 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Influences of Multi-Component Supplementary Cementitious Materials on the Performance of Metakaolin Based Geopolymer
1
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, 430070, China
2
Wuhan Hanyang Municipal Construction Group Co., Ltd., Wuhan, 430050, China
3
Faculty of Materials Science and Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Geological Survey and Evaluation of Ministry of Education, China
University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074, China
4
Guangxi Key Laboratory of New Energy and Building Energy Saving, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, 541004, China
5
Zhejiang Institute, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Hangzhou, 311305, China
6
Key Laboratory of Advanced Building Materials of Anhui Province, Anhui Jianzhu University, Hefei, 230022, China
7
Key Laboratory of Road Structure and Materials of Ministry of Transport, Chang’an University, Xi’an, 710064, China
* Corresponding Author: Ping Duan. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Material from Agricultural Waste and By-Product and Its Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(7), 1813-1828. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.018771
Received 16 August 2021; Accepted 14 October 2021; Issue published 07 March 2022
Abstract
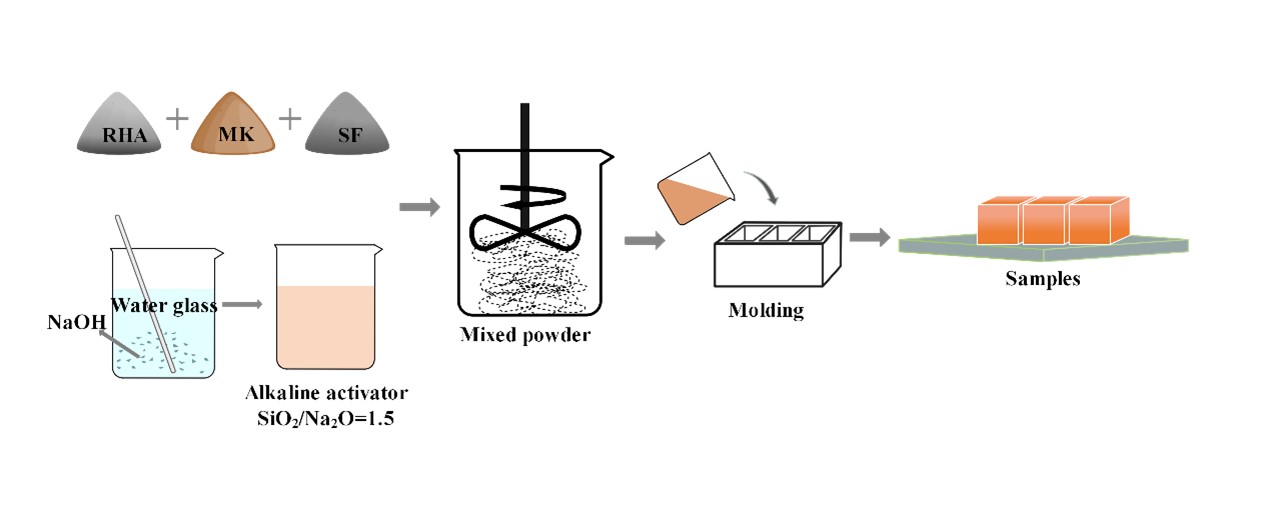
In this study, the workability and reaction mechanism of metakaolin (MK) based geopolymer blended with rice husk ash (RHA) and silica fume (SF) was investigated. The prepared samples were subjected to tests including compressive strength and fluidity tests. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Scanning electron microscope (SEM) were employed to explore the phase composition and microstructure of geopolymers. The molecular bonding information of geopolymer was provided by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Meanwhile, the porosity of geopolymer was obtained by Mercury intrusion porosimeter (MIP) analysis. The high-activity RHA obtained after calcination at 600°C was used as a supplementary cementitious material to prepare geopolymer. The properties of preventing morphology cracking and compressive strength are improved. The addition of RHA and SF changes the working performance of MK based geopolymer and provided a theoretical basis for future practical applications. Meanwhile, the high chemical activity of SF and RHA contributes to the healing of microcracks.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools