 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Improvement of the Birch Outer Bark Plywood Binder: The Impact of the Bark Fractional Composition and the Binder Preparation Methodology
Latvian State Institute of Wood Chemistry, Riga, LV-1006, Latvia
* Corresponding Author: Rūdolfs Bērziņš. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Biorefinery Technologies and Products – 2024)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(12), 2095-2113. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.056769
Received 30 July 2024; Accepted 21 October 2024; Issue published 20 December 2024
Abstract
Birch outer bark (BOB) from Betula pendula Roth. is a unique and valuable biomass feedstock that contains suberin. The biopolyester suberin is built from bifunctional fatty acids-suberinic acids (SA)-which can be obtained through a depolymerization process in an alkaline medium and used as a binder due to their adhesive properties. The aim of this study was to develop the SA-containing binder and identify suitable pressing conditions to produce plywood that meets the shear strength requirements of the EN 314-2 standard 3rd moisture resistance class for bonding quality, ensuring durability in unprotected exterior conditions (shear strength ≥ 1 N/mm2). The raw BOB material was modified by extraction, milling, and fractionation, and the depolymerization methodology was enhanced by additional sieving to improve the adhesive properties of the obtained binders. Several analytical methods were used to characterize the feedstock and the binders. Higher heating value was used to assess the pure outer bark content of BOB. GC-MS and GPC were used to describe the monomeric and oligomeric composition of binders. TGA was used to describe the biopolymeric composition and DSC was used to determine the thermal behavior of the binders. As a result, successful modification of feedstock (extracted BOB, milled through 2 mm sieve, 1–2 mm fraction used) and its depolymerization process (implementing the separation of coarse ligno-carbohydrate particles by 1 mm mesh sieve) was employed to obtain a binder for which suitable hot-pressing parameters were determined −200°C for 5 min at 1.8 MPa. Consequently, plywood with shear strength of 1.26 ± 0.18 N/mm2, which adheres to the EN 314-2 standards 3rd moisture resistance class, was obtained.Graphic Abstract
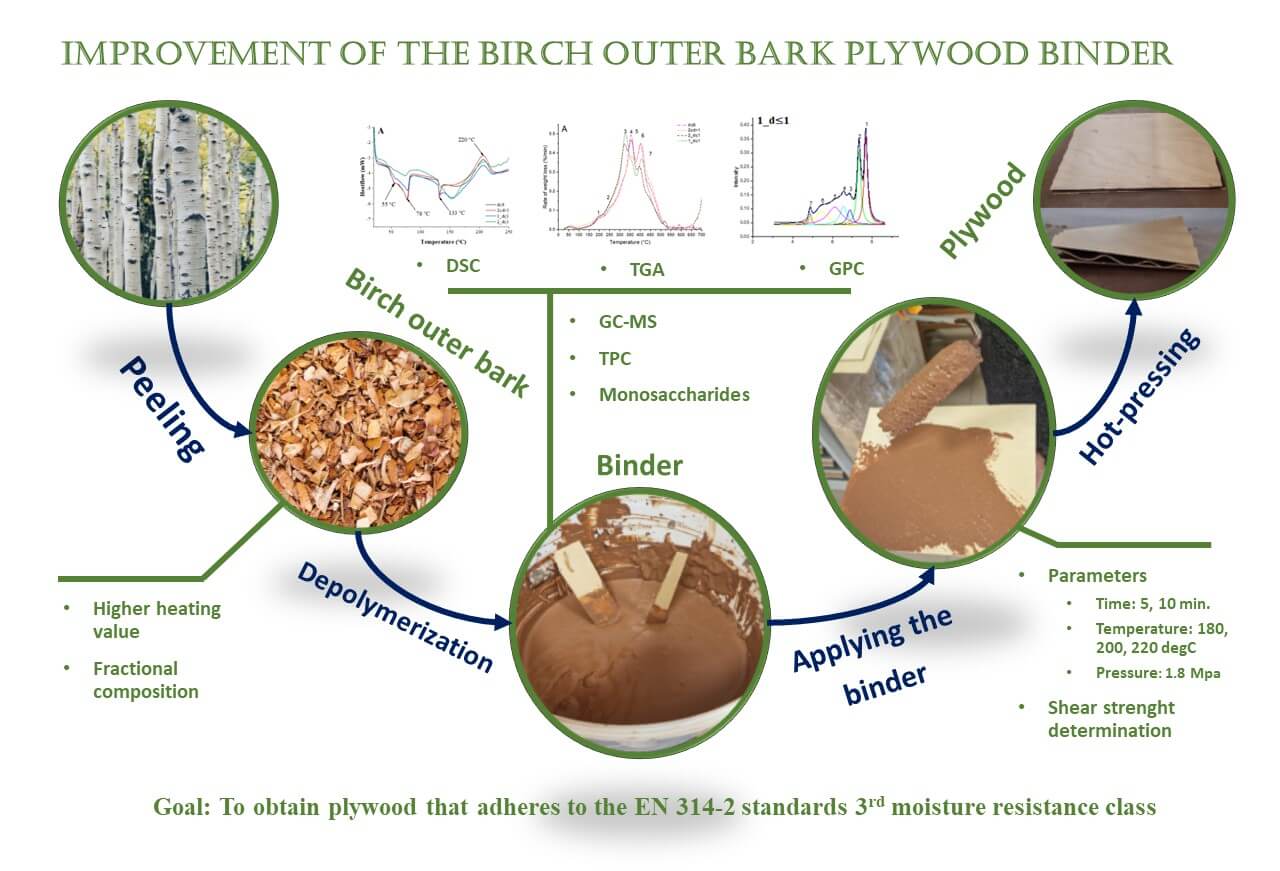
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools