 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fine Characterization and Analysis of Drying Strain of the ELM Board via DIC Technology
Key Laboratory of Bio-Based Material Science and Technology (Ministry of Education), College of Material Science and Engineering, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 150040, China
* Corresponding Authors: Yingchun Cai. Email: ; Jingyao Zhao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Tools for Renewable Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(2), 567-580. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.023037
Received 07 April 2022; Accepted 18 May 2022; Issue published 22 September 2022
Abstract
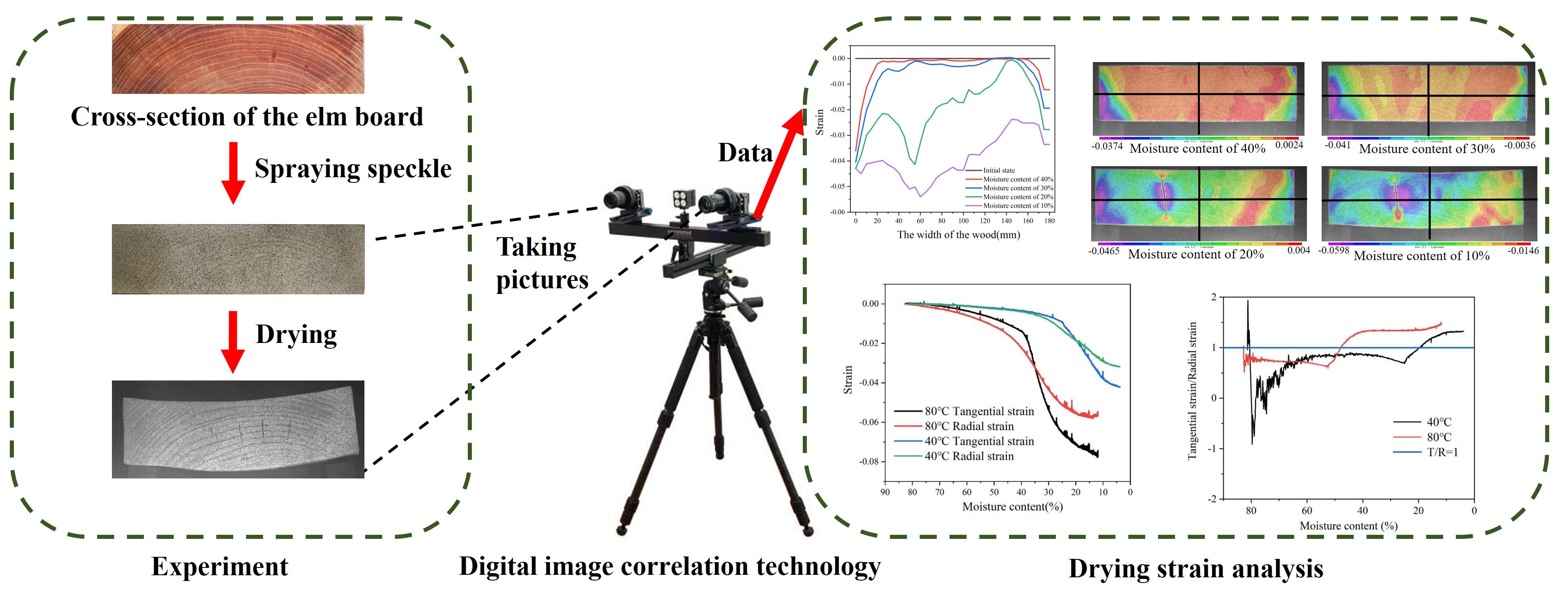
In this paper, the occurrence and development mechanism of strain on the cross-section during the wood drying is explored. Therefore, strain regularity on the cross-section of 50 mm thickness elm (Ulmus rubra) board at the temperature of 40°C and 80°C is detected via digital image correlation technology. Hence, the difference between tangential and radial strain at surface and core layers was denoted. The results showed that strain distribution in the width direction of the board is uneven. Moreover, a large drying shrinkage strain occurs at the near-core layer, while the maximum strain difference reaches 4.08%. Hence, the surface of the board is cracked along the thickness direction. The radial strain of the board is higher than the tangential strain in the early stage of drying, while these strains are reversed in the later stage of drying. The temperature is related to the difference between the tangential and radial strains of the elm board. These differences at the core layer are larger than those of the surface layer. The conducted research results provide a theoretical basis for process optimization.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools