 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Multi-Layer and Multi-Objective Optimization Design of Supporting Structure of Large-Scale Spherical Solar Concentrator for the Space Solar Power Station
School of Chemical Engineering, Northwest University, Xi’an, 710069, China
* Corresponding Author: Lin Zhu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Tools for Renewable Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(11), 2835-2849. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.021840
Received 08 February 2022; Accepted 21 March 2022; Issue published 29 June 2022
Abstract
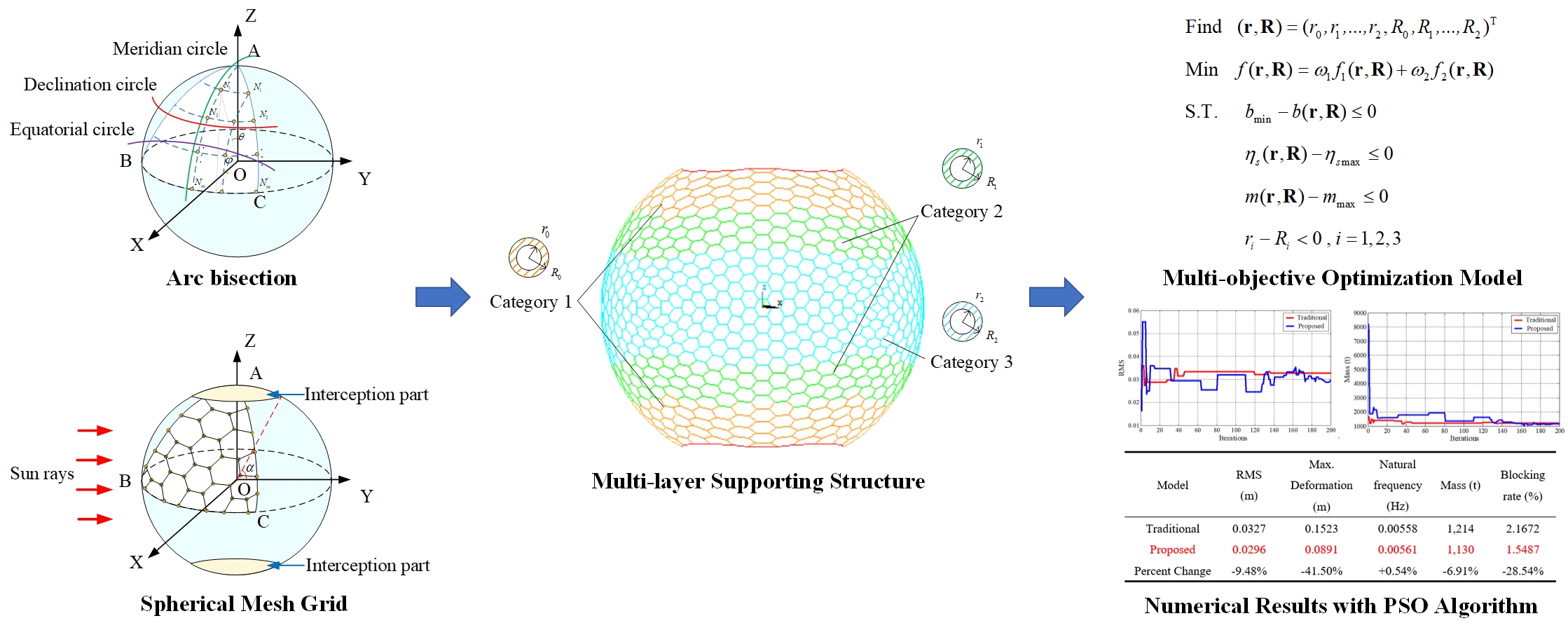
Space solar power station is a novel renewable energy equipment in space to provide the earth with abundant and continuous power. The Orb-shaped Membrane Energy Gathering Array, one of the alternative construction schemes in China, is promising for collecting space sunlight with a large-scale spherical concentrator. Both the structural and optical performances such as root mean square deformation, natural frequency, system mass, and sunlight blocking rate have significant influences on the system property of the concentrator. Considering the comprehensive performance of structure and optic, this paper proposes a novel mesh grid based on normal polyhedron projection and spherical arc bisection for the supporting structure to deal with the challenge of the large-scale structural modular design. For both achieving low system mass and high surface precision, a multilayer and multi-objective optimization model is proposed by classifying the supporting structure into different categories and optimizing their internal and external diameters. The Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm is adopted to find optimal sectional dimensions of the different kinds of supporting structure. The infinite model is also established and structural analysis is carried out, which are expected to provide a certain reference for the subsequent detailed structural design. The numerical results indicate that the spherical concentrator designed by the novel mesh grid would obtain as high as 94.37% sunlight collection efficiency. The supporting structure constructed with the multiple layers would reduce the system quality by 6.92%, sunlight blocking rate by 28.54%, maximum deformation by 41.50%, and root mean square by 9.48% to the traditional single layer, respectively.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools