 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Recent Technologies for the Extraction and Separation of Polyphenols in Different Plants: A Review
1 Co-Innovation Center for Efficient Processing and Utilization of Forest Products, College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing
Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, China
2 Nexus of Rare Neurodegenerative Diseases, School of Life Sciences, Faculty of Science, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong
Kong, China
3 College of Food Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 266003, China
* Corresponding Author: Caoxing Huang. Email:
# Yingying Hu and Bowen Yan contributed equally to this work, regarding as the first author
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(6), 1471-1490. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.018811
Received 19 August 2021; Accepted 24 September 2021; Issue published 20 January 2022
Abstract
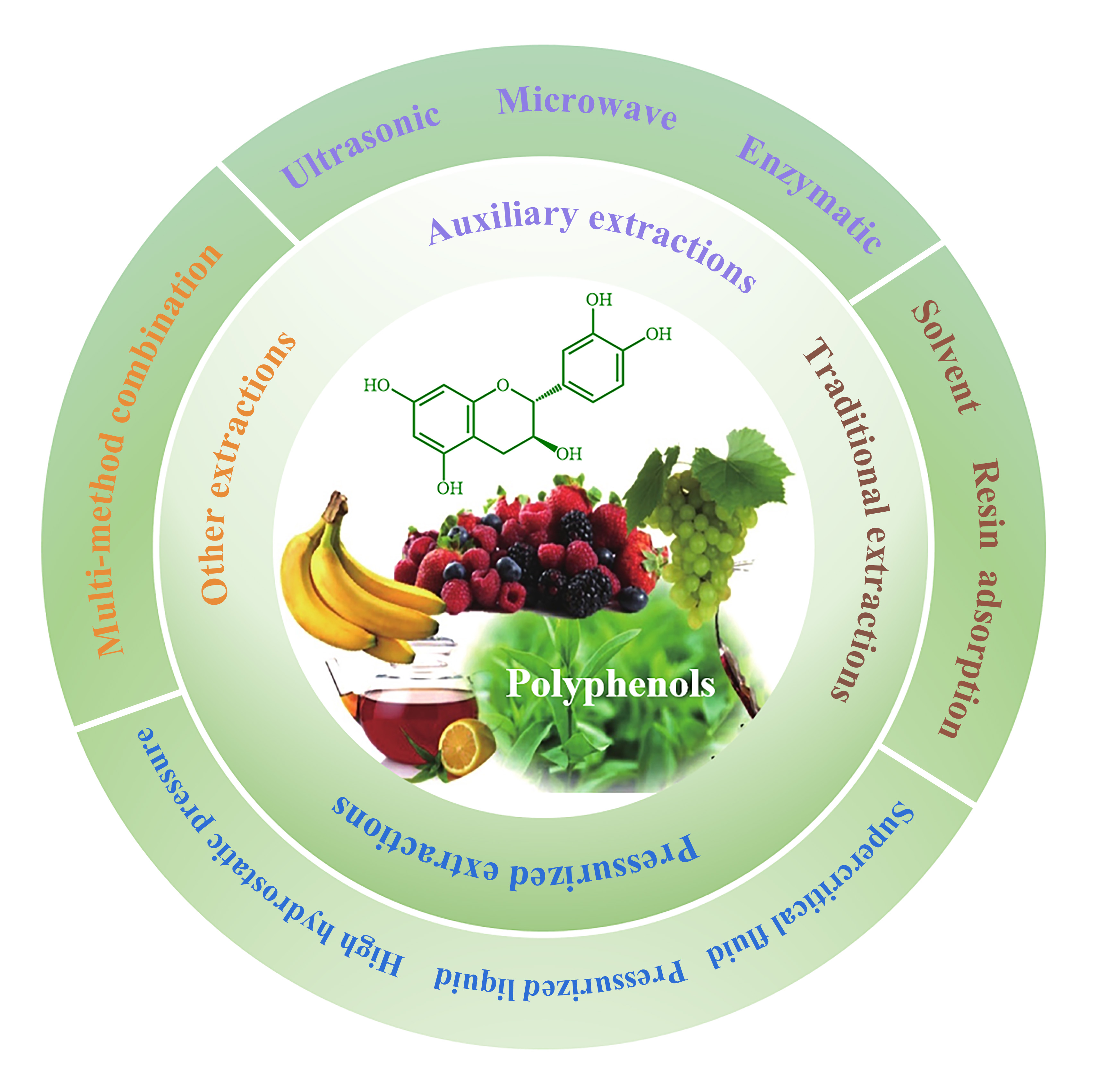
Polyphenol is an important secondary metabolite with unique physiological functions and biological activity. The polyphenols in different plants and biomass have different chemical structures, which needs various extraction methods to obtain them. Recently, plant polyphenols and their application research in food and medicine have become a research hotspot, which is mainly focused on preparation, purification, structural identification, and biological activity assays. Among these researches, extraction and separation are the key sections to investigate the structure and activity of polyphenol. Hence, this review summarized the recent extraction and separation techniques of polyphenol, including solvent extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, ultrasonic extraction, enzymatic extraction, resin adsorption extraction, and electric field method, etc. In addition, this review also reveals the current problems and proposes future extraction research of polyphenol. It is hoped that this review will provide a guide for the researchers who are actively committed to promoting progress in the field of polyphenolics.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools