Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Jin Shang1,#, Weimin Zhang2,#, Landuo Zhang1, Xiangwen Li1, Qi Wang1, Peng Zhao3, Liangliang Duan1,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2026.02025-0124
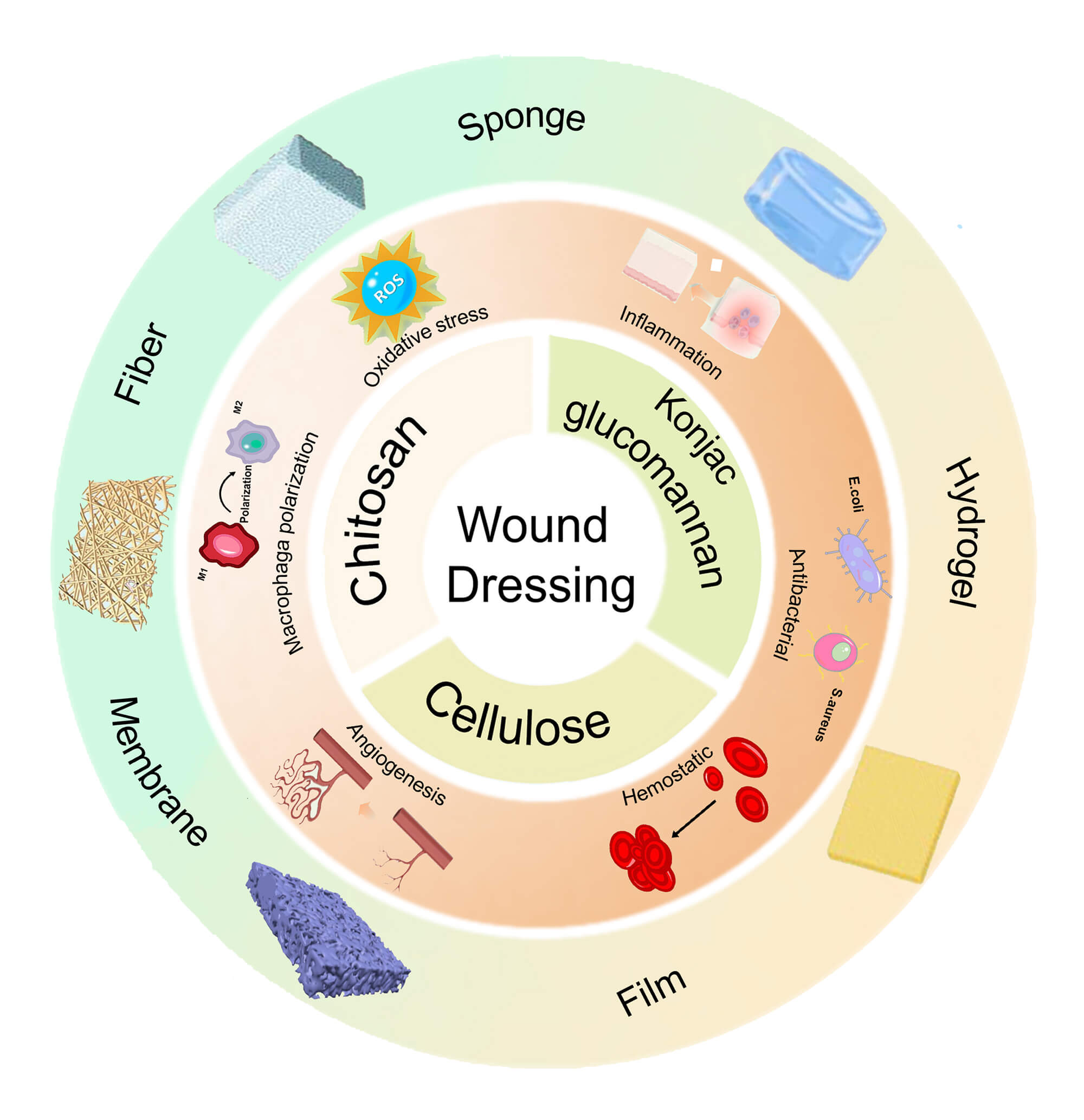
Abstract Wound healing is a complex and dynamic process essential for restoring the integrity of damaged skin. It requires wound dressings that actively regulate the wound microenvironment by preventing infection, maintaining moisture balance, allowing gas exchange, and managing exudate. Natural polysaccharides, such as konjac glucomannan (KGM), chitosan, and cellulose, are well suited to this role because of their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and intrinsic bioactivity. Extensive research has focused on developing polysaccharide-based wound dressings with enhanced functionality to promote healing. This review examines recent scientific research published mostly in the past five years on the development and application… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Megabi Adane Yizengaw1,*, Alehegn Atalay Birlie1, Tamerat Tesfaye2, Rajan Katrikan1, Eldana Bizuneh Cheklie1, Zelalem Girma1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0175
Abstract Grape by-product of the wine industry, rich in polyphenols, tannins, lignin, and natural waxes, the chemical constituents grape skins 45%–55%, seeds 25%–35%, and stems or stalks 25%–35% weight of grape provide intrinsic cross-linking, mechanical reinforcement, antioxidant activity, and water resistance, closely replicating the effects of conventional vegetable tanning without using toxic chemicals. This review comprehensively examines current eco-friendly extraction methods to isolate bioactive compounds, as well as fiber modification techniques to improve polymer compatibility. Composite fabrication involves blending processed grape waste fibers with bio-based polymers and renewable plasticizers to produce materials exhibiting competitive tensile strength,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Adib Hafiizhullah Mohamad Prim Nasir1,2, Mohd Nurazzi Norizan1,2,3,*, Nur Izzaati Saharudin1,2, Sumarni Mansur1,2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0156
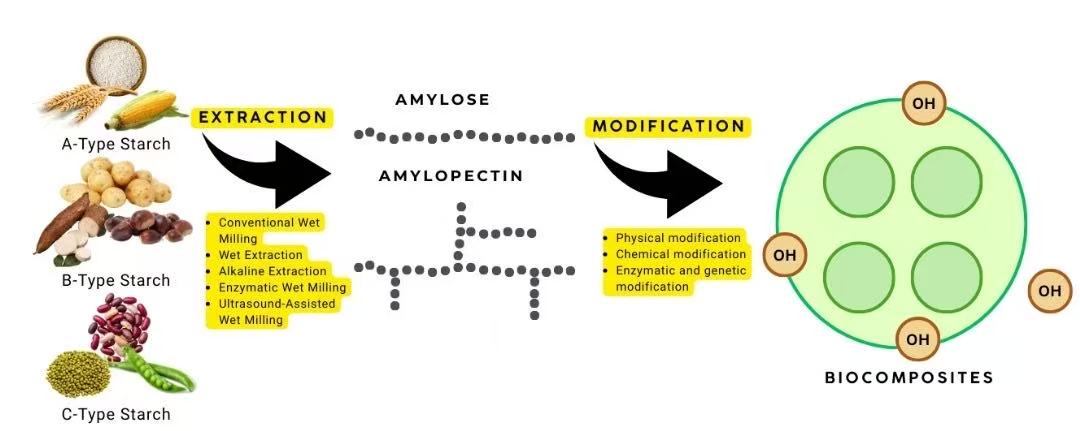
Abstract Plant-based starch has emerged as a promising natural binder in biocomposites owing to its biodegradability, renewability, and functional adaptability. This study critically reviews the extraction, modification, and performance of starches derived from sources such as corn, potato, and cassava, with particular attention to their calorific behaviour as measured through bomb calorimetry. Calorimetric analysis provides insight into the energy density and combustion efficiency of starch binders, parameters that influence both processing and End-of-life valorisation of biocomposites. Through physical, chemical, enzymatic, and genetic modifications, the inherent limitations of native starch such as moisture sensitivity and low mechanical More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Belén Rovira1,*, Aude Chabrelie1, Sauro Bianchi2, Frédéric Pichelin1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0173
Abstract The construction sector is facing significant challenges in transitioning to a defossilised system. While wood-based products have considerable potential, reliance on adhesives derived from fossil fuels poses significant sustainability concerns. Tannin-based adhesives present a compelling bio-based alternative, offering advantageous bonding properties with the potential to reduce toxicity, minimise fossil resource use, and enhance end-of-life scenarios. Despite extensive research demonstrating the technical potential of tannin-based adhesives, industrial adoption remains limited—partly due to the paucity of studies addressing their environmental impacts. The present study investigates the use of tannin-based adhesives in the production of interior-grade plywood, employing… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fitra Yurid1,2, Nadiatus Silmi3, Heni Rachmawati4,5, Nanda Nagara2, Riyanti Ekafitri6, Athanasia Amanda Septevani2,7,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0118
Abstract This study investigates the potential of starch extracted from underutilized agro-industrial resources as non-food-competing raw materials for the development of flexible bioplastics for food packaging applications. Starch was extracted from three biomass sources: rubber cassava (Manihot glaziovii), banana stem, and banana peel from Ambonese banana (Musa acuminata L.). Rubber cassava starch (SRC) exhibited the highest starch yield (50.68 ± 0.28%), significantly surpassing banana stem (SBS, 14.20 ± 0.25%) and banana peel (SBP, 3.07 ± 0.15%). The amylose contents of SRC, SBS, and SBP were 28.18%, 52.80%, and 56.57%, respectively, while their amylopectin contents were 71.83%, 47.20%, and 43.43%. FTIR spectra… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
I. Nur Azreena*, H. A. Aisyah, A. W. Noorshamsiana
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0178
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Harnessing the Potential of Natural Fiber Composites: A Paradigm Shift Towards Sustainable Materials )
Abstract This study examined the impact of various pre-treatment techniques on the physical and mechanical characteristics of particleboards derived from oil palm trunks (OPT). Thermal and chemical pre-treatments of the fibers, including hot water, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and acetic acid, were applied prior to board production. In addition, antifungal agents were incorporated as supplementary additives during the manufacturing process at varying percentages to evaluate their effect on panel performance. Morphology of the treated OPT fibers was examined, and panel properties such as thermal behavior, bending strength, bonding strength, and dimensional stability were evaluated. Statistically significant improvements (p… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
José Marcelo Faria de Queiroz Júnior1, Nathália Ramos de Melo2,3, Ulisses Oliveira Costa1, Letícia Vitorazi1,*, Flavia Lega Braghiroli4,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0163
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Nanostructured Porous Materials: Synthesis, Processing, and Applications)
Abstract The development of sustainable materials has encouraged the use of biopolymers as alternatives to synthetic polymers. Polymeric films have stood out for their high potential in environmentally sustainable applications. Conventional cellulose acetate (CA)-based films are attractive due to their biodegradability and film-forming ability. However, their functional performance often requires enhancement through the incorporation of additives. In this context, two bio-based additives were investigated: condensed tannin (0%, 5% and 10%wt.), a natural polyphenol known for its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, and nanocrystalline cellulose (CNC) (0%, 0.5% and 1%wt.), which act as reinforcing agents to improve mechanical… More >
Graphic Abstract

 Open Access
Open Access
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Siti Norasmah Surip1, Wan Nor Raihan Wan Jaafar1,*, Jaka Fajar Fatriansyah2, Ing Kong3
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0182
Abstract Most studies on kenaf fibre composites focus on the bast due to its higher fibre yield and strength, while the core is often neglected. In this work, Polylactic Acid (PLA) matrix was reinforced with both kenaf bast and core fibres at a 49:1 wt% ratio. The fibres were chemically treated and cryo-crushed to improve bonding and dispersion. Mechanical testing revealed that treated Kenaf Core Composites (KCC) exhibited comparable flexural and impact properties to Kenaf Bast Composites (KBC), with flexural strengths of 46.19 and 46.52 MPa, respectively, and impact strengths of 5.8 and 4.4 J/m. Meanwhile, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nur ‘Aisyah Ar-Raudhoh Mohammad Tahar1, Muhammad Haziq Mohd Fadzli1, Siti Nur Liyana Mamauod1,2,*, Nahrul Hayawin Zainal3
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0177
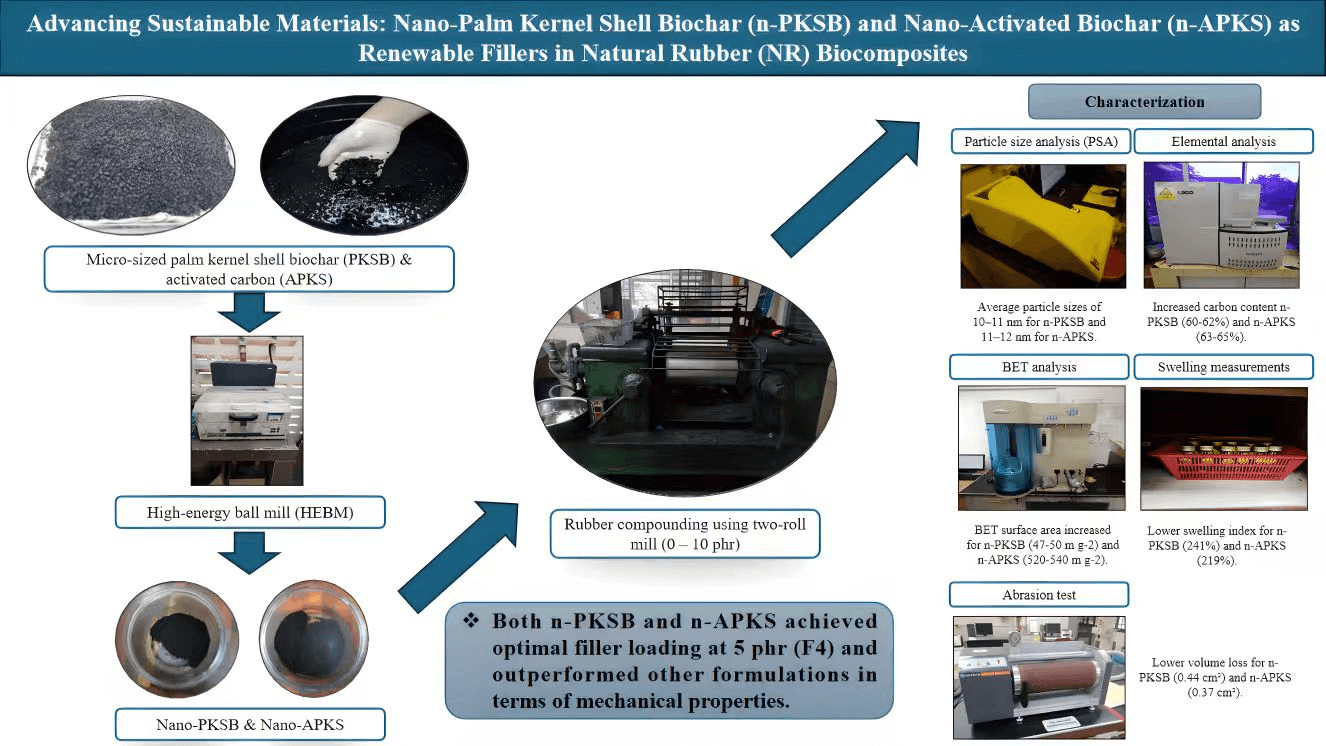
Abstract The palm oil industry is a major contributor to Malaysia’s economy, but its huge production has generated large amounts of oil palm biomass, particularly palm kernel shell (PKS), which poses environmental challenges if not properly managed. Converting PKS into biochar (PKSB) and activated carbon (APKS) offers a sustainable way to valorise this waste as potential bio-fillers in rubber composites. This study investigates the influence of nano-sized PKSB (n-PKSB) and activated PKS (n-APKS) as bio-fillers on the mechanical performance of natural rubber (NR) vulcanizates, with filler loadings ranging from 0 to 10 parts per hundred rubber… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Rasdianah Dahali1, Edi Syams Zainudin1,2,*, Mohammed Abdillah Ahmad Farid1, Tarique Jamal3, Mohd Sapuan Salit1,2, Muhammad Firdaus Abdul Halim2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0139
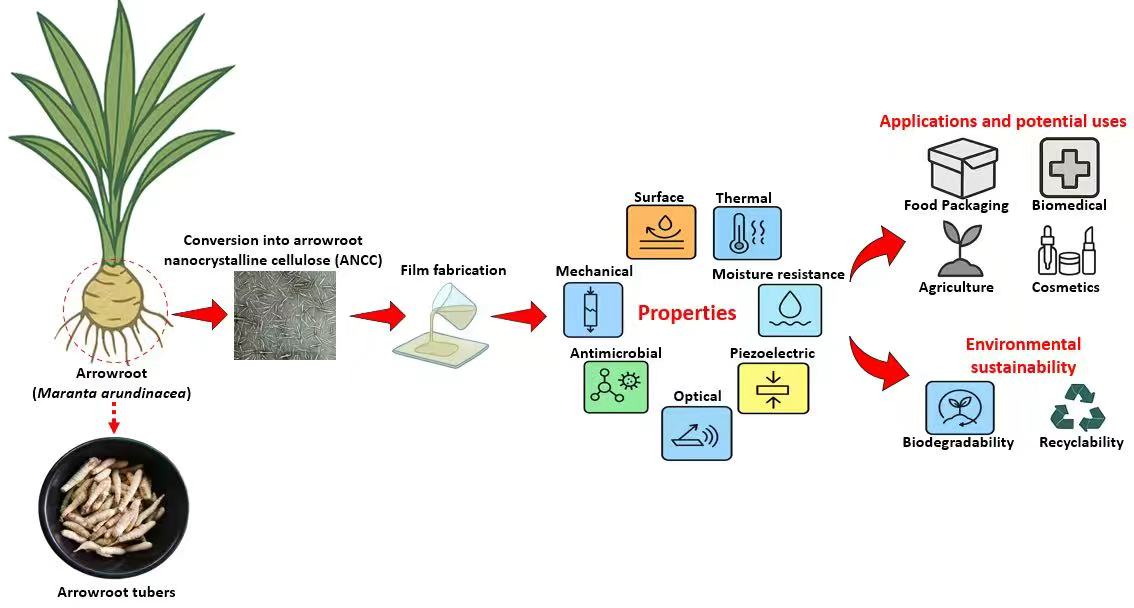
Abstract This review draws attention to the innovative use of arrowroot (Maranta arundinacea) fiber as a unique and underutilized biomass source for nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC)-based nanocomposites, presenting a noteworthy alternative to extensively researched materials like wood pulp, bacterial cellulose, and chemically modified NCCs. In contrast to traditional sources, arrowroot possesses a naturally elevated cellulose and diminished lignin content, facilitating more effective NCC extraction requiring reduced chemical input and enabling environmentally friendly processing techniques. The review evaluates the performance of arrowroot-derived nanocomposites against systems documented in the literature, including NCC-based shape memory composites and nanoparticle-reinforced films, demonstrating enhanced More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
John Letwaba1, Sudhakar Muniyasamy2,3,*, Nagarethinam Rakku1, Lucey Mavhungu1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0132
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
Abstract Melt blending of biodegradable polyesters such as poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate co-terephthalate) (PBAT) with a compatibilizer and natural filler offers a chance to develop biodegradable biocomposites with improved performance. In this study, we examined how PLA/PBAT blends behave during ultimate biodegradation (mineralization), both with and without compatibilizer and algae as a reinforcement, under controlled composting conditions using carbon dioxide (CO2) respirometry techniques. Throughout the biodegradation process, the disintegration behaviour, thermal, chemical, and morphological properties of test samples before and after biodegradation were analyzed using FTIR, TGA, DSC, and SEM techniques. The results… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Muhammad Ilham Aulia1, Alifah Syahfitri1, Imam Busyra Abdillah1, Abdus Syukur1, Dede Hermawan1,*, Rita Kartika Sari1, Mahdi Mubarok1, Muhammad Adly Rahandi Lubis2, Sukma Surya Kusumah2, Sarah Augustina2, Jajang Sutiawan2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0160
Abstract Citric acid adhesive is an alternative to formaldehyde-based adhesives that are more environmentally friendly because they are non-toxic and made from natural ingredients. This study aims to determine the effect of variations in citric acid adhesive concentrations on the physical and mechanical properties of jabon plywood. This study used citric acid adhesive with variations in citric acid (CA) concentrations of 59%, 69%, and 79%. Physical property tests include density, moisture content (MC), water absorption (WA), thickness expansion (TS), and delamination, while mechanical tests include modulus of rupture (MOR), modulus of elasticity (MOE), and shear stress… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Tamer Y. A. Fahmy1, Samir Kamel1, Ahmed M. Khalil2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0180
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
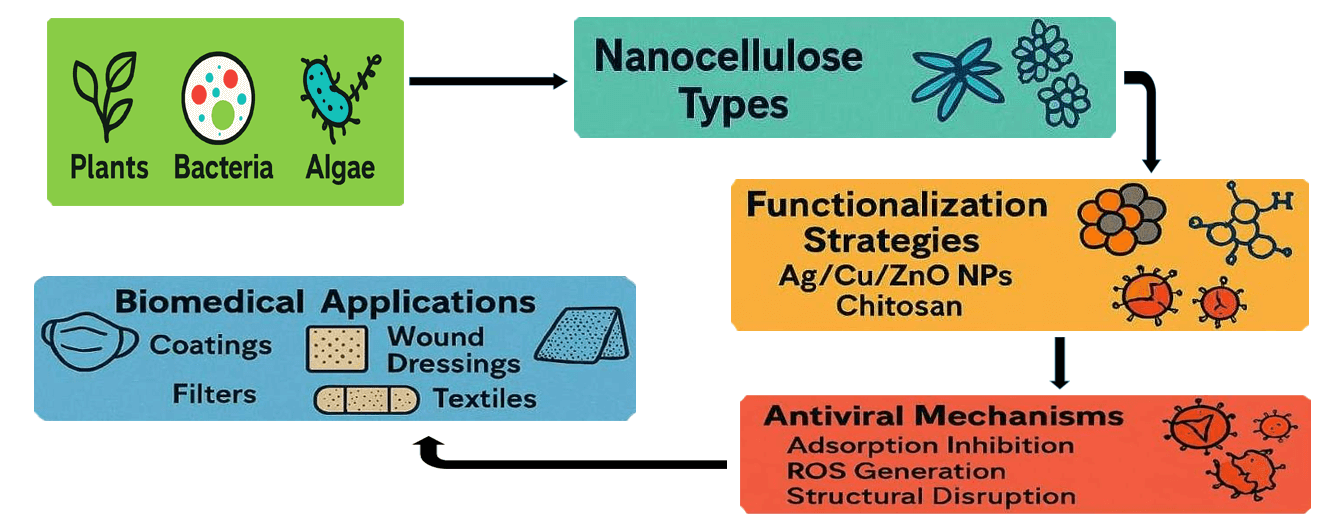
Abstract The growing threat of viral pandemics necessitates innovative antiviral strategies that are effective, sustainable, and scalable. This review highlights nanocellulose as a renewable, biocompatible nanomaterial and a promising multifunctional antiviral platform. We examine cellulose nanocrystals, nanofibrils, and bacterial nanocellulose, emphasizing their synergistic antiviral mechanisms, including nanoscale viral entrapment and surface-mediated inactivation via sulfation, cationic groups, and metal nanoparticles. Key advances include photothermally active nanocellulose-graphene composites for on-demand viral deactivation, sulfated nanocellulose mimicking heparin’s virus-trapping properties, and engineered biopolymer hybrids for targeted drug delivery and mucosal immunity. Translational applications span antiviral coatings, self-sterilizing filters, and regenerative More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ros Syazmini Mohd Ghani1,2,3,*, Mohamad Saiful Sulaiman1,2,3, Sofiyah Mohd Razali2,4, Madihan Yusof2, Ellisha Iling1,2,3
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0174
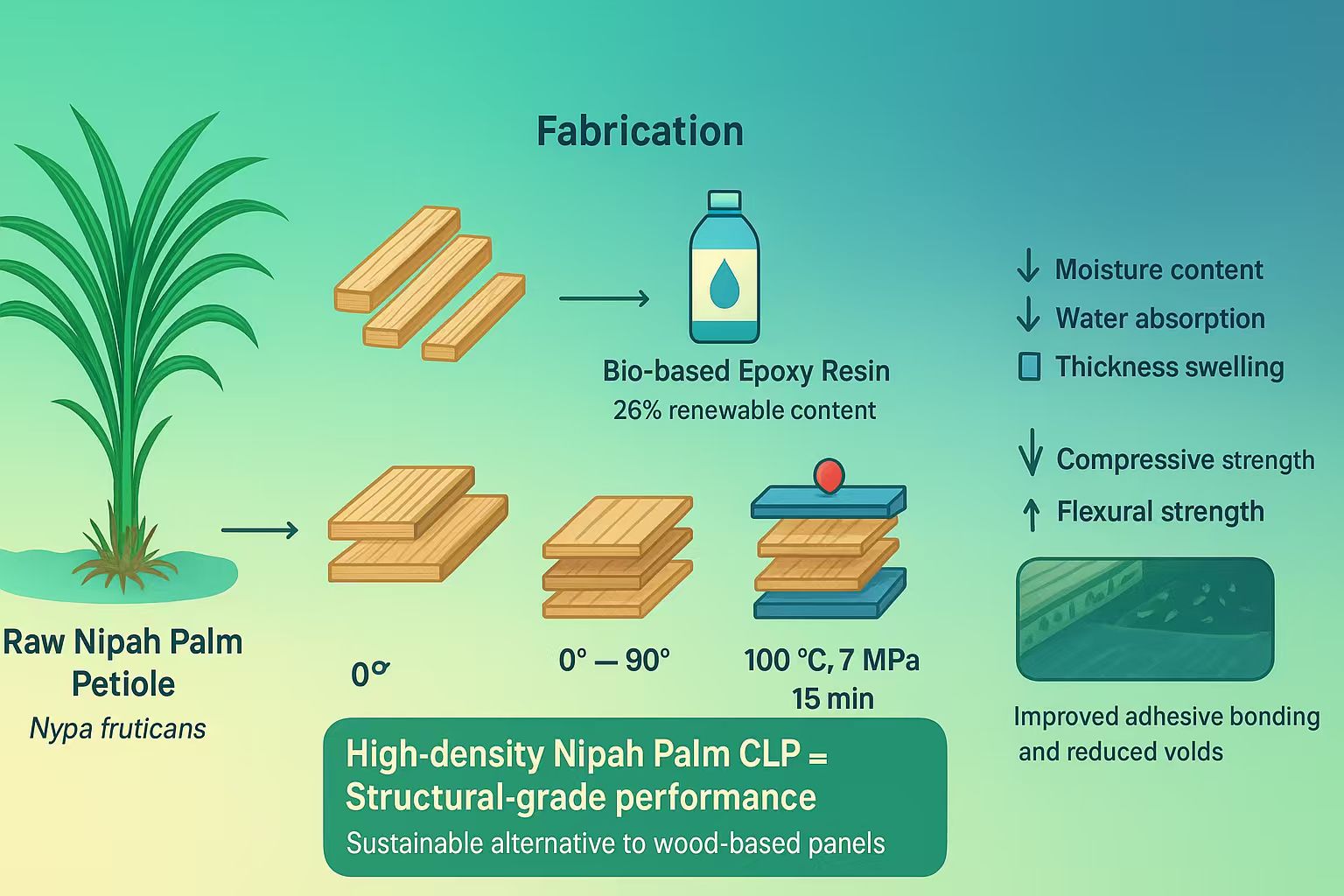
Abstract The increasing demand for sustainable construction materials has driven research into non-wood biomass for engineered composites. This study reports the preliminary fabrication and evaluation of cross-laminated panels (CLPs) made from Nipah palm (Nypa fruticans) petioles bonded with a bio-epoxy resin adhesive. Panels were manufactured at three target densities (400, 600, and 800 kg/m3) and evaluated for their physical, mechanical, and microstructural properties. Physical tests included moisture content, water absorption, and thickness swelling, while mechanical tests measured compressive and flexural strength in accordance with JIS A 5908:2022 and ASTM D1037 standards. The results showed that higher panel density More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sevakumaran Vigneswari1,2,*, Muhammad Shahrul Md Noor3, Fazilah Ariffin3,4, Azila Adnan3,4, Amirah Alias3, Lakshmanan Muthulakshmi5, Hemalatha Murugaiah6, Nor Omaima Harun3,4, Nurul Nadhirah Ruzelan3, Lakshiminarayanan Rajamani2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0148
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Valorization of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Functional Materials)
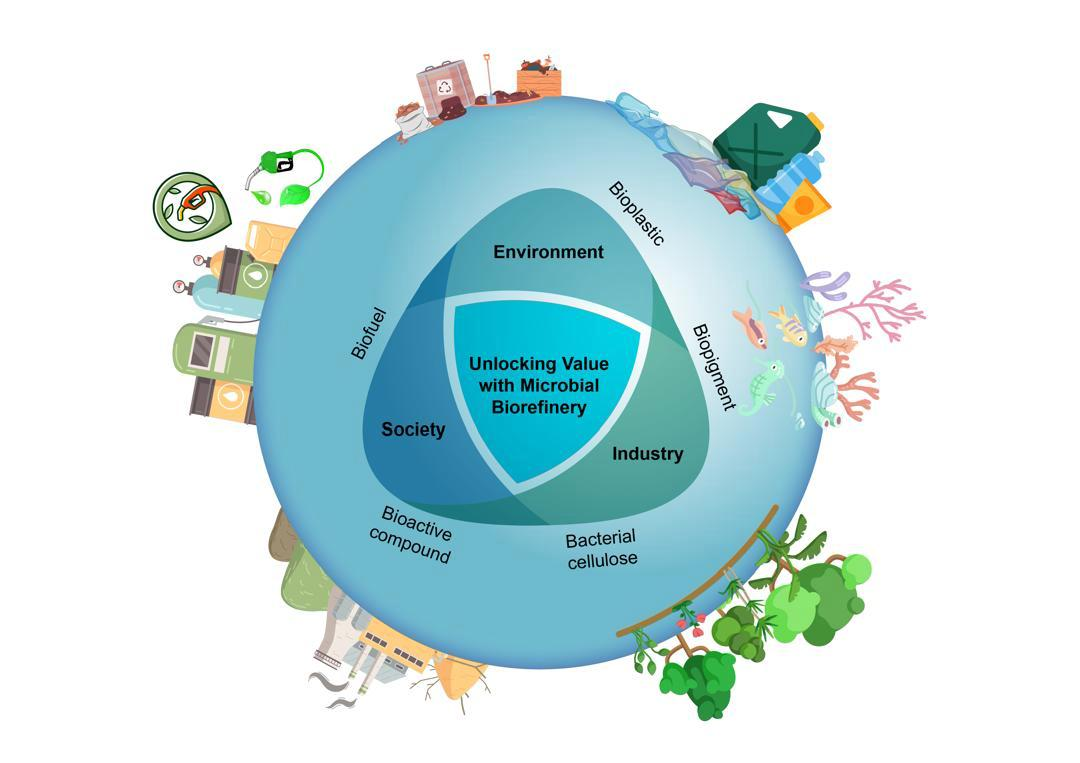
Abstract The escalating accumulation of agro-industrial waste—exceeding 350 million tons annually from post-harvest residues, food processing, and aquaculture—poses serious environmental threats, including greenhouse gas emissions, groundwater contamination, and excessive landfill usage. Although conventional treatment methods such as composting, incineration, and recycling offer partial mitigation, they often fall short of delivering scalable, circular solutions. Microbial biorefineries have emerged as a transformative approach, enabling the conversion of diverse biomass streams into high-value renewable materials. Through microbial fermentation, agricultural and municipal waste can be repurposed into functional outputs such as nanocellulose, biochar, and biocompatible compounds with applications in packaging, More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Claudia M. L. Bevilaqua1,*, José Vilemar de Araújo-Filho2, Livia F. Ximenes1, Henety N. Pinheiro1, Flávia O. M. da Silva Abreu3, Débora S. C. M. Castelo Branco4, Ana Carolina F. L. Melo4, Weibson P. P. André1, Wesley L. C. Ribeiro5, Lorena M. B. de Oliveira1
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0138
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Biobased Nanoemulsions for a Sustainable Future)
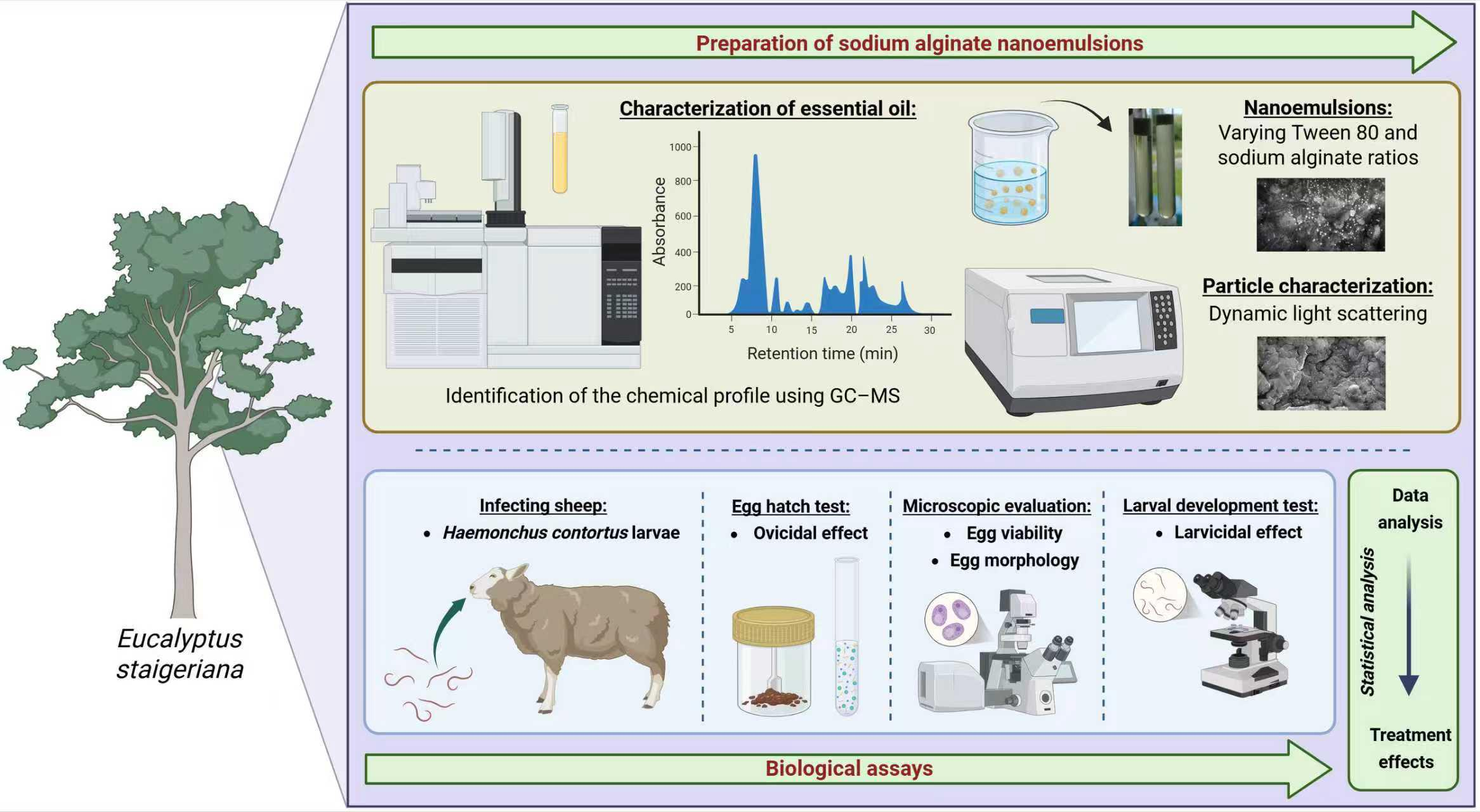
Abstract Eucalyptus staigeriana essential oil (EsEO) has well-known anthelmintic activity in small ruminants. However, its volatility limits its therapeutic action. The aim of this study was to develop a water-in-oil sodium alginate-based nanoemulsion with an effective in vitro effect on the eggs and larvae of Haemonchus contortus, a gastrointestinal parasite of sheep and goats. Four oil-in-water sodium alginate-based emulsions were prepared using a high-energy method with different proportions of Tween 80, EsEO, and sodium alginate (ALG) 4%. The physical-chemical characterization included stability, particle size, zeta potential and infrared spectra. The effects of the emulsions were evaluated against H. contortus via… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Devita Amelia1, R. A. Ilyas1,2,*, Hairul Abral2,3, Mochamad Asrofi4, Muhammad Asyraf Muhammad Rizal2,5, Mohamad Zaki Hassan6, Mohamad Haafiz Mohamad Kassim2,7,8, Nurul Fazita Mohammad Rawi2,7,8, Nasrullah Razali9, Melbi Mahardika2,7,8,10,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0147
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: From Nature to Function: Natural Fiber Cellulose and Starch-Based Materials for a Sustainable Composites)
Abstract This study characterizes biocomposites derived from jicama starch and reinforced with microfibers obtained from jicama bagasse (JB). The incorporation of jicama bagasse microfibers into the jicama matrix was systematically varied at concentrations of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 wt%. The starch film and biocomposite were prepared using solution casting methodologies, employing glycerol as a plasticizing agent. The biocomposites were characterized using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. In addition, the moisture absorption and tensile properties were evaluated. The jicama starch contained 44% w/w amylose, whereas the jicama bagasse microfiber contained… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cristiane Michele Alves de Oliveira1, Bruna Carolina Dorm1, Antonio José Felix Carvalho2, Deliane da Silva Cabral2, Flávia Aparecida Resende Nogueira1, Nádia Andrade Aleixo1, Mônica Rosas Costa Iemma1, Eliane Trovatti1,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0166
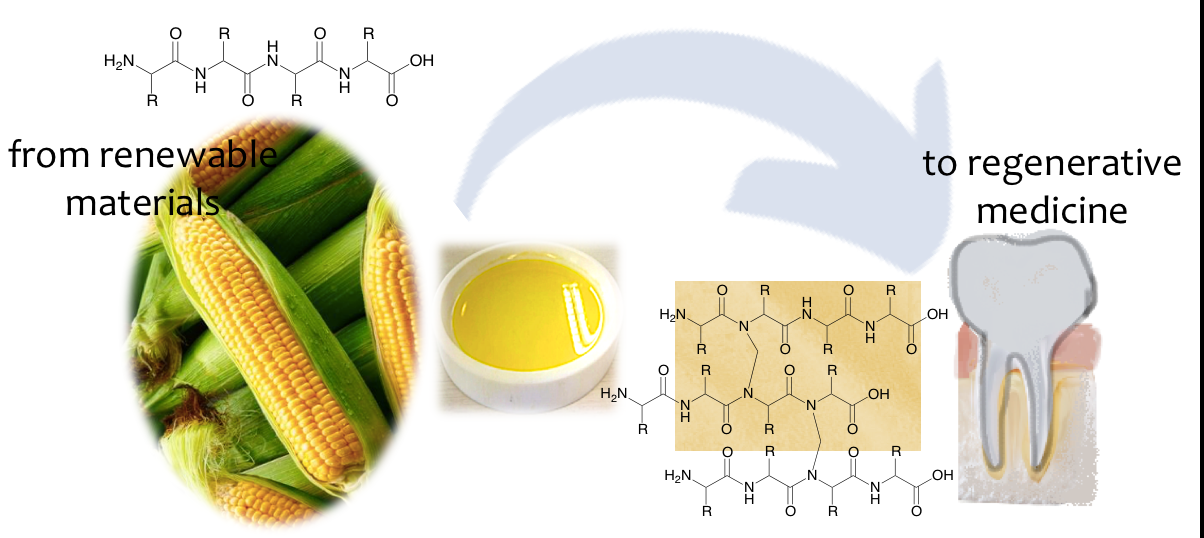
Abstract Materials from natural sources have been studied to replace the conventional synthetic or animal-derived products as a safer alternative to be used in the healthcare field. In dentistry, guided bone regeneration (GBR) relies on barrier membranes, predominantly from animals or synthetic materials, to improve osteogenesis by avoiding undesired soft tissue cells from defect sites. In this study, membranes were prepared from zein, a corn-derived protein, using a simple extraction and casting method, followed by optional formaldehyde cross-linking to evaluate their behavior for application in GBR. The membranes were characterised by FTIR, DSC, TGA, tensile strength… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hikaru Kobori1, Emilia-Adela Manea Salca2,*, Tetsuya Inagaki3, Shigehiko Suzuki4, Sahriyanti Saad5, Aujchariya Chotikhun6
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0152
Abstract Heat treatment is applied to wood to improve various properties of the material. The present study focuses on the colour changes of wood veneer samples due to heat treatment. Native wood species from Japan and Europe, such as Japanese oak (Quercus mongolica var. crispula), field maple (Acer campestre) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) were used in the experiments. A laboratory-type oven was used to apply the heat at a temperature of 190°C, in the presence of oxygen, for different periods, gradually increasing from 5 to 40 min. The CIELab system (a colour space defined by the International Commission… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
H. A. Aisyah1,*, I. Nur Azreena2, E. Hishamuddin1, A.W. Noorshamsiana1, N. M. Nurazzi2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0141
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: From Nature to Function: Natural Fiber Cellulose and Starch-Based Materials for a Sustainable Composites)
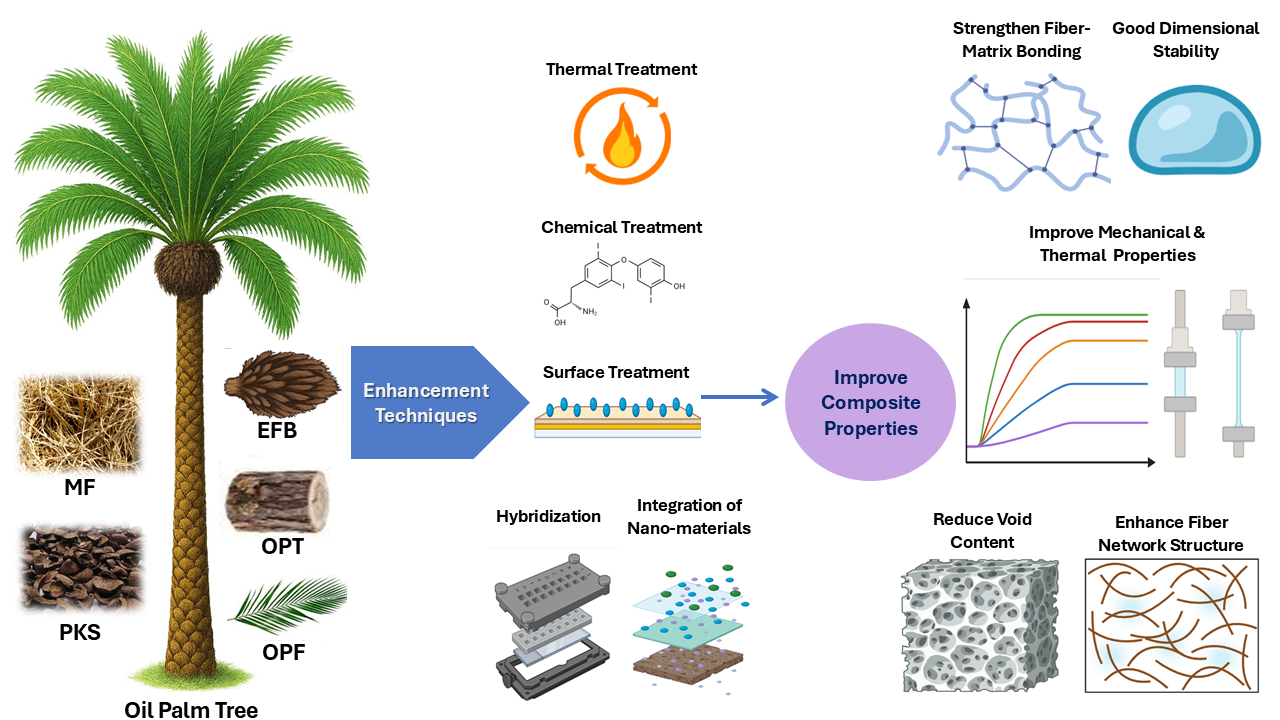
Abstract Oil palm fiber is a natural fiber derived from agricultural biomass and has gained significant attention as an alternative reinforcement material in composite materials due to its abundance, renewability, and environmental benefits. This review explores the various enhancement techniques applied to oil palm fiber to improve its properties for composite material development. Key areas of focus include chemical treatments, physical modifications, and hybridization with other fibers to improve fiber-matrix bonding, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. Integration of nanomaterials and bio-based resins to enhance the performance and sustainability of oil palm fiber composites is also discussed. More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
Jiazi Wang, Yanxia An*, Jingyuan Su, Keke Liu, Jian Zhang, Yang Zhao, Linlin Li
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0151
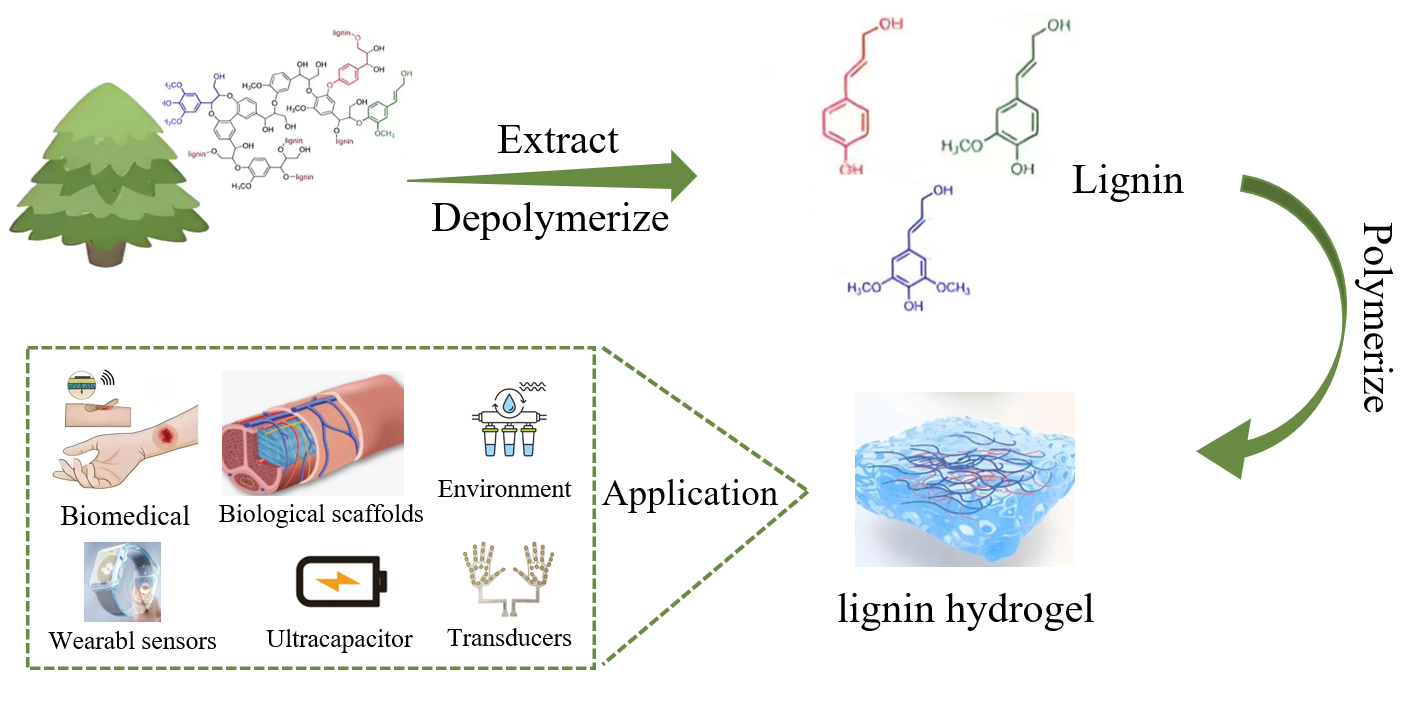
Abstract Lignin, the most abundant natural aromatic polymer globally, has garnered considerable interest due to its rich and diverse active functional groups and its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and adhesive properties. Recent research has significantly improved the performance of lignin-based hydrogels, suggesting their substantial potential in fields such as biomedicine, environmental science, and agriculture. This paper reviews the process of lignin extraction, systematically introduces synthesis strategies for preparing lignin-based hydrogels, and discusses the current state of research on these hydrogels in biomedical and environmental protection fields. It concludes by identifying the existing challenges in lignin hydrogel research and More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
Awanda Wira Anggini1,2, Rita Kartika Sari1,*, Dede Hermawan1, Muhammad Iqbal Maulana2, Wahyu Hidayat3, Bora Jeong4, Muhammad Adly Rahandi Lubis2,5,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0114
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable and Biosourced Adhesives-2023)
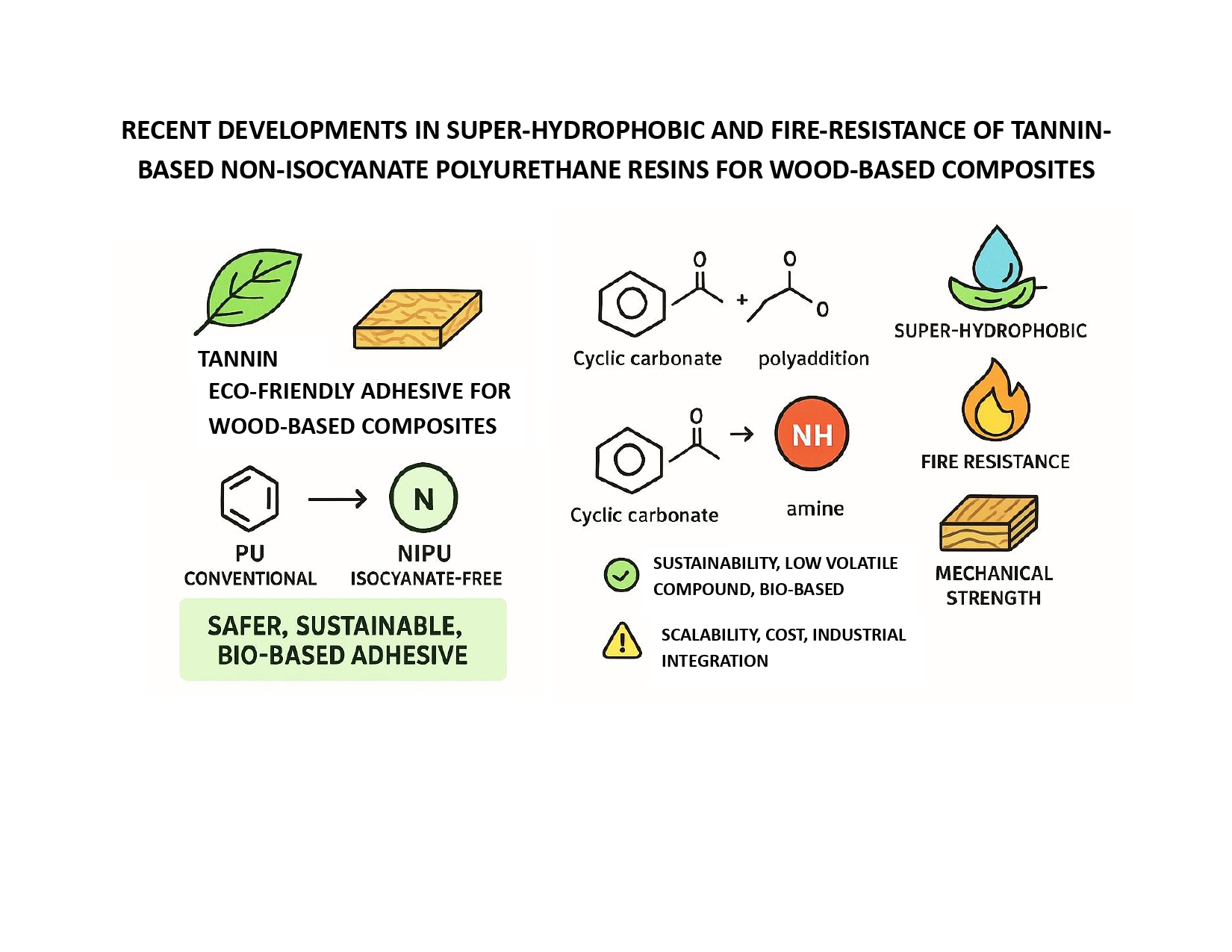
Abstract Recent advancements in developing tannin-based non-isocyanate polyurethane (NIPU) resins have unlocked new possibilities for sustainable and eco-friendly wood adhesives. Unlike conventional polyurethane, NIPUs eliminate hazardous isocyanates, offering safer alternatives for industrial applications. Tannin, a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound, plays a pivotal role in enhancing these resins’ fire-resistance and super-hydrophobic properties. This review highlights key developments in synthesizing tannin-based NIPU, focusing on various polymerization techniques such as polyaddition, polycondensation, ring-opening polymerization, and rearrangement. These strategies contribute to improved mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to water absorption. Recent studies demonstrate that tannin-based NIPU adhesives meet or… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Naile Karakehya1,2,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0131
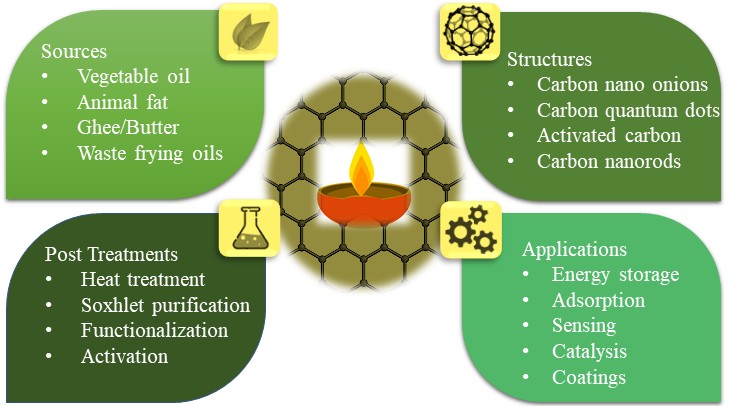
Abstract In the early years of the Industrial Revolution, the extensive use of fossil resources and energy-intensive production methods was widely accepted, even celebrated, as signs of progress. However, growing concerns over environmental degradation, resource depletion, and climate change have necessitated a transition toward more sustainable and environmentally responsible production strategies. Within this context, wick-and-oil flame synthesis has emerged as a simple, energy-efficient, and cost-effective method that utilizes natural oils as both fuel and renewable carbon sources for the generation of carbon nanoparticles, particularly carbon nano-onions. This review presents a comprehensive overview of this emerging synthesis… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Valentina Sergeevna Borovkova1,2,*, Yuriy Nikolaevich Malyar1,2, Vladislav Alexandrovich Ionin1,2, Alexander Sergeevich Kazachenko1,2
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0067
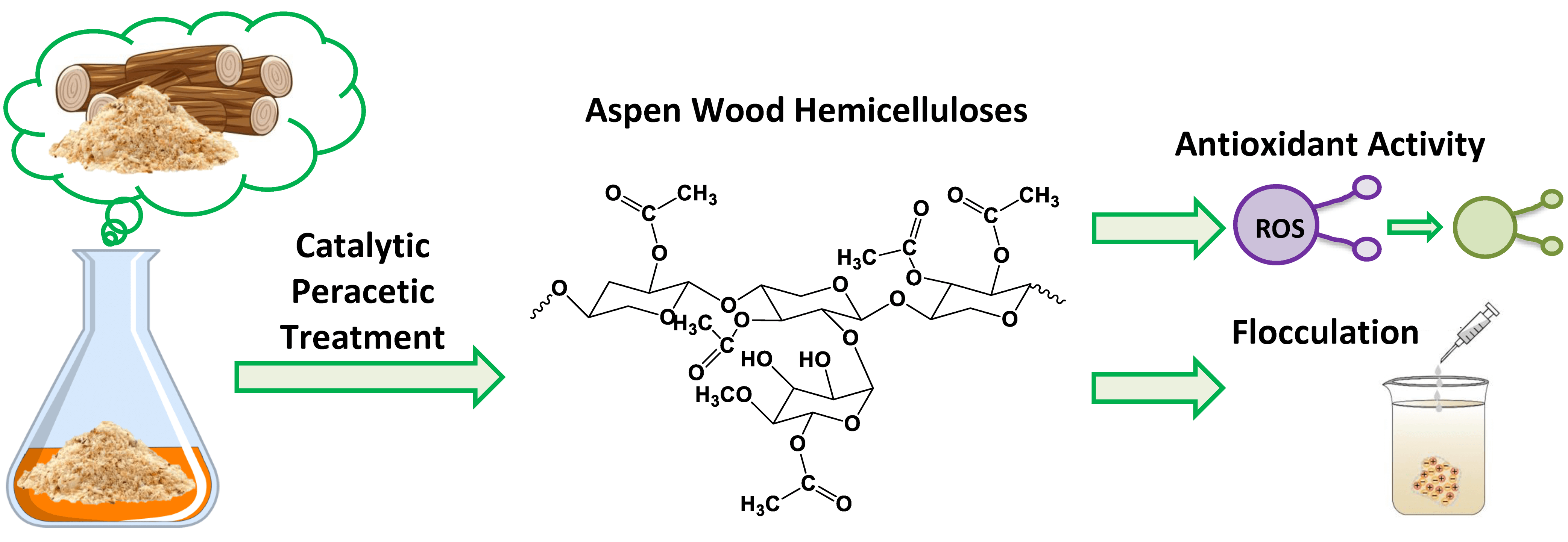
Abstract The valorization of plant biomass towards high-value chemicals is a global trend aimed at solving the problem of the huge accumulation of lignocellulosic waste. Plant polysaccharides are natural polymers that make up about 20% by weight of biomass, with a unique variety of structures and properties that depend on the type of raw materials and the method of their extraction. In this study, the effect of variability of the oxidative delignification process conditions in the «acetic acid-hydrogen peroxide-water-(NH4)6Mo7O24» on the extraction and properties of aspen (Populus tremula) wood hemicelluloses was investigated for the first time. The developed… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhiying Lin1, Boju Deng1, Qianqian Zhang1, Jingming Chen2, Xinqiang Ye3, Yuling Lan1, Jiuping Rao1,*, Mizi Fan4, Weigang Zhao1,*
Journal of Renewable Materials, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0096
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Nanostructured Porous Materials: Synthesis, Processing, and Applications)
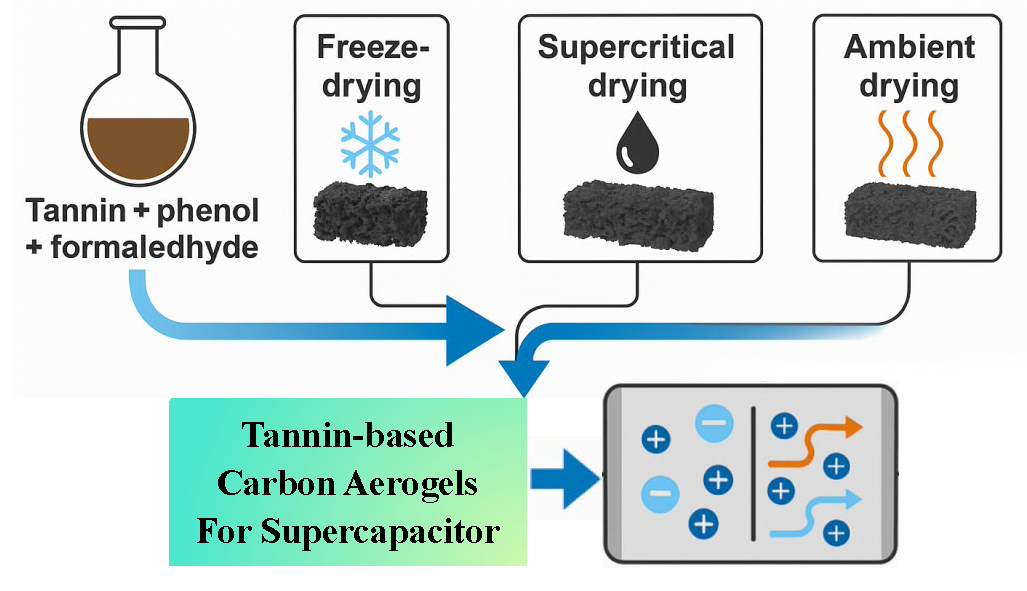
Abstract Bio-derived carbon cryogels have garnered significant interest as promising electrode materials for supercapacitors due to their high specific surface area (SSA), hierarchical porosity, and eco-friendly synthesis methods. In this study, a tannin-modified phenolic hydrogel was synthesized using a sustainable tannin–phenol precursor system and subsequently subjected to three distinct drying methods-freeze-drying (FD), supercritical drying (SCD), and ambient pressure drying (APD)-to systematically evaluate their influence on structural integrity, porosity, and electrochemical behavior. Among these, the sample obtained via freeze-drying (TPUF-FD) maintained the most intact porous network, minimizing structural collapse during sublimation of ice under vacuum. This preservation… More >
Graphic Abstract