 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Determination of Physical, Mechanical and Fire Retardancy Properties of Innovative Particleboard Made from Corn Stalk (Zea mays L.) Particles
1 School of Agriculture, Food and Ecosystem Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, 3121, Australia
2 Research Center for Biomass and Bioproducts, National Research and Innovation Agency, Bogor, 16911, Indonesia
3 Research Institute of Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Kyoto, 611-0011, Japan
4 School of Agriculture, Food and Ecosystem Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Creswick, 3363, Australia
5 Faculty of Architecture, Building and Planning, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, 3010, Australia
* Corresponding Author: Lilik Astari. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Valorization of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Functional Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(10), 1729-1756. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.054786
Received 07 June 2024; Accepted 02 September 2024; Issue published 23 October 2024
Abstract
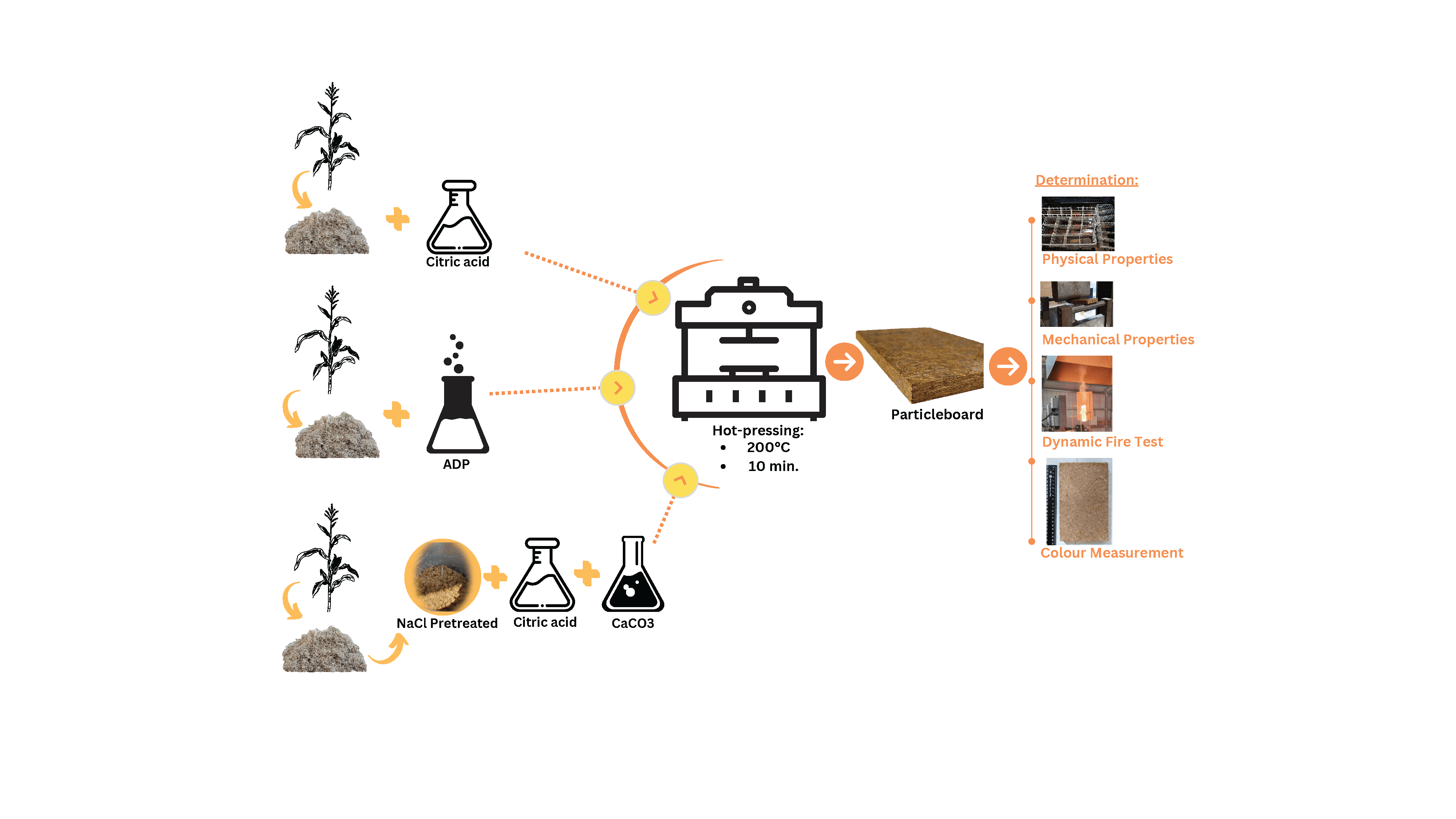
The demand for particleboard is increasing along with economic and population growth. However, two major barriers to the manufacture of particleboard are a shortage of raw materials (woodchips) and the emission of formaldehyde from conventional adhesives. Agricultural by-products such as corn stalks contain an abundance of renewable lignocellulosic fiber. This study evaluates the effect of citric acid as a natural adhesive and fire retardant addition on the physical, mechanical, and fire retardancy properties of particleboards fabricated from corn stalks. A cost-effective and inorganic salt, calcium carbonate, was tested to enhance the fire retardancy. Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate was also considered as a comparative control. Particleboards with the addition of calcium carbonate was pretreated with sodium chloride. The particleboards were pressed for 10 min at 200°C. Japanese Industrial Standard JIS A 5908:2022 was used as the benchmark for the physical and mechanical tests. Fire retardancy was dynamically tested by simulating a Bushfire Attack Level of 19 kW/m2. The particleboard with 25 wt% citric acid had superior mechanical properties and complied with the JIS A 5908 standard for Type 13 base particleboard. Particleboard with the addition of calcium carbonate (5% and 10%) showed significantly delayed pyrolysis time.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools