 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
One Step Regioselective Acylation of Polyphenolic Wood Extractive and Its Application for Wood Treatment
Université de Lorraine-Institut National de Recherche Pour l’Agriculture, L’Alimentation et L’Environnement (INRAE), Laboratoire d’Etudes et de Recherche sur le Matériau Bois (LERMAB), Nancy, France
* Corresponding Author: Christine Gérardin-Charbonnier. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Material from Agricultural Waste and By-Product and Its Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(6), 1491-1503. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.016364
Received 01 March 2021; Accepted 21 July 2021; Issue published 20 January 2022
Abstract
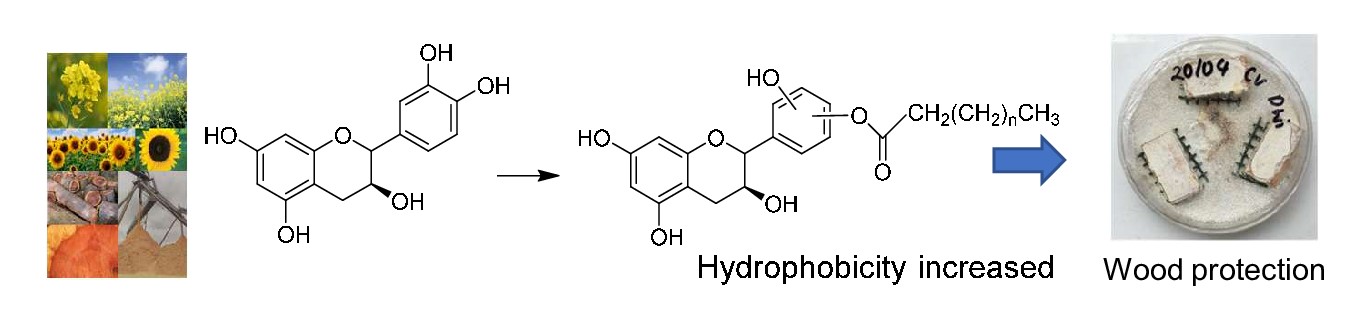
This study evaluated the methods of grafting commercial catechin with fatty acids, namely capric acid (C10), lauric acid (C12), and myristic acid (C14) through esterification. Specimens of beech wood (Fagus sylvatica L.) were impregnated with catechin and modified catechin-fatty acids, separately, at a 5% concentration diluted in ethanol using vacuum pressure treatment and subjected to leaching. The weight percentage gain before leaching (WPG), after leaching (WPGAL), and weight loss due to leaching (PL) were investigated. Both leached and unleached samples were tested against white-rot fungi (Trametes versicolor) in Petri-dishes for twelve weeks. Results show that samples treated with modified catechin-fatty acids provide improved resistance towards leaching. Catechin-C14 was found to be more promising, possibly due to its chain length. The decay weight loss for samples treated with modified catechin-fatty acids does not differ significantly between the samples that leached and not. Despite the antifungal properties of catechin, the treatment with catechin alone was insufficient to protect wood samples from fungi. Further, it is recommended to increase the concentration level of modified catechin to obtain a significant effect on the decay resistance.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools