 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Evaluation on Physical Characteristics of Konjac Polysaccharides-Based Film Coating and Its Application for Strawberries Preservation
1 Department of Agricultural Industrial Technology, Faculty of Agro-Industrial Technology, Universitas Padjadjaran, Jatinangor, 45363, Indonesia
2 Research Center for Biomass and Bioproducts, National and Innovation Agency, Cibinong, 1691, Indonesia
3 Research Collaboration Center for Biomass and Biorefinery between BRIN and Universitas Padjadjaran, Jatinangor, 45363, Indonesia
4 Research Center for Appropriate Technology, Universitas Padjadjaran, Jatinangor, 45363, Indonesia
5 Department of Food Industrial Technology, Faculty of Agro-Industrial Technology, Universitas Padjadjaran, Jatinangor, 45363, Indonesia
6 Department of Forest Products, Faculty of Forestry and Environment, IPB University, Bogor, 16680, Indonesia
7 Institute of Wood Technology and Renewable Materials, Department of Material Sciences and Process Engineering, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna (BOKU), Vienna, 1180, Austria
* Corresponding Authors: Roni Kastaman. Email: ; Lukmanul Hakim Zaini. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(1), 181-197. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.056475
Received 23 July 2024; Accepted 10 October 2024; Issue published 20 January 2025
Abstract
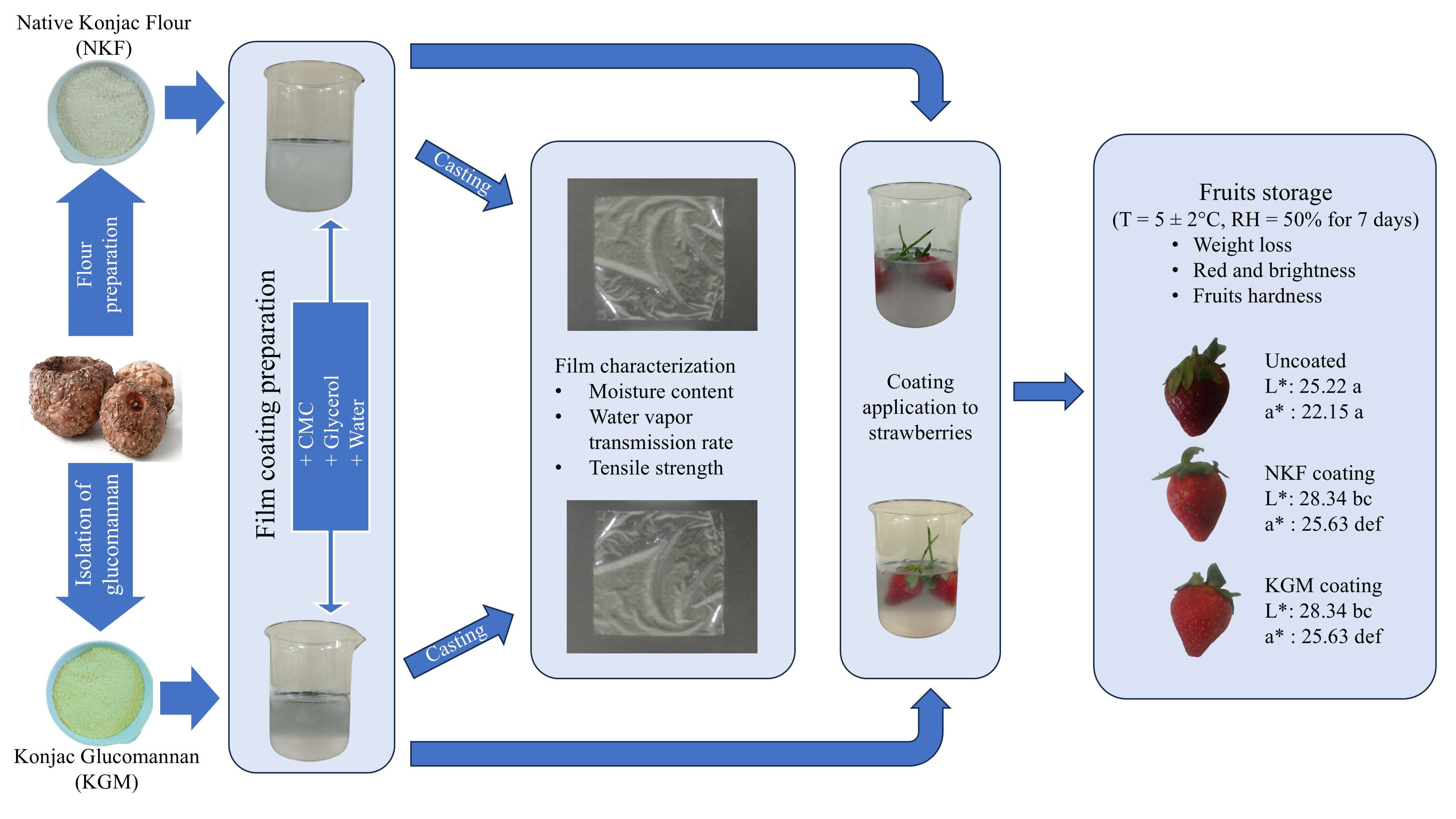
Konjac is an ideal candidate for edible coatings on fruits due to its hydrophilic properties, film-forming ability, barrier properties, safety, and biodegradability. Meanwhile, the high market demand for strawberries necessitates post-harvest treatment to extend their shelf life and preserve their quality, as strawberries are known for their fragile skin and soft texture. To fully utilize konjac and develop high-quality coating films, native konjac flour (NKF) and konjac glucomannan (KGM) were extracted from its corm and used as a coating film for strawberries in the present study. Therefore, this study aimed to compare the physical properties of the film coatings between NKF and KGM, and evaluate their effects on strawberries preservation over 7 days of storage. A multistage extraction process was employed to isolate NKF and KGM, after which the glucomannan content was measured. NKF yield was 31.81%, exceeding KGM yield of 26.42%, and the glucomannan content obtained of NKF (25.93%) was higher than KGM (21.41%). Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy confirmed that both NKF and KGM contain glucomannan in their structure. Furthermore, both NKF and KGM were combined with carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and glycerol to produce eight thin-layer films to assess their physical and mechanical properties. Compared to the KGM variant, the NKF variant generally exhibited higher moisture content, water vapor transmission rate, and tensile strength. However, NKF was less effective than KGM in extending strawberry storage life, leading to faster color changes and greater weight loss, despite maintaining similar hardness values. Nonetheless, konjac-based coatings were generally effective at maintaining the freshness and quality of strawberries compared to uncoated samples. Konjac shows promise as an edible coating, improving fresh produce shelf life and appeal, aligning with consumer preferences for natural and sustainable products.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools