 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Grain Boundary Passivation Modulated by Molecular Doping for High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells
College of Chemical and Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, 266042, China
* Corresponding Authors: Guorui Cao. Email: ; Yue Liu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Perovskite Solar Cells)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(12), 3505-3519. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.023122
Received 11 April 2022; Accepted 12 May 2022; Issue published 14 July 2022
Abstract
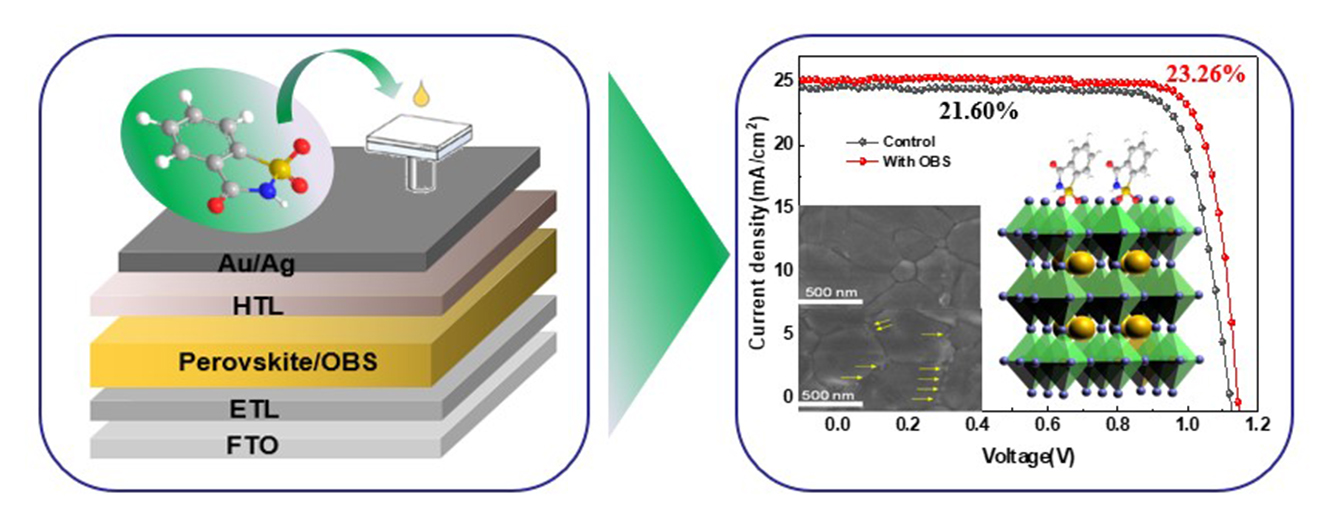
Aiming to reduce the defects of perovskite film and improve carrier transport, an organic small molecule, benzo [d]isothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxide (OBS), is introduced as an additive in the solution-processing of perovskite and prepare uniform perovskite films with a continuous distribution of OBS at grain boundaries. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy are conducted to reveal the interactions of hydrogen bonding and coordination bonding between OBS and perovskite. Various characterizations (including X-ray diffraction, UV-vis spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, etc.) are conducted to uncover the effect of OBS on device performance. Consequently, high efficiency of 23.26% is obtained for the OBS-treated device, while the control device shows only a companion efficiency of 21.60%.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools