 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effect of Bio-Based Organic‒Inorganic Hybrid Hydrogels on Fire Prevention of Spontaneous Combustion of Coals
State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026, China
* Corresponding Authors: Xin Wang. Email: ; Yuan Hu. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(12), 3991-4006. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.029888
Received 13 March 2023; Accepted 10 May 2023; Issue published 10 November 2023
Abstract
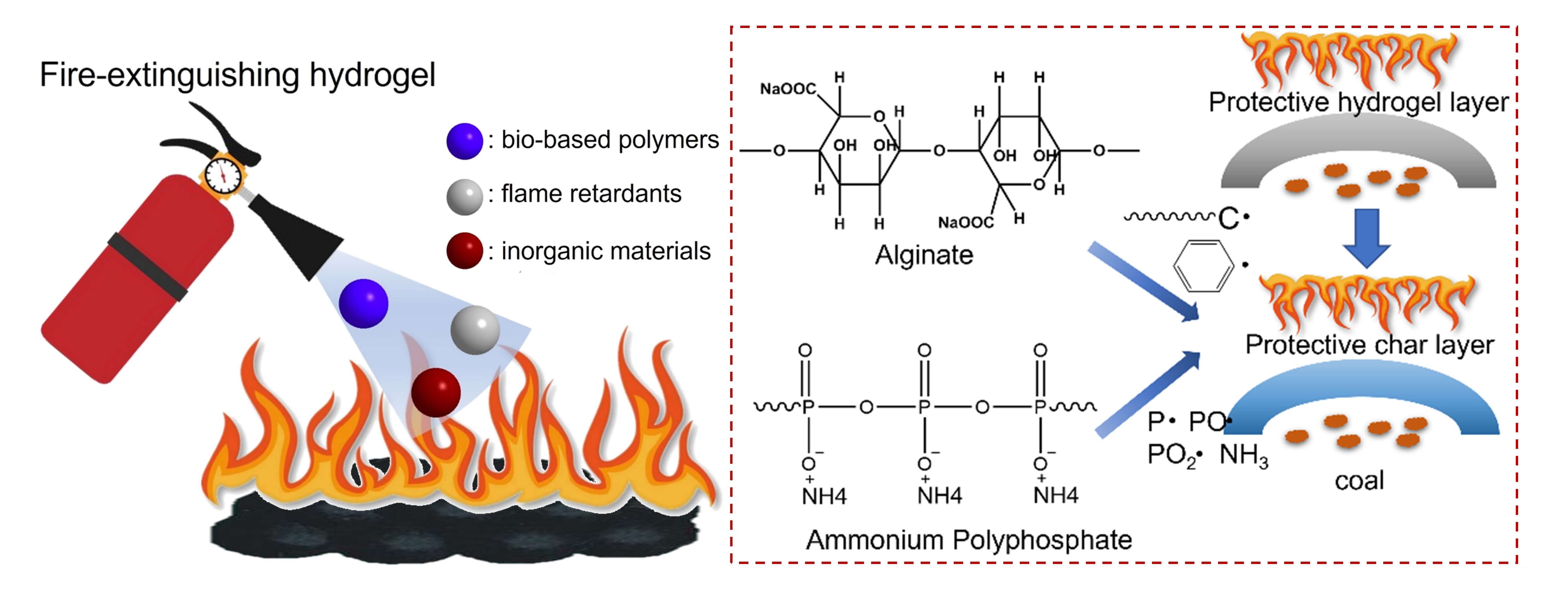
To solve the fire accidents caused by coal combustion, this work prepared four hybrid hydrogel materials using bio-based polymers, flame retardants, and inorganic materials. Compared to pure water and 3.5 wt% MgCl2 solution, the as-prepared hydrogel presents good fire prevention performance. In addition, it is found that CO and CO2 are not produced by coal when the pyrolysis temperature is lower than 200°C. During low-temperature pyrolysis, CO is more likely to be produced than CO2, indicating inadequate pyrolysis behavior. At the same time, the addition of fire-preventing hydrogel can not only decrease the maximum CO2 concentration before the critical temperature but also prolong the corresponding time. In addition, based on the cone calorimeter test, the inhibition effects of pure water, magnesium chloride solution, and four hybrid hydrogels on heat release behavior are evaluated. It is demonstrated that different dosages of different hydrogels affected the fire prevention effect. Phosphorous-modified cellulose/silica and carrageenan/DMMP/vermiculite composite hydrogels have the weakest fire prevention effect at 20 g, which is weaker than that of water. However, the fire prevention effect of carrageenan/ DMMP/vermiculite composite hydrogels exceeded that of water at 40 and 60 g. Additionally, the fire prevention effect of the sodium alginate/sepiolite/ammonium polyphosphate composite hydrogel is most significant in common tests, attributed to the intumescent flame retardant system.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools