 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Biomass Carbon Improves the Adsorption Performance of Gangue-Based Ceramsites: Adsorption Kinetics and Mechanism Analysis
1
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, 710054, China
2
Shccig Yulin Chemical Co., Ltd., Management Committee of Yushen Industrial Zone, Yulin, China
* Corresponding Author: Huiling Du. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Eco-Friendly Waste-Base Materials for Pollution Control Sustainable Technologies)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(12), 4161-4174. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.028877
Received 12 January 2023; Accepted 15 March 2023; Issue published 10 November 2023
Abstract
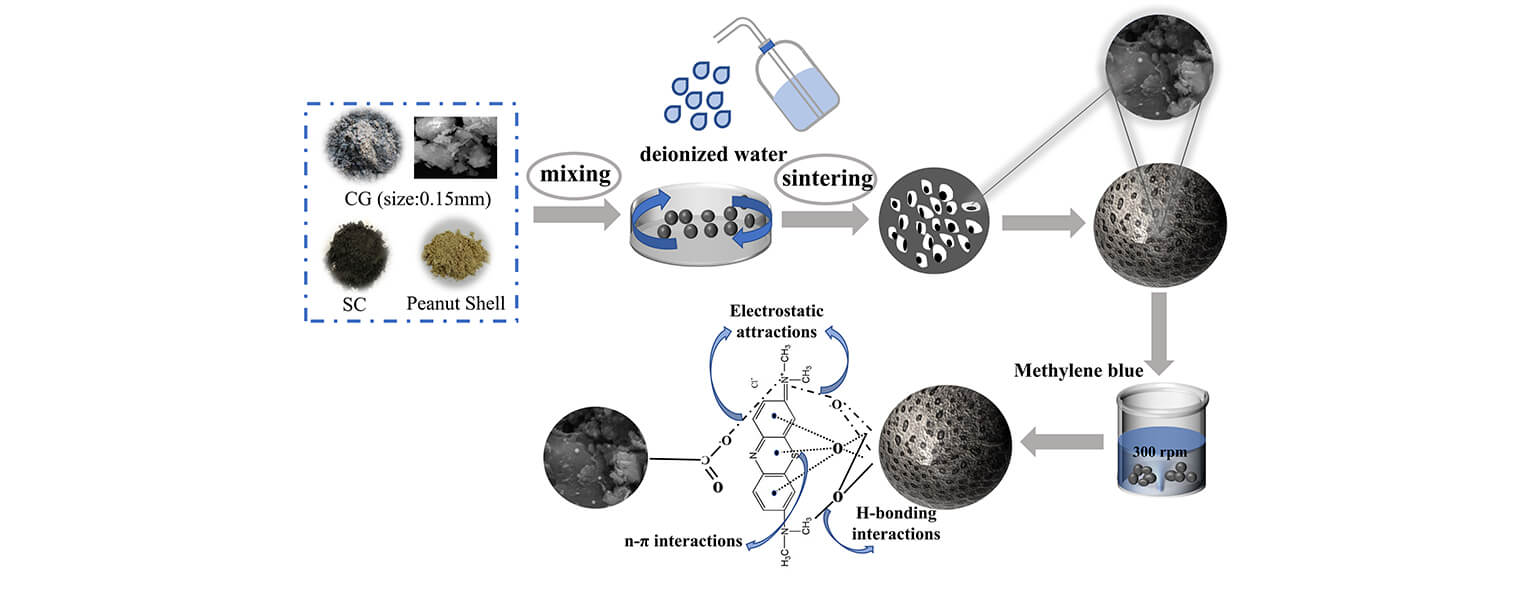
The large accumulation of coal gangue, a common industrial solid waste, causes severe environmental problems, and green development strategies are required to transform this waste into high-value-added products. In this study, low-cost ceramsites adsorbents were prepared from waste gangue, silt coal, and peanut shells and applied to remove the organic dye methylene blue from wastewater. We investigated the microstructure of ceramsites and the effects of the sintering atmosphere, sintering temperature, and solution pH on their adsorption performance. The ceramsites sintered at 800°C under a nitrogen atmosphere exhibited the largest three-dimensional-interconnected hierarchical porous structure among the prepared ceramsites; further, it exhibited the highest methylene blue adsorption performance, with an adsorption capacity of 0.954 mg·g−1 , adsorption efficiency of over 95%, and adsorption equilibrium time of 1 h at a solution pH of 9. The removal efficiency remained greater than 75% after five adsorption cycles. The adsorption kinetics data were analyzed using various models, including the pseudosecond-order kinetic model and Langmuir equation, and the adsorption was attributed to electrostatic interactions between the dyes and ceramsites, n-interactions, and hydrogen bonds. The prepared coal gangue ceramsites exhibited excellent adsorption capacities, removal rates, and cyclic stabilities, demonstrating their promising application prospects for the comprehensive utilization of solid waste and for wastewater treatment.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools