 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Morphological Evaluation of PLA/Soybean Oil Epoxidized Acrylate Three-Dimensional Scaffold in Bone Tissue Engineering
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Al Nahrain University, Al Jadriya Bridge, Baghdad, 64074, Iraq
* Corresponding Authors: Mahmood Hameed Majeed. Email: ;
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(9), 2391-2408. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.019887
Received 22 October 2021; Accepted 14 January 2022; Issue published 30 May 2022
Abstract
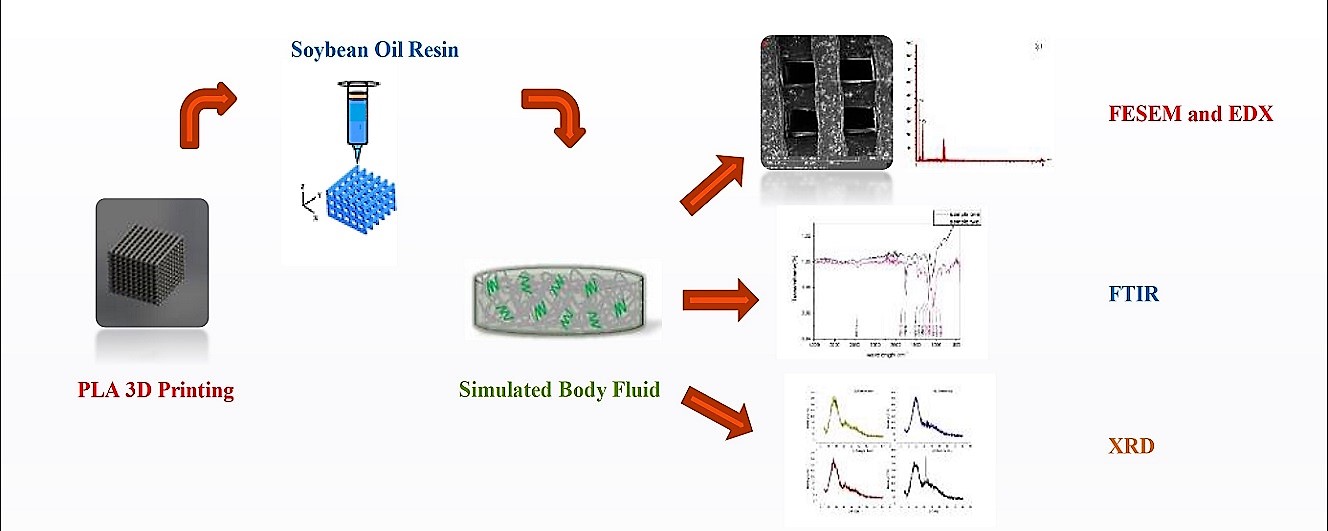
Tissue engineering’s main goal is to regenerate or replace tissues or organs that have been destroyed by disease, injury, or congenital disabilities. Tissue engineering now uses artificial supporting structures called scaffolds to restore damaged tissues and organs. These are utilized to attach the right cells and then grow them. Rapid prototyping appears to be the most promising technology due to its high level of precision and control. Bone tissue replacement “scaffolding” is a common theme discussed in this article. The fused deposition technique was used to construct our scaffold, and a polymer called polylactic acids and soybean oil resin were used to construct our samples. The samples were then divided into two groups; the first group was left without immersion in the simulated body fluid and served as a control for comparison. The second group was immersed in the simulated body fluid. The results of the Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were utilized to interpret the surface attachment to ions, elements, and compounds, giving us a new perspective on scaffold architecture. In this study, an innovative method has been used to print therapeutic scaffold that combines fused deposition three-dimensional printing with ultraviolet curing to create a high-quality biodegradable polymeric scaffold. Finally, the results demonstrate that adding soybean oil resin to the PLA increased ion attachment to the surface while also attracting tricalcium phosphate formation on the surface of the scaffold, which is highly promising in bone tissue replacement. In conclusion, the soybean oil resin, which is new in the field of bone tissue engineering, shows magnificent characteristics and is a good replacement biopolymer that replaces many ceramic and polymeric materials used in this field that have poor morphological characteristics.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools