 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Production of Bio-Calcium Oxide Derived from Hatchery Eggshell Waste Using an Industrial-Scale Car Bottom Furnace
1 Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok, 65000, Thailand
2 Sustainable Environment and Energy Research Unit, Mahasarakham University, Mahasarakham, 44150, Thailand
* Corresponding Author: Apipong Putkham. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Material from Agricultural Waste and By-Product and Its Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(4), 1137-1151. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.018560
Received 03 August 2021; Accepted 01 October 2021; Issue published 02 November 2021
Abstract
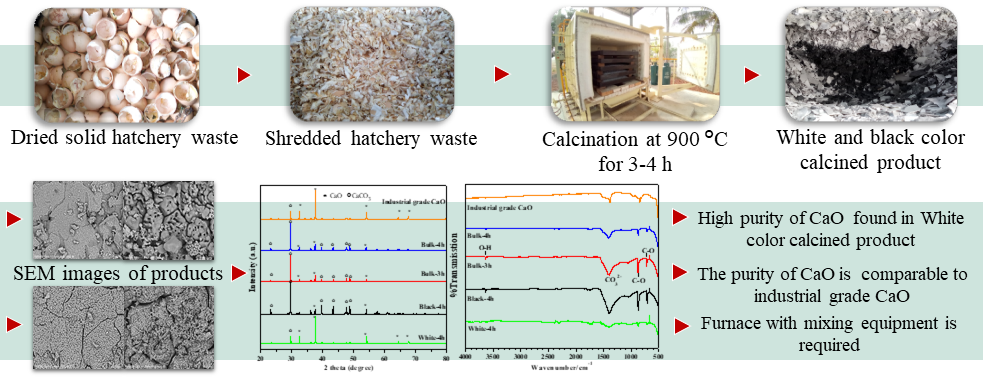
The valorization of eggshell waste as bio-calcium oxide is crucial for pollution prevention and supporting sustainable development. There are several reports on the thermal conversion of eggshell waste to calcium oxide for the partial or complete substitution of natural lime applications. However, this paper reports the thermal decomposition of large amounts of hatchery eggshell waste on an industrial-scale car bottom furnace for the first time. The hatchery eggshell waste was sundried and placed into five stacked trays in the car bottom furnace. The calcination of the eggshell waste was conducted at 900°C for 3 and 4 h under an atmosphere of air. Both the physical and chemical properties of the eggshell samples and the bio-quicklime products were carefully examined by TGA, SEM, XRD, FTIR, and XRF. The results demonstrate that the purity of calcium oxide in the quicklime products increased from 79% to 87% upon increasing the calcination time from 3 to 4 h. However, the color of the calcined eggshell samples at the surface of the pile was white while the color of the product beneath the surface was black or dark gray. The purity of the calcium oxide of both the black and white calcined samples was 76.4% and 91.5%, respectively. These results indicate the limited efficacy of the car bottom furnace for thermal decomposition of the large amount of eggshell waste to calcium oxide. Additionally, the production cost of bio-calcium oxide is approximately twice the cost of industrial grade lime. For further industrial applications, the furnace should contain the mixing equipment for improving the thermal decomposition of the large pile of eggshell waste. Furthermore, the oil burner system may be used in order to reduce fuel costs.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools