was found in BT samples from wet to dry, indicating that the ultimate capacities of bare E. nitens timber (BT samples) were more sensitive to moisture content than the composite columns filled with E. nitens timber (ST samples).
3.4 Probability Distributions of the Compressive Strength for Composite Column Filled with E. nitens Timber
For practical use, failure strength, which shows the maximum load carrying capacity of the timber [29], at a 95% confidence level has gained the attention of the designers. The histograms of compressive failure strengths based on the test data were fitted by lognormal and normal probability distribution functions (Fig. 8).

Figure 8: Histograms of compressive strengths for dry (a, c) and wet (b, d) samples: top row: the bare E. nitens timber (BT) samples (a, b); bottom row: the composite column filled with E. nitens timber (ST) samples (c, d)
Both the normal probability distribution and the lognormal probability distribution showed good fits (Table 3). The normal distribution was preferable for determining the design characteristic values as it was simpler and was correlated with previous studies for bare E. nitens timber samples [10] and traditional construction timbers, e.g., Spruce and Pine [30].

The distributions of measured compressive strengths for ST samples were relatively broader than for BT samples (Fig. 9). An obvious impact of high MC on the design value of the samples was found. Both ST samples and BT samples were comparable because they had similar MCs. ST samples lay a higher value region compared with the corresponding BT samples (Fig. 9), implying that the composite materials (steel tube and E. nitens timber infill) rose the compressive strength of the columns under axial compression. The remarkable increases up to 163.2% for dry ST samples and 266.9% for wet ST samples, respectively, were found compared with their bare E. nitens timber counterparts (Table 4).
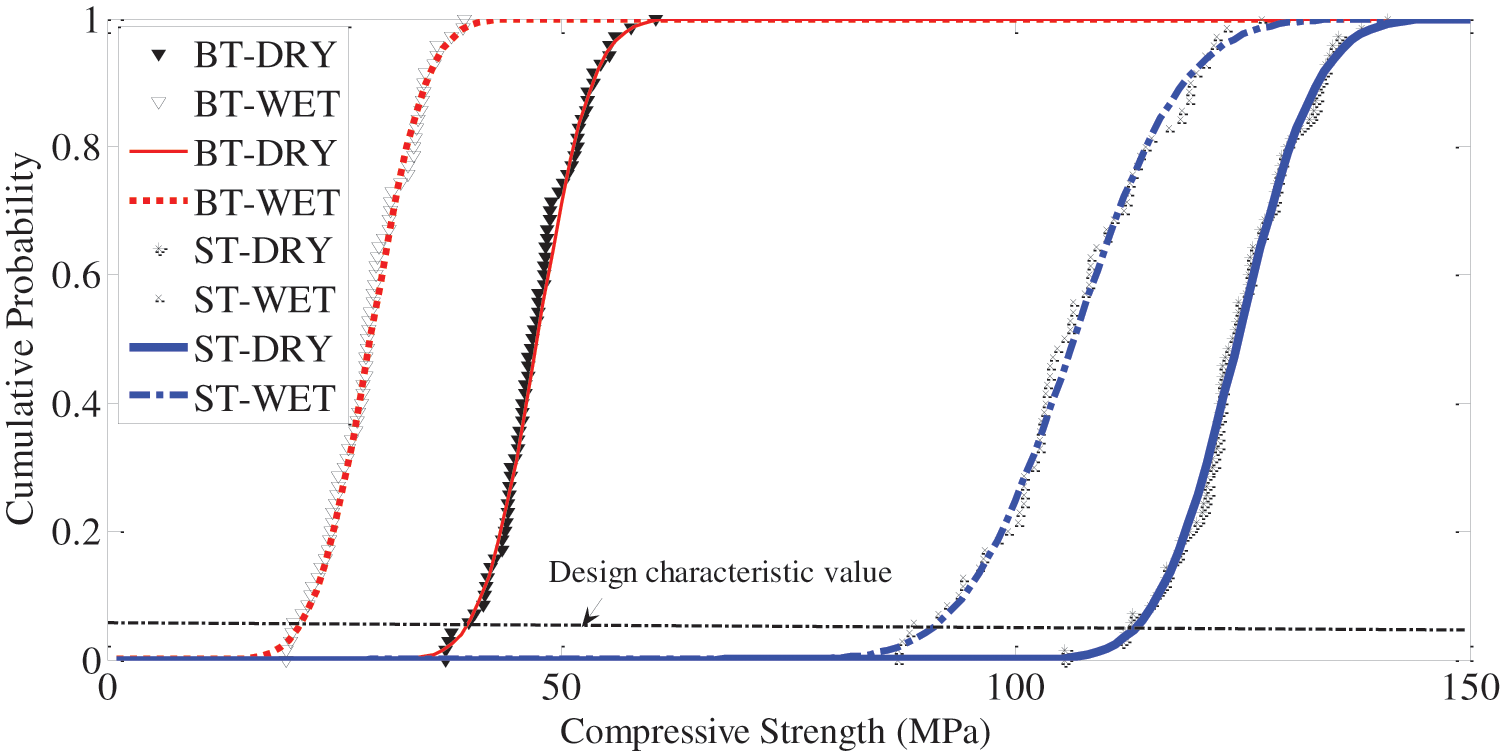
Figure 9: Probability distribution of the compressive strengths for composite columns filled with dry and wet E. nitens timber compared with the bared timber counterparts

For both ST and BT samples, the COVs among the samples under wet conditions were higher than those under dry conditions due to a broader range of MC for the wet samples (Table 4). A smaller COV of ST samples than BT samples was found. This lower variance was because the ST samples were more consistent because of the effect of greater uniformity of the steel tubes than the E. nitens timber samples. When both ST samples and BT samples had a similar MC range, the high moisture content produced less decline in compressive strengths and COVs of the composite columns filled with E. nitens timber compared with the bare E. nitens timber samples. This showed that composite columns filled with E. nitens timber were promising as structural compressive members, especially in water-saturated conditions. This was because of the lower strength reduction compared with those of the bare E. nitens timber counterparts. The suggested design characteristic values for composite columns, i.e., rectangular steel tubes filled with E. nitens timber, were 113.5 MPa for low MC and 91.0 MPa for high MC, respectively (Table 4).
This study characterized the compressive behaviour of composite columns filled with E. nitens timber, proposed as the new application of E. nitens for structural use. It examined the suitability of composite columns filled with E. nitens timber both below and above FSP as structural members for the first time.
The findings can be summarised as follows:
• The effect of the steel tube was that it caused more ductility and higher load carrying capacity of the composite column. E. nitens timber in the steel tube supported the samples. The steel tube filled with E. nitens timber samples performed relatively higher slopes of the elastic stage together with higher maximum loads, while the bare timber samples showed quite smaller maximum loads with less ductile compressive behaviour. Wet samples were lower in failure strengths and had more ductile compressive behaviours.
• A notable difference can be seen in the values of ultimate capacity of the samples with different configurations. The composite materials (i.e., steel tube and E. nitens timber infill) increased the ultimate capacity of the columns under axial compression, and the steel tube played more of a role in the ultimate capacity of composite columns than the moisture content (MC) of the E. nitens timber infill. Lower moisture content was linked with stronger samples.
• The probability distributions of compressive strengths were determined using the test data and design characteristic values of composite columns filled with E. nitens timber were suggested. The composite columns can potentially be used by designers as structural members.
Acknowledgement: The authors are grateful for the help and support of all scientists contributing to the development of this paper.
Funding Statement: The authors received no specific funding for this study.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
References
1. Kia, L., Valipour, H. R. (2021). Composite timber-steel encased columns subjected to concentric loading. Engineering Structures, 232(1), 111825. DOI 10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.111825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
2. Karampour, H., Bourges, M., Gilbert, B. P., Bismire, A., Bailleres, H. et al. (2020). Compressive behaviour of novel timber-filled steel tubular (TFST) columns. Construction and Building Materials, 238(9), 117734. DOI 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
3. Kramer, A., Barbosa, A. R., Sinha, A. (2016). Performance of steel energy dissipators connected to cross-laminated timber wall panels subjected to tension and cyclic loading. Journal of Structural Engineering, 142(4). DOI 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
4. Way, D., Sinha, A., Kamke, F., Fujii, J. (2016). Evaluation of a wood-strand molded core sandwich panel. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 28(9), 04016074. DOI 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
5. Ghanbari Ghazijahani, T., Jiao, H., Holloway, D. (2017). Composite timber beams strengthened by steel and CFRP. Journal of Composites for Construction, 21(1), 04016059. DOI 10.1061/(ASCE)CC.1943-5614.0000714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
6. Derikvand, M., Nolan, G., Jiao, H., Kotlarewski, N. (2017). What to do with structurally low-grade wood from Australia’s plantation Eucalyptus; Building application? BioResources, 12(1), 4–7. DOI 10.15376/biores.12.1.4-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
7. Derikvand, M., Kotlarewski, N., Lee, M., Jiao, H., Chan, A. et al. (2019). Short-term and long-term bending properties of nail-laminated timber constructed of fast-grown plantation eucalypt. Construction and Building Materials, 211, 952–964. DOI 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
8. Derikvand, M., Jiao, H., Kotlarewski, N., Lee, M., Chan, A. et al. (2019). Bending performance of nail-laminated timber constructed of fast-grown plantation eucalypt. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 77(3), 421–437. DOI 10.1007/s00107-019-01408-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
9. Cheng, Y., Chan, A. H. C., Holloway, D., Nolan, G. (2022). Anisotropic material behaviour under compression of Eucalyptus nitens with high moisture content. Construction and Building Materials, 314, 124788. DOI 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
10. Cheng, Y., Nolan, G., Holloway, D., Kaur, J., Lee, M. et al. (2021). Flexural characteristics of Eucalyptus nitens timber with high moisture content. BioResources, 16(2), 2921–2936. DOI 10.15376/biores.16.2.2921-2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
11. Pagel, C. L., Lenner, R., Wessels, C. B. (2020). Investigation into material resistance factors and properties of young, engineered Eucalyptus grandis timber. Construction and Building Materials, 230(1), 117059. DOI 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
12. Derikvand, M., Kotlarewski, N., Lee, M., Jiao, H., Nolan, G. (2019). Characterisation of physical and mechanical properties of unthinned and unpruned plantation-grown Eucalyptus nitens H. Deane & Maiden Lumber. Forests, 10(2), 194. DOI 10.3390/f10020194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
13. NEN5491 (1999). Quality requirements for timber—piles—coniferous timber. Delft, Netherlands: Netherlands Standardisation Institute (NEN). [Google Scholar]
14. NEN-EN1995-1-1NB (2011). National annex to NEN-EN 1995-1-1. Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures—Part 1-1: General—common rules and rules for buildings (includes C1: 2006 and A1: 2008). Delft, Netherlands: Netherlands Standardisation Institute (NEN). [Google Scholar]
15. Nocetti, M., Brunetti, M., Bacher, M. (2014). Effect of moisture content on the flexural properties and dynamic modulus of elasticity of dimension chestnut timber. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 73(1), 51–60. DOI 10.1007/s00107-014-0861-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
16. Nocetti, M., Brunetti, M., Bacher, M. J. M. (2016). Efficiency of the machine grading of chestnut structural timber: Prediction of strength classes by dry and wet measurements. Materials and Structures, 49(11), 4439–4450. DOI 10.1617/s11527-016-0799-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
17. Nocetti, M., Pröller, M., Brunetti, M., Dowse, G. P., Wessels, C. B. (2017). Investigating the potential of strength grading green Eucalyptus grandis lumber using multi-sensor technology. BioResources, 12(4), 9273–9286. [Google Scholar]
18. Gong, Y., Wu, G., Luo, X., Wang, Z., Jiang, J. et al. (2017). Research on design value of compressive strength for Chinese fir dimension lumber based on full-size testing. Journal of Wood Science, 63(1), 56–64. DOI 10.1007/s10086-016-1592-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
19. AS1720 (2010). Timber structures. Part 1: Design methods. Sydney, Australia: Standards Australia. [Google Scholar]
20. ASTMD2899 (2012). Standard practice for establishing allowable stresses for round timber piles. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International. [Google Scholar]
21. ASTMD143-09 (2009). Standard test methods for small clear specimens of timber. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International. [Google Scholar]
22. Crespo, J., Majano-Majano, A., Lara-Bocanegra, A. J., Guaita, M. (2020). Mechanical properties of small clear specimens of Eucalyptus globulus labill. Materials, 13(4), 906. DOI 10.3390/ma13040906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
23. AS/NZS4063.1 (2010). Characterization of structural timber. Part 1: Test method. Sydney, Australia: Standards Australia. [Google Scholar]
24. Koloo, F., Badakhshan, A., Fallahnejad, H., Ebadi-Jamkhaneh, M., Ahmadi, M. (2018). Investigation of proposed concrete filled steel tube connections under reversed cyclic loading. International Journal of Steel Structures, 18(1), 163–177. DOI 10.1007/s13296-018-0313-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
25. Mander, J. B., Priestley, M. J., Park, R. (1988). Theoretical stress strain model for confined concrete. Journal of Structural Engineering, 114, 1804–1826. [Google Scholar]
26. AS2082 (2007). Timber-Hardwood-Visually stress graded for structural purposes. Sydney, Australia: Standards Australia. [Google Scholar]
27. Medhurst, J., Downes, G., Ottenschlaeger, M., Harwood, C., Evans, R. et al. (2012). Intra-specific competition and the radial development of wood density, microfibril angle and modulus of elasticity in plantation-grown Eucalyptus nitens. Trees, 26(6), 1771–1780. DOI 10.1007/s00468-012-0746-z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
28. Yang, J., Evans, R. (2003). Prediction of MOE of eucalypt wood from microfibril angle and density. Holz als Roh-und Werkstoff, 61(6), 449–452. DOI 10.1007/s00107-003-0424-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
29. Ross, R. J. (2010). Wood handbook: Wood as an engineering material. General Technical Report FPL-GTR-190. USDA Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory. [Google Scholar]
30. AS/NZS4063 (2010). Structural timber-Characteristic values of strength graded timber. Sydney, Australia: Standards Australia. [Google Scholar]
31. Bryc, W. (2012). The normal distribution: Characterizations with applications, vol. 100. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media. [Google Scholar]
32. Anderson, T. W., Darling, D. A. (1954). A test of goodness of fit. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 49(268), 765–769. DOI 10.1080/01621459.1954.10501232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools