
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer is an open access and peer-reviewed online journal that provides a central vehicle for the exchange of basic ideas in heat and mass transfer between researchers and engineers around the globe. It disseminates information of permanent interest in the area of heat and mass transfer. Theory and fundamental research in heat and mass transfer, numerical simulations and algorithms, experimental techniques, and measurements as applied to all kinds of current and emerging problems are welcome. Contributions to the journal consist of original research on heat and mass transfer in equipment, thermal systems, thermodynamic processes, nanotechnology, biotechnology, information technology, energy and power applications, as well as security and related topics.
Emerging Source Citation Index (Web of Science): 2024 Impact Factor 0.7; Ei Compendex; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 2.0; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.336; Google Scholar; Open J-Gate, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1701-1720, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074045 - 31 December 2025
Abstract Flow and heat transfer characteristics during droplet impact on hot walls are pivotal for elucidating the mechanisms of spray cooling and exploring pathways for heat transfer enhancement. When the wall temperature exceeds the Leidenfrost point, a vapor film forms between the droplet and the wall, rendering the heat transfer process highly complex. Furthermore, for droplet impact on curved walls, the presence of curvature introduces additional factors that modify the spreading behavior of the droplet and necessitate in-depth analysis. Therefore, this work investigates the flow and heat transfer dynamics of droplet impact on hot planes and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1721-1740, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.073226 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Microscale Fluid Flow, Heat Transfer, and Phase Change)
Abstract This experimental investigation was conducted on the flow boiling performance of refrigerant R134a in two types of parallel microchannels: sintered porous microchannels (PP-MCs) and smooth parallel microchannels (SP-MCs). The tests were performed under controlled conditions including an inlet subcooling of 5 ± 0.2°C, saturation temperature of 33°C, mass fluxes of 346 and 485 kg/m2·s, and a range of heat fluxes. Key findings reveal that the sintered porous microstructure significantly enhances bubble nucleation, reducing the wall superheat required for the onset of nucleate boiling (ONB) to only 0.13°C compared to 2.2°C in smooth channels. The porous structure… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1741-1765, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.069560 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Cooling Systems: Design, Optimization, and Applications)
Abstract A numerical study analyzed double diffusion caused by convective and radiative heat transfer in a greenhouse with and without internal humidity sources. Two cases were examined: one considering temperature and mass concentration gradients on vertical walls and another incorporating internal humidity sources, enhancing convective and diffusive flows. Four configurations were analyzed by varying the length of the greenhouse, and the Rayleigh number was calculated over a range from 2.29 × 1010 to 6.07 × 1012. Simulations modeled the greenhouse interior six times a day (8:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m.), accounting for external temperature, humidity, and solar More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1767-1788, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.070537 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Microscale Heat and Mass Transfer and Efficient Energy Conversion)
Abstract Hazardous gas intrusion in tightly sealed and geometrically complex confined spaces, such as armored tanks, poses a critical threat to occupant health. The intricate internal structure of these systems may lead to non-intuitive pollutant transport pathways. However, the spatial and temporal evolution of these structures, as well as the intrinsic mechanisms of the purification systems, remain poorly elucidated. In this study, a high-fidelity, transient three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model was developed to simulate the leakage and dispersion of carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) using the RNG k-ε turbulence model. Scenarios with and without… More >
Graphic Abstract
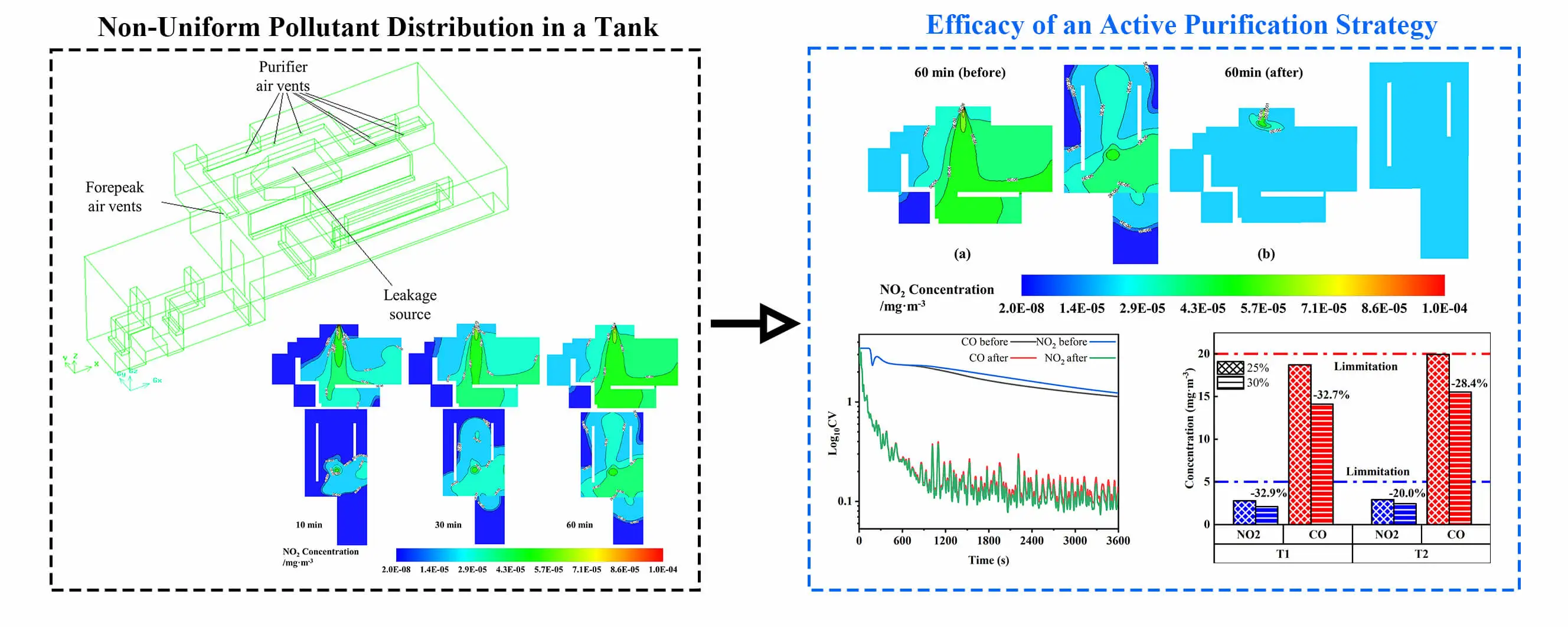
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1789-1809, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.066953 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat and Mass Transfer in Energy Equipment)
Abstract The work presents new methods for selecting adaptive artificial viscosity (AAV) in iterative algorithms of completely conservative difference schemes (CCDS) used to solve gas dynamics equations in Euler variables. These methods allow to effectively suppress oscillations, including in velocity profiles, as well as computational instabilities in modeling gas-dynamic processes described by hyperbolic equations. The methods can be applied both in explicit and implicit (method of separate sweeps) iterative processes in numerical modeling of gas dynamics in the presence of heat and mass transfer, as well as in solving problems of magnetohydrodynamics and computational astrophysics. In… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1811-1832, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.071222 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhancement Technologies for Fluid Heat and Mass Transfer)
Abstract Membrane gas absorption and solar-assisted absorbent regeneration offer a sustainable approach to reduce the energy penalty of post-combustion CO2 capture. This study introduces a novel system integrating solar thermal energy with membrane gas absorption to capture CO2 from a 580 MWe pulverized coal power plant. The environmental impacts across six scenarios at varying solar fractions are evaluated via life cycle assessment. Results show a 7.61%–13.04% reduction in global warming potential compared to a steam-driven CO2 capture system. Electricity and steam consumption dominate the operational phase, contributing 15%–64% and 18%–61% to environmental impacts in non-TES scenarios, respectively. While More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1833-1846, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.069711 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Computational Thermo-Fluids and Nanofluids)
Abstract This comprehensive research examines the dynamics of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow and heat transfer within a couple stress fluid. The investigation specifically focuses on the fluid’s behavior over a vertical stretching sheet embedded within a porous medium, providing valuable insights into the complex interactions between fluid mechanics, thermal transport, and magnetic fields. This study accounts for the significant impact of heat generation and thermal radiation, crucial factors for enhancing heat transfer efficiency in various industrial and technological contexts. The research employs mathematical techniques to simplify complex partial differential equations (PDEs) governing fluid flow and heat transfer.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1847-1864, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.070378 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat Transfer Analysis and Optimization in Energy Systems)
Abstract To address the issue of uneven temperature distribution in shale gas oil-based drill cuttings pyrolysis furnaces, a numerical model was developed using Fluent software. The effects of nitrogen flow rate, heating tube spacing, and furnace dimensions on the internal temperature field were thoroughly analyzed from a mechanistic perspective. The results indicated that non-uniform radiation from the heating tubes and flow disturbances induced by the nitrogen stream were the primary causes of localized heat concentration. Under no-load conditions, the maximum deviation between simulated and on-site measured temperatures was 1.5%, validating the model’s accuracy. Furthermore, this study More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1865-1882, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.073409 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhancement Technologies for Fluid Heat and Mass Transfer)
Abstract With the acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, ammonia nitrogen pollution in water bodies has become increasingly severe, making the development of efficient and low-consumption wastewater treatment technologies highly significant. This study employs three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to investigate the cavitation mechanisms and flow field characteristics in a novel jet impingement-negative pressure ammonia removal reactor. The simulation, validated by experimental pressure data with a high degree of consistency, utilizes the Mixture model, the Realizable k-ε turbulence model, and the Schnerr-Sauer cavitation model. The results demonstrate that the flow velocity undergoes a substantial acceleration within the… More >
Graphic Abstract
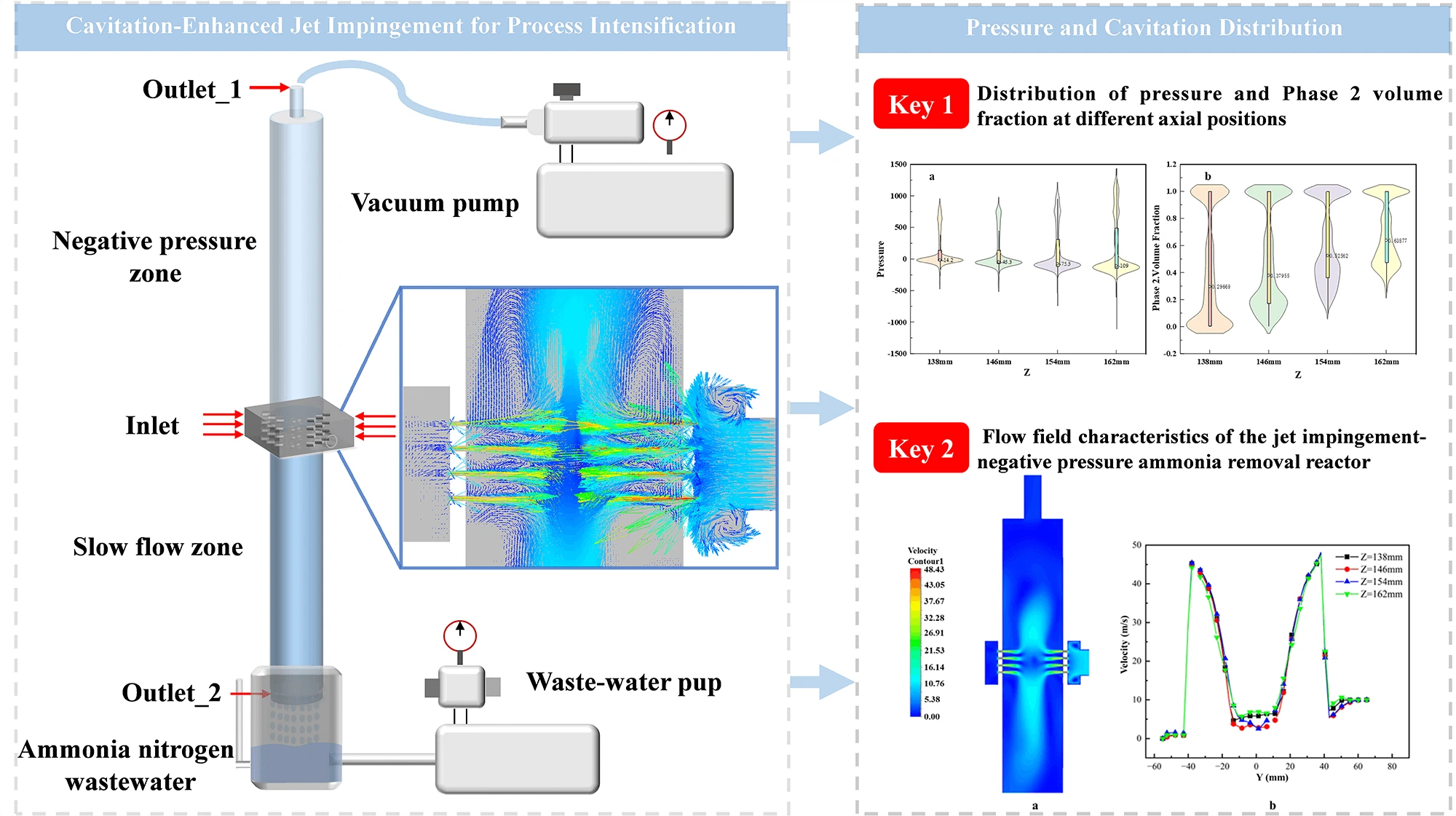
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1883-1905, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074656 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Thermal Management and Modeling in Concentrating Photovoltaic Systems)
Abstract Conventional concentrator photovoltaics (CPV) face a persistent trade-off between high efficiency and high cost, driven by expensive multi-junction solar cells and complex active cooling systems. This study presents a computational investigation of a novel Multi-Focal Pyramidal Array (MFPA)-based CPV system designed to overcome this limitation. The MFPA architecture employs a geometrically optimized pyramidal concentrator to distribute concentrated sunlight onto strategically placed, low-cost monocrystalline silicon cells, enabling high efficiency energy capture while passively managing thermal loads. Coupled optical thermal electrical simulations in COMSOL Multiphysics demonstrate a geometric concentration ratio of 120×, with system temperatures maintained below More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1907-1932, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.071910 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat Transfer in Built Environments)
Abstract A sealed portal could significantly alter the flame shape and smoke flow characteristics in inclined tunnel fires. In inclined tunnels, two typical sealing conditions could be defined, namely the upper portal sealed and the lower portal sealed. In this study, the effects of tunnel slope on flame shape, flame length, along with smoke mass flow rate and induced velocity at the tunnel portal, are numerically investigated. The results show that, in all scenarios, flames initially rise vertically but tilt toward the sealed portal during the quasi-steady stage, with the largest tilt angle observed in tunnels… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1933-1956, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.070118 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Microscale Heat and Mass Transfer and Efficient Energy Conversion)
Abstract The pivotal role microchannels play in the thermal management of electronic components has, in recent decades, prompted extensive research into methods for enhancing their heat transfer performance. Among these methods, surface wettability modification was found to be highly effective owing to its significant influence on boiling dynamics and heat transfer mechanisms. In this study, we modified surface wettability using a nanocomposite coating composed of graphene nano plate (GNPs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and then examined how the modification affected the transfer of boiling heat in microchannels. The resultant heat transfer coefficients for hydrophilic and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1957-1980, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.070396 - 31 December 2025
Abstract Ice accretion on aircraft poses a critical threat to flight safety by significantly altering aerodynamic performance. This study presents a novel numerical framework for ice accretion prediction, developed by extending the Myers model and incorporating an advanced multi-step approach. The proposed framework integrates ice layer growth into the modeling of unsteady water film dynamics and introduces a revised criterion for determining the icing condition. A multi-step scheme, accounting for the continuous variation of physical parameters, is implemented to enhance computational accuracy. The framework is validated through simulations on both 2D and 3D configurations. For the… More >
Graphic Abstract
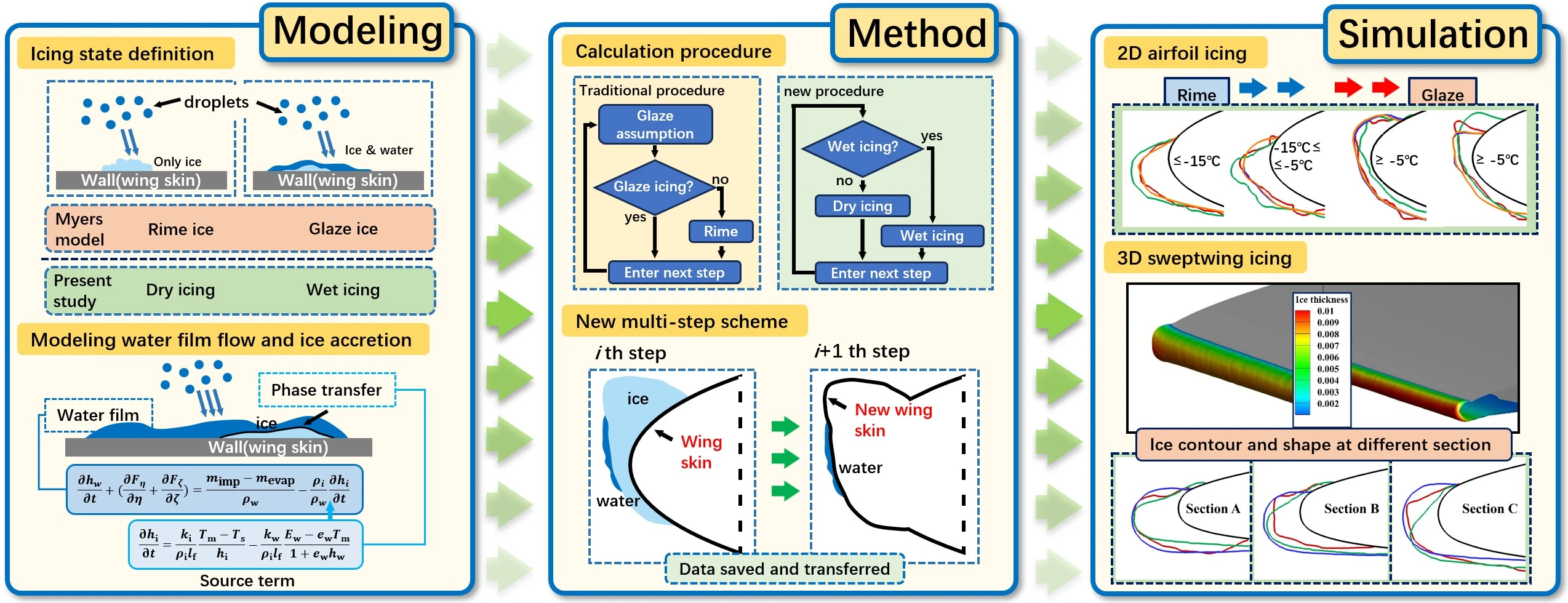
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 1981-1999, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.074593 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations in Drying Technologies: Bridging Industrial, Environmental, and Energy Efficiency Challenges)
Abstract Bananas are highly perishable after harvest, and processing them into dried products is a crucial approach to reducing losses and adding their economic values. To address the inefficiency and prolonged duration of traditional hot air drying (HAD) and the quality inconsistency associated with single infrared drying (IRD), this study proposed a novel hot air-infrared combined drying (HAD-IRD) strategy. The effects of HAD, IRD, and HAD-IRD on the drying kinetics, color, rehydration capacity, moisture diffusion mechanism, and sensory quality of banana slices were systematically investigated. The parameters of the combined drying process were optimized using an L9(33)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 2001-2024, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.066997 - 31 December 2025
Abstract The energy consumption of a Split air conditioning unit (ACU) inside a building is extremely large, and efforts to decrease this issue are ongoing. The current work aims to experimentally investigate the thermal performance of ACU using an external cooling-water loop for pre-cooling the condenser to improve the efficiency and to reduce energy consumption by reducing refrigerant temperature before entering the condenser, thereby reducing the coefficient of performance. The experiments are performed on ACU with and without using an external cooling-water loop under different climate conditions. By using the experimental data, the systems’ performances for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 2025-2049, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.072260 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Direct Energy Conversion of Solar Energy: Photovoltaic-Thermoelectric Combinations, Hybrids, and Effects)
Abstract The growing demand for energy-saving and renewable heating solutions has made photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) heat pump systems a promising technology. However, their thermal and electrical performance, as well as the overall utilization of solar energy, strongly depend on capacity configuration and operating parameters. To address this issue, this study proposes a PV/T heat pump system featuring a novel rhombic flow channel structure that functions as the collector-evaporator. An experimental test bench was established to evaluate system performance, and a one-dimensional numerical model was developed to investigate the effects of environmental and operating parameters. The simulation results… More >
Graphic Abstract
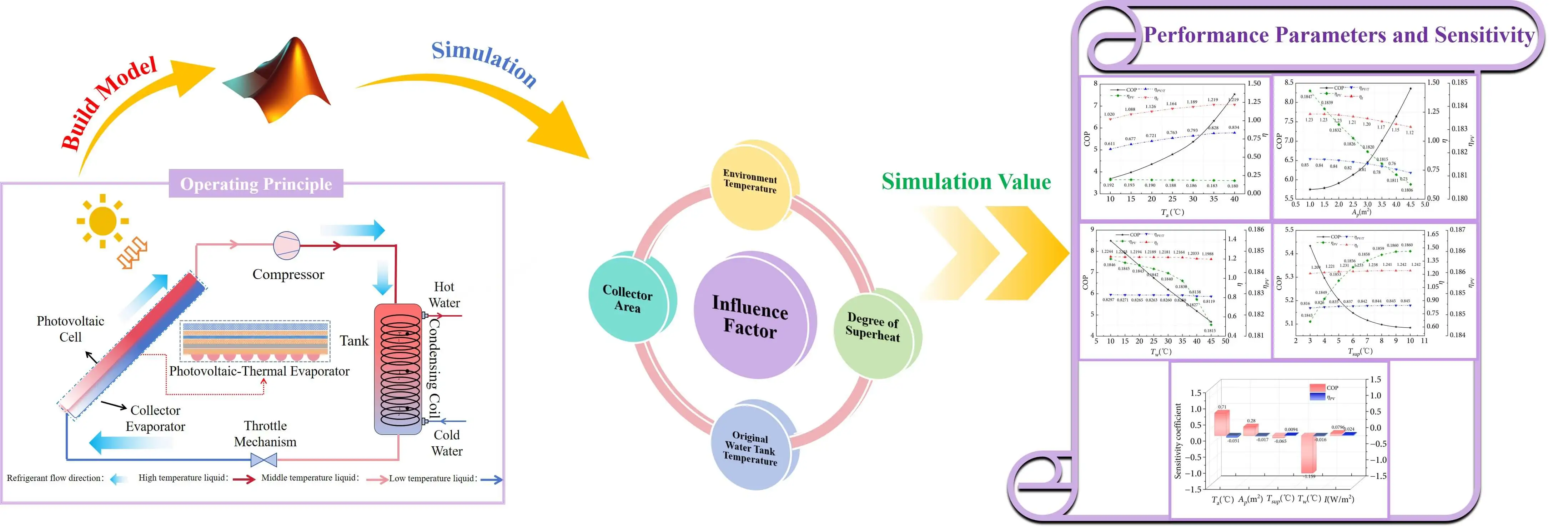
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 2051-2072, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.070138 - 31 December 2025
Abstract This study experimentally investigates the operational performance of a scroll compressor using R513A to expand its application range as a substitute for R134a. A vapor compression heat pump test platform was established to analyze the variation trends of heating capacity, refrigerant mass flow rate, compressor power consumption, and current by controlling the compressor inlet and outlet pressures (i.e., evaporating and condensing temperatures). The results indicate that both heating capacity and refrigerant mass flow rate decrease with increasing pressure ratio. Compressor power consumption and current initially increase and then decrease with rising evaporating temperature, whereas they… More >
Graphic Abstract
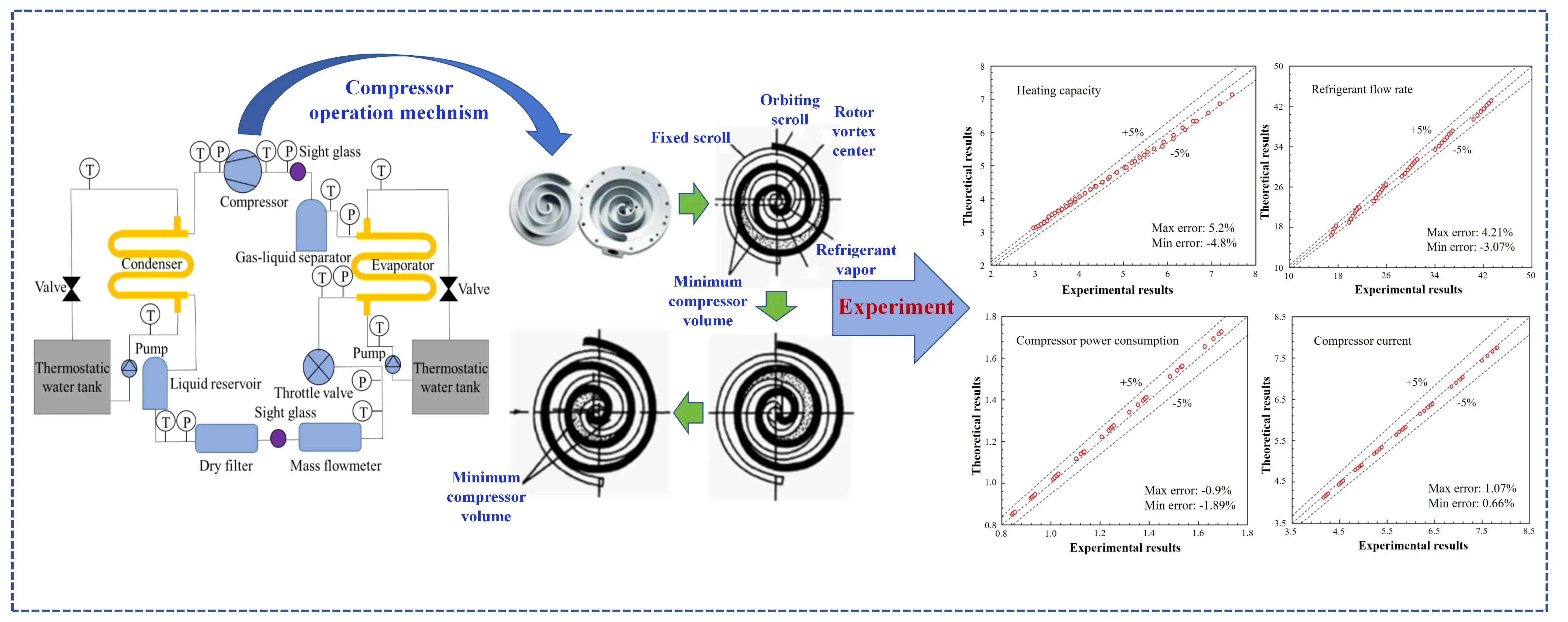
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 2073-2107, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.069564 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Cooling Systems: Design, Optimization, and Applications)
Abstract The Trombe Wall (TW) is a low-cost, passive heating system known for its high thermal efficiency, particularly in cold and temperate climates. Recent research has explored its adaptability to warm-dry climates with high thermal variability, such as those found in central Mexico. This study presents a dynamic simulation-based analysis of the TW’s thermal performance in a representative social housing unit located in Pachuca de Soto, Hidalgo. Two models were compared—one with a south-facing TW system and one without—to evaluate indoor thermal comfort throughout a full annual cycle. The simulations were conducted using OpenStudio and EnergyPlus,… More >
Graphic Abstract

 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 2109-2126, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.072643 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heat Transfer Analysis and Optimization in Energy Systems)
Abstract Internal thermal mass, such as furniture and partitions, plays a crucial role in enhancing building energy efficiency and indoor thermal comfort by passively regulating temperature fluctuations. However, the irregular geometry of these elements poses a significant challenge for accurate modeling in building energy simulations. This study addresses this gap by developing a rigorous analytical model that idealizes internal thermal mass as a sphere, thereby capturing multi-directional heat conduction effects that are neglected in simpler one-dimensional slab models. The transient heat conduction within the sphere is solved analytically using Duhamel’s theorem for three representative indoor air… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, Vol.23, No.6, pp. 2127-2146, 2025, DOI:10.32604/fhmt.2025.070973 - 31 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations in Drying Technologies: Bridging Industrial, Environmental, and Energy Efficiency Challenges)
Abstract This study evaluated corn kernel drying performance and quality changes using hot air drying (HAD) and infrared drying (ID) across temperatures ranging from 55°C to 80°C. Optimal drying parameters were determined by using the entropy weight method, with drying time, specific energy consumption, damage rate, fatty acids, starch, polyphenols, and flavonoids as indicators. Results demonstrated that ID significantly outperformed HAD, achieving drying times up to 20% shorter and reducing specific energy consumption and kernel damage by up to 79.3% and 66.7%, respectively, while also better preserving quality attributes. Both methods exhibited drying profiles characterized by More >