 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Eco-Friendly Composites Made from Wood Dust and Recycled Polystyrene
1 Department of Forestry and Natural Environment, International Hellenic University, Drama, Greece
2 Department of Forestry, Wood Sciences and Design, University of Thessaly, Karditsa, Greece
3 Wood Science and Technology Department, Faculty of Materials Engineering & New Technologies, Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University, Tehran, Iran
* Corresponding Author: Antonios N. Papadopoulos. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Wood Composites from Renewable Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2022, 10(1), 75-88. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2022.017759
Received 04 June 2021; Accepted 15 June 2021; Issue published 27 July 2021
Abstract
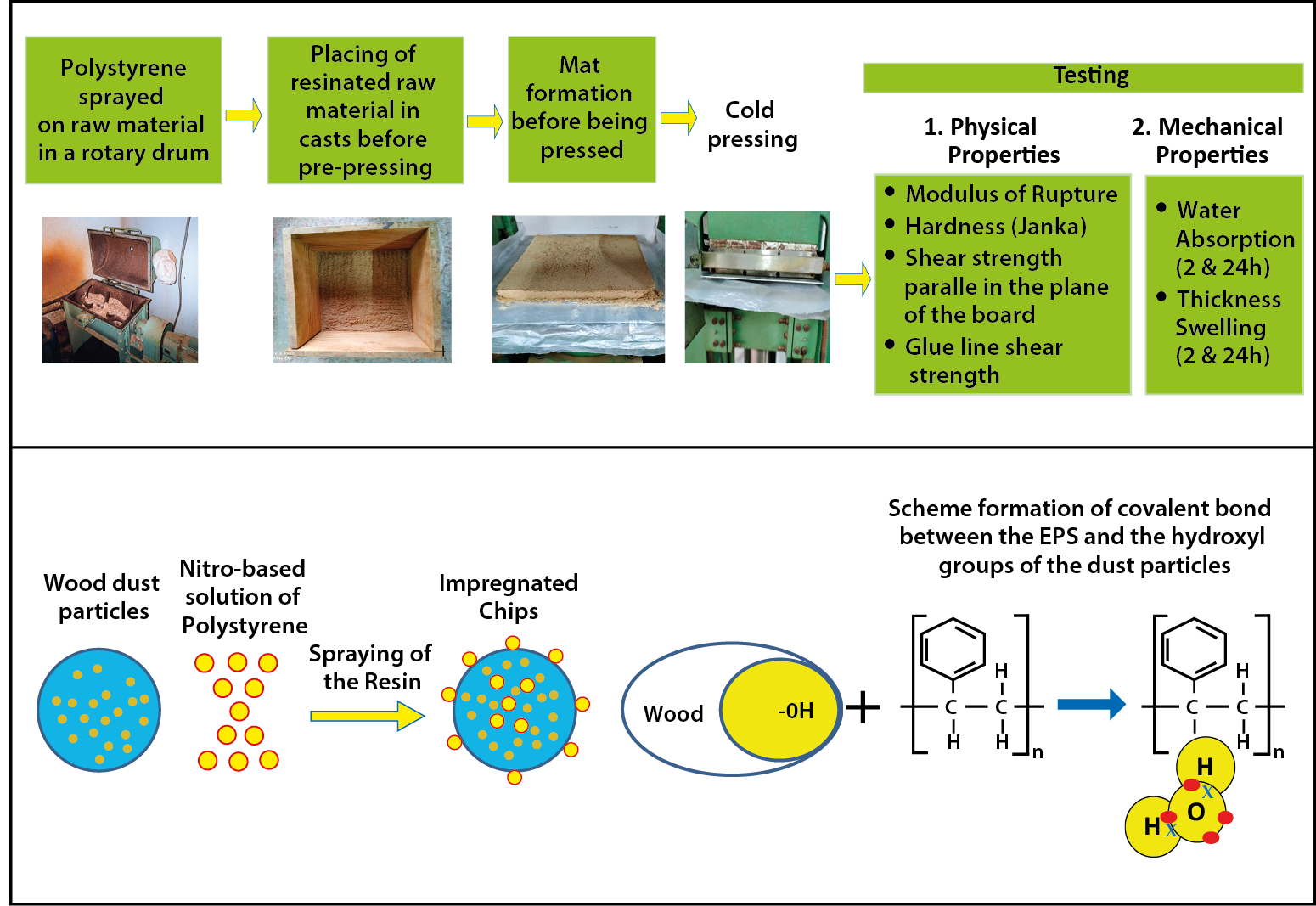
The development of alternative wood composites based on the use of waste or recycled materials can be beneficial due to over exploitation of natural resources. Under this frame, an option for the successful utilization of waste polystyrene which avoids environmental problems that formaldehyde adhesives cause and also reduces waste disposal, is its potential application as a binder for the production of value-added environmentally friendly and low cost wood composites. Two types of panel were successfully made, consisting of wood dust and two recycled polystyrene contents, namely, 15% and 30%. Both physical properties, water absorption and thickness swelling, and mechanical properties, modulus of rupture, shear strength parallel in the plane of the board and glue line shear strength, were significantly improved as the recycled polystyrene content increased from 15% to 30%. Water absorption and thickness swelling after 24 h immersion in water were improved by 165% and 750% as the recycled polystyrene content increased from 15% to 30%. The magnitude of the improvement in mechanical properties however, was less pronounced than of the physical properties since modulus of rupture, shear strength parallel in the plane of the board and glue line shear strength were increased by 43.6%, 50% and 61.5%, respectively. The low viscosity of the recycled polystyrene caused more mobility inside the panel matrix and therefore, an improved penetration took place into adequate depth of the compressed dust particles. It is concluded that boards can be successfully produced using these waste raw materials, wood dust and recycled polystyrene in organic solvent as a binder, and therefore it can reduce waste disposal and provide cleaner production for the development of wood-based boards.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools