 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Synthesis of Carbon dots from Biomass Chenpi for the Detection of Hg2+
1
Pharmaceutical and Food Molecular Science Research Team, Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Central South University,
Changsha, 410083, China
2
Department of Food Testing and Research, Hunan Testing Institute of Product and Commodity Supervision, Changsha, 410007,
China
* Corresponding Author: Jun Xiang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Carbon-Based Nanomaterials from Renewable Materials: Synthesis, Properties and Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(10), 3739-3750. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.028090
Received 29 November 2022; Accepted 26 January 2023; Issue published 10 August 2023
Abstract
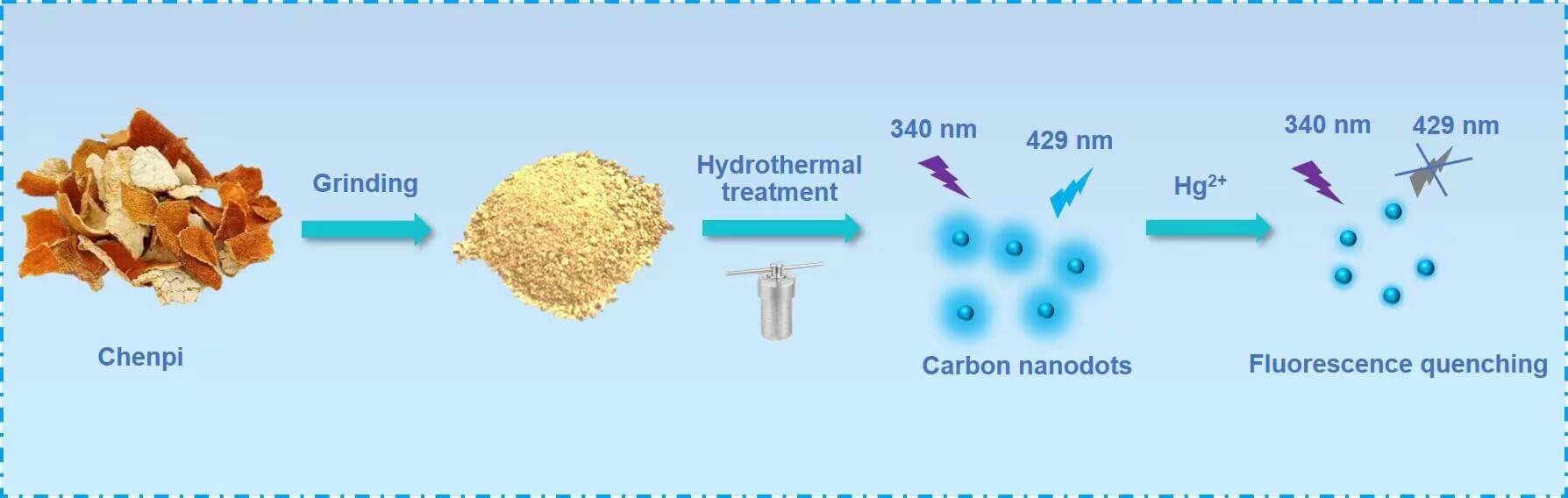
Biomass-derived carbon dots (C-dots) are considered a very important carbon material in metal ion detection of their small environmental impact, simple preparation process, and relatively low cost. A green approach for synthesizing biomass-derived C-dots from Chenpi using a hydrothermal method without further processing is proposed in the present study. The as-synthesized C-dots show excellent fluorescence properties, superior resistance to UV irradiation photobleaching, and high photostability in salt-containing solutions. The C-dots were used in the form of label-free fluorescent probes for sensitively detecting Hg2+ selectively. The outcome relationship behaved linearly and was established based on a given range between 10–300 nM concentration, with a detection limit of 7.0 nM. This green strategy obtains a high C-dot quantum yield of 10.8% and satisfactory results in detecting Hg2+ in actual water samples.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools