 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Study on Mechanical Properties and Action Mechanism of Leather Industrial Sludge Aggregate Baking-Free Bricks
1 School of Water Conservancy, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, Zhengzhou, 450046, China
2 Henan Water Valley Research Institute, Zhengzhou, 450046, China
3 Henan Key Laboratory of Water Environment Simulation and Treatment, Zhengzhou, 450002, China
* Corresponding Author: Lixia Guo. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Potential Materials Towards Sustainable Construction)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(1), 453-471. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.023315
Received 20 April 2022; Accepted 25 May 2022; Issue published 10 August 2022
Abstract
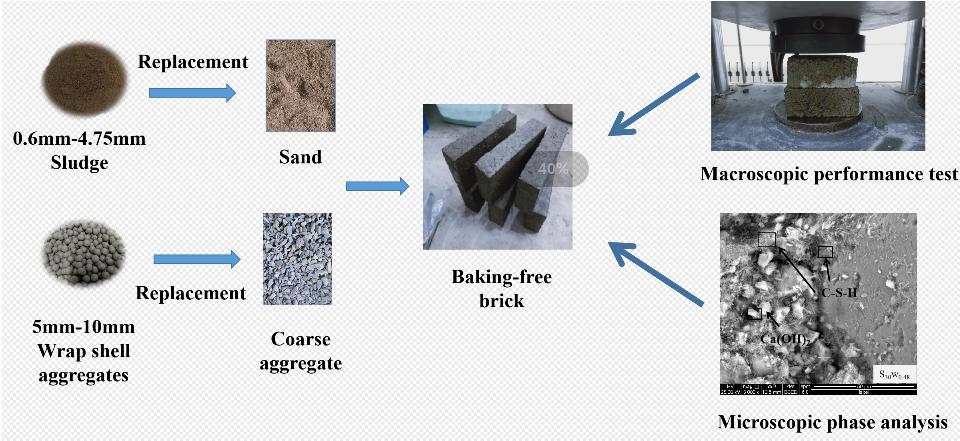
Taking an industrial sludge and its preparation of sludge wrap shell aggregates (WSAs) instead of sand to prepare baking-free brick as the research object, the development law of mechanical properties and the influence mechanism of macro and micro characteristic parameters of the bricks under different sludge and WSAs replacement rates were studied through the macroscopic mechanical properties test, with the help of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), transmission electron microscopy-energy spectrum and other testing technology and pores and cracks analysis system (PCAS) software. The results showed that the compressive strength of each sample decreased with the increase of sludge content. When the sludge content was less than 30%, it was mainly affected by the water-binder ratio. When the sludge content was more than 30%, it was mainly affected by the sludge content. At the age of 7 days, with the increase in replacement rate of WSAs, the compressive strength of the S10 and S30 groups was higher than that of the control group. The compressive strength of the S50 experimental group was 30.38 MPa, and the loss of compressive strength was slight compared with the control group. The water absorption rate of the 28 days S100 experimental group increased by 10.71% compared with the control group. When the content of WSAs was less than 50%, the holes above 0.1 μm in the brick can be reduced and transformed into smaller holes, with a decreasing trend of the plane porosity of the brick. The microscopic results of the baking-free brick showed that the three-phase system of WSAs-interface transition area-mortar was poorly bonded and delaminated compared with the gravel aggregate-interface transition area-mortar system, and damage was more likely to occur in the WSAs and interface transition area. The above results show that it is feasible to use sludge and WSAs instead of sand for the preparation of baking-free bricks. This technology not only solves the problem of sludge disposal, but also protects the over-exploitation of mineral resources, and the technology has a broad application prospect and market value.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools