
Sound & Vibration is a journal intended for individuals with broad-based interests in noise and vibration, dynamic measurements, structural analysis, computer-aided engineering, machinery reliability, and dynamic testing. The journal strives to publish referred papers reflecting the interests of research and practical engineering on any aspects of sound and vibration. Of particular interest are papers that report analytical, numerical and experimental methods of more relevance to practical applications.
Web of Science Coverage Emerging Sources Citation Index (2023 Impact Factor 0.9); Emerging Source Citation Index (Web of Science); Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2023): 1.5; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2023): 0.47; Portico, etc...
Starting from Volume 59, 2025, Sound & Vibration will be published by Academic Publishing. As of 5 September 2024, new submissions should be made to the Open Journal Systems. To view your previous submissions, please access TSP system.
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 171-183, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.056968 - 21 October 2024
Abstract Helmholtz resonators are widely used to control low frequency noise propagating in pipes. In this paper, the elastic bottom plate of Helmholtz resonator is simplified as a single degree of freedom (SDOF) vibration system with acoustic excitation, and a one-dimensional lumped-parameter analytical model was developed to accurately characterize the structure-acoustic coupling and sound transmission loss (STL) of a Helmholtz resonator with an elastic bottom plate. The effect of dynamical parameters of elastic bottom plate on STL is analyzed by utilizing the model. A design criterion to circumvent the effect of wall elasticity of Helmholtz resonators More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 151-169, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.045193 - 19 March 2024
Abstract User authentication on smart devices is crucial to protecting user privacy and device security. Due to the development of emerging attacks, existing physiological feature-based authentication methods, such as fingerprint, iris, and face recognition are vulnerable to forgery and attacks. In this paper, GestureID, a system that utilizes acoustic sensing technology to distinguish hand features among users, is proposed. It involves using a speaker to send acoustic signals and a microphone to receive the echoes affected by the reflection of the hand movements of the users. To ensure system accuracy and effectively distinguish users’ gestures, a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 133-150, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.047762 - 19 March 2024
Abstract A significant aerodynamic noise from wind turbines arises when the rotating blades interact with turbulent flows. Though the trailing edge of the blade is an important source of noise at high frequencies, the present work deals with the influence of turbulence distortion on leading edge noise from wind turbine blades which becomes significant in low-frequency regions. Four quasi-empirical methods are studied to verify the accuracy of turbulent inflow noise predicted at low frequencies for a 2 MW horizontal axis wind turbine. Results have shown that all methods exhibited a downward linear trend in noise spectra More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 119-131, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.048861 - 19 March 2024
Abstract Noise is one of the environmental factors with mental and physical effects. The workload is also the multiple mental and physical demands of the task. Therefore, his study investigated the relationship between noise exposure and mood states at different levels of workload. The study recruited 50 workers from the manufacturing sector (blue-collar workers) as the exposed group and 50 workers from the office sector (white-collar workers) as the control group. Their occupational noise exposure was measured by dosimetry. The Stress-Arousal Checklist (SACL) and the NASA Task Load Index (NASA-TLX) were used to measure mood and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 101-117, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.047082 - 11 March 2024
Abstract In order to study the effect of splitter blades on the internal and external sound field of the hydraulic turbine, the paper chose a centrifugal pump with a specific speed ns = 33 reversed as a hydraulic turbine as the research object, and added the short blades on the original impeller to form a new splitter impeller. Based on the Re-Normalization Group (RNG) k-ε turbulence model to conduct numerical simulation for the hydraulic turbine, this thesis calculated the internal and external acoustic field by means of the acoustic boundary element (BEM) and finite element (FEM) and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 81-100, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.048897 - 27 February 2024
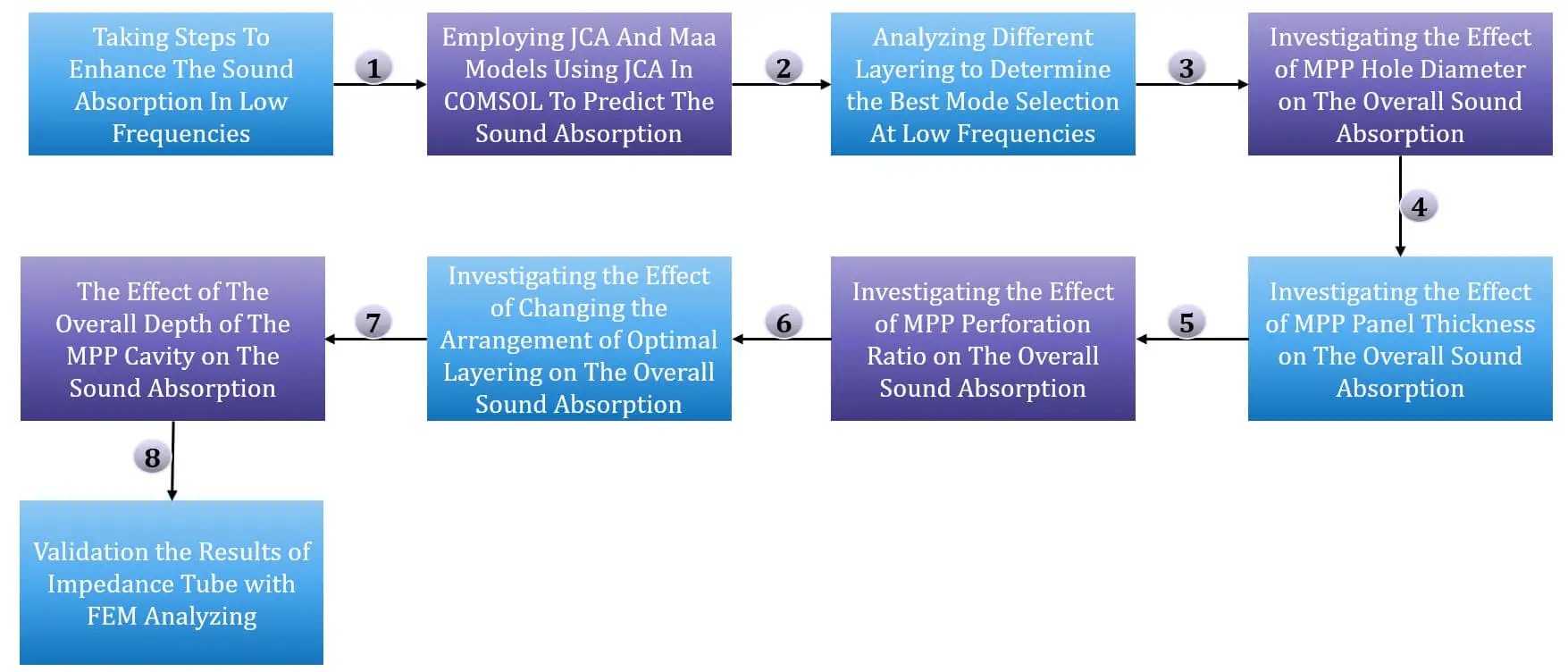
Abstract Mitigating low-frequency noise poses a significant challenge for acoustic engineers, due to their long wavelength, with conventional porous sound absorbers showing limitations in attenuating such noise. An effective strategy involves combining porous materials with micro-perforated plates (MPP) to address this issue. Given the significant impact of structural variables like panel thickness, hole diameter, and air gap on the acoustic characteristics of MPP, achieving the optimal condition demands numerous sample iterations. The impedance tube’s considerable expense for sound absorption measurement and the substantial cost involved in fabricating each sample using a 3D printer underscore the advantage… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 59-80, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.046247 - 27 February 2024
Abstract Currently, the inexorable trend toward the electrification of automobiles has heightened the prominence of road noise within overall vehicle noise. Consequently, an in-depth investigation into automobile road noise holds substantial practical importance. Previous research endeavors have predominantly centered on the formulation of mechanism models and data-driven models. While mechanism models offer robust controllability, their application encounters challenges in intricate analyses of vehicle body acoustic-vibration coupling, and the effective utilization of accumulated data remains elusive. In contrast, data-driven models exhibit efficient modeling capabilities and can assimilate conceptual vehicle knowledge, but they impose stringent requirements on both… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 47-58, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.045470 - 27 February 2024
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Passive and Active Noise Control for Vehicle)
Abstract When designing and optimizing the hull of vehicles, their sound quality needs to be considered, which greatly depends on the psychoacoustic parameters. However, the traditional psychoacoustic calculation method does not consider the influence of the real human ear anatomic structure, even the loudness which is most related to the auditory periphery. In order to introduce the real physiological structure of the human ear into the evaluation of vehicle sound quality, this paper first carried out the vehicle internal noise test to obtain the experimental samples. Then, the physiological loudness was predicted based on an established More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 25-46, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.046940 - 06 February 2024
Abstract The Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) experience during driving is significantly influenced by the sound insulation performance of the car floor acoustic package. As such, accurate and efficient predictions of its sound insulation performance are crucial for optimizing related noise reduction designs. However, the complex acoustic transmission mechanisms and difficulties in characterizing the sound absorption and insulation properties of the floor acoustic package pose significant challenges to traditional Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) methods, leading to low modeling efficiency and prediction accuracy. To address these limitations, a hierarchical multi-objective decomposition system for predicting the sound insulation performance More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sound & Vibration, Vol.58, pp. 1-24, 2024, DOI:10.32604/sv.2024.046723 - 31 January 2024
Abstract In the context of Arab cities, this study explores the intricate interplay between cultural, historical, and environmental elements that shape their unique soundscapes. The paper aims to shed light on this underrepresented field of study by employing a three-fold research approach: systematic review, a comprehensive literature review, and the formulation of a future research agenda. The first part of the investigation focuses on research productivity in the Arab world regarding soundscape studies. An analysis of publication trends reveals that soundscape research in Arab cities is still an emerging area of interest. Critical gaps in the… More >