
The Computer Systems Science and Engineering journal is devoted to the publication of high quality papers on theoretical developments in computer systems science, and their applications in computer systems engineering. Original research papers, state-of-the-art reviews and technical notes are invited for publication.
EBSCO, OpenAIRE, OpenALEX, CNKI Scholar, PubScholar, Portico, etc.
Starting from January 2025, Computer Systems Science and Engineering will transition to a continuous publication model, and accepted articles will be promptly published online upon completion of the peer review and production processes.
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 533-555, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.072267 - 08 December 2025
Abstract Attribute-based Encryption (ABE) enhances the confidentiality of Electronic Health Records (EHR) (also known as Personal Health Records (PHR)) by binding access rights not to individual identities, but to user attribute sets such as roles, specialties, or certifications. This data-centric cryptographic paradigm enables highly fine-grained, policy-driven access control, minimizing the need for identity management and supporting scalable multi-user scenarios. This paper presents a comprehensive and critical survey of ABE schemes developed specifically for EHR/PHR systems over the past decade. It explores the evolution of these schemes, analyzing their design principles, strengths, limitations, and the level of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 499-531, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.068151 - 10 October 2025
Abstract The 6G network architecture introduces the paradigm of Trust + Security, representing a shift in network protection strategies from external defense mechanisms to endogenous security enforcement. While ZTNs (zero-trust networks) have demonstrated significant advancements in constructing trust-centric frameworks, most existing ZTN implementations lack comprehensive integration of security deployment and traffic monitoring capabilities. Furthermore, current ZTN designs generally do not facilitate dynamic assessment of user reputation. To address these limitations, this study proposes a DPZTN (Data-plane-based Zero Trust Network). DPZTN framework extends traditional ZTN models by incorporating security mechanisms directly into the data plane. Additionally, blockchain infrastructure… More >
Graphic Abstract
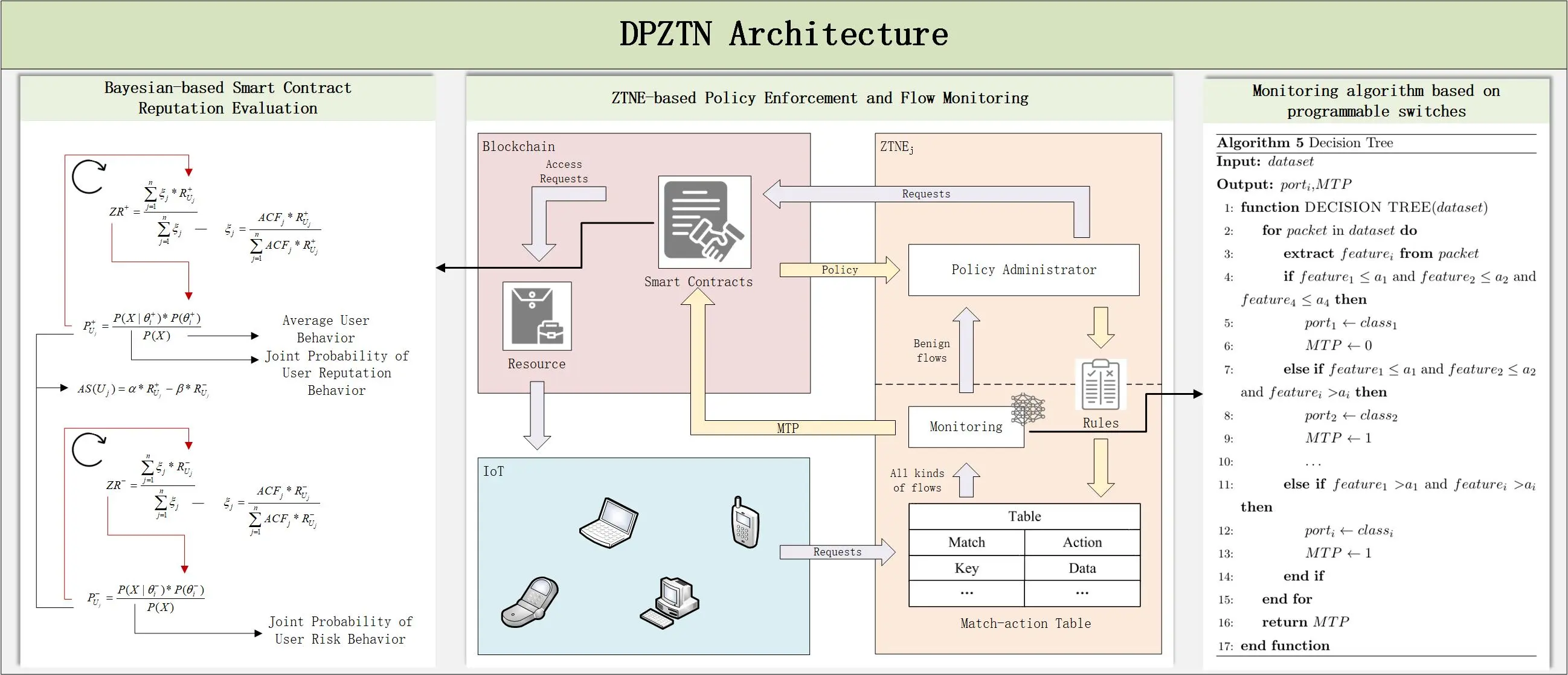
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 481-497, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.068616 - 10 October 2025
Abstract Diagnosing dental disorders using routine photographs can significantly reduce chair-side workload and expand access to care. However, most AI-based image analysis systems suffer from limited interpretability and are trained on class-imbalanced datasets. In this study, we developed a balanced, transformer-based pipeline to detect three common dental disorders: tooth discoloration, calculus, and hypodontia, from standard color images. After applying a color-standardized preprocessing pipeline and performing stratified data splitting, the proposed vision transformer model was fine-tuned and subsequently evaluated using standard classification benchmarks. The model achieved an impressive accuracy of 98.94%, with precision, recall and F1 scores More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 455-479, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.069213 - 19 August 2025
Abstract Employee turnover presents considerable challenges for organizations, leading to increased recruitment costs and disruptions in ongoing operations. High voluntary attrition rates can result in substantial financial losses, making it essential for Human Resource (HR) departments to prioritize turnover reduction. In this context, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a vital tool in strengthening business strategies and people management. This paper incorporates two new representative features, introducing three types of feature engineering to enhance the analysis of employee turnover in the IBM HR Analytics dataset. Key Machine Learning (ML) techniques were subsequently employed in this work,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 435-453, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.062432 - 13 May 2025
Abstract Many existing watermarking approaches aim to provide a Robust Reversible Data Hiding (RRDH) method. However, most of these approaches degrade under geometric and non-geometric attacks. This paper presents a novel RRDH approach using Polar Harmonic Fourier Moments (PHFMs) and linear interpolation. The primary objective is to enhance the robustness of the embedded watermark and improve the imperceptibility of the watermarked image. The proposed method leverages the high-fidelity and anti-geometric transformation properties of PHFMs. The image is transformed into the frequency domain of RRDH, after which compensation data is embedded using a two-dimensional RDH scheme. Linear… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 419-434, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.064195 - 30 April 2025
Abstract Plant diseases pose a significant challenge to global agricultural productivity, necessitating efficient and precise diagnostic systems for early intervention and mitigation. In this study, we propose a novel hybrid framework that integrates EfficientNet-B8, Vision Transformer (ViT), and Knowledge Graph Fusion (KGF) to enhance plant disease classification across 38 distinct disease categories. The proposed framework leverages deep learning and semantic enrichment to improve classification accuracy and interpretability. EfficientNet-B8, a convolutional neural network (CNN) with optimized depth and width scaling, captures fine-grained spatial details in high-resolution plant images, aiding in the detection of subtle disease symptoms. In… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 401-417, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.062413 - 25 April 2025
Abstract A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack poses a significant challenge in the digital age, disrupting online services with operational and financial consequences. Detecting such attacks requires innovative and effective solutions. The primary challenge lies in selecting the best among several DDoS detection models. This study presents a framework that combines several DDoS detection models and Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) techniques to compare and select the most effective models. The framework integrates a decision matrix from training several models on the CiC-DDOS2019 dataset with Fuzzy Weighted Zero Inconsistency Criterion (FWZIC) and Multi-Attribute Boundary Approximation Area Comparison (MABAC) methodologies.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 377-399, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.059634 - 09 April 2025
Abstract Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) has become one of the most effective tools in ship detection. However, due to significant background interference, small targets, and challenges related to target scattering intensity in SAR images, current ship target detection faces serious issues of missed detections and false positives, and the network structures are overly complex. To address this issue, this paper proposes a lightweight model based on YOLOv8, named OD-YOLOv8. Firstly, we adopt a simplified neural network architecture, VanillaNet, to replace the backbone network, significantly reducing the number of parameters and computational complexity while ensuring accuracy. Secondly,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 353-376, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.062433 - 21 March 2025
Abstract Data security is crucial for improving the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the image content. Maintaining these security factors poses significant challenges, particularly in healthcare, business, and social media sectors, where information security and personal privacy are paramount. The cryptography concept introduces a solution to these challenges. This paper proposes an innovative hybrid image encryption algorithm capable of encrypting several types of images. The technique merges the Tiny Encryption Algorithm (TEA) and Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) algorithms called (TEA-RSA). The performance of this algorithm is promising in terms of cost and complexity, an encryption time which is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 333-351, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.061285 - 19 March 2025
Abstract In recent years, the analysis of encrypted network traffic has gained momentum due to the widespread use of Transport Layer Security and Quick UDP Internet Connections protocols, which complicate and prolong the analysis process. Classification models face challenges in understanding and classifying unknown traffic because of issues related to interpret ability and the representation of traffic data. To tackle these complexities, multi-modal representation learning can be employed to extract meaningful features and represent them in a lower-dimensional latent space. Recently, auto-encoder-based multi-modal representation techniques have shown superior performance in representing network traffic. By combining the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 317-331, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.061118 - 19 March 2025
Abstract The migration of tasks aided by machine learning (ML) predictions IN (DPM) is a system-level design technique that is used to reduce energy by enhancing the overall performance of the processor. In this paper, we address the issue of system-level higher task dissipation during the execution of parallel workloads with common deadlines by introducing a machine learning-based framework that includes task migration using energy-efficient earliest deadline first scheduling (EA-EDF). ML-based EA-EDF enhances the overall throughput and optimizes the energy to avoid delay and performance degradation in a multiprocessor system. The proposed system model allocates processors… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 301-316, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.060757 - 27 February 2025
Abstract Mitigating tag collisions is paramount for enhancing throughput in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems. However, traditional algorithms encounter challenges like slot wastage and inefficient frame length adjustments. To tackle these challenges, the Slot Prediction Q (SPQ) algorithm was introduced, integrating the Vogt-II prediction algorithm and slot grouping to improve the initial Q value by predicting the first frame. This method quickly estimates the number of tags based on slot utilization, accelerating Q value adjustments when slot utilization is low. Furthermore, a Markov decision chain is used to optimize the relationship between the number of slot groupings (x) More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 287-300, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.061655 - 20 February 2025
Abstract In the broader field of mechanical technology, and particularly in the context of self-driving vehicles, cameras and Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) sensors provide complementary modalities that hold significant potential for sensor fusion. However, directly merging multi-sensor data through point projection often results in information loss due to quantization, and managing the differing data formats from multiple sensors remains a persistent challenge. To address these issues, we propose a new fusion method that leverages continuous convolution, point-pooling, and a learned Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) to achieve superior detection performance. Our approach integrates the segmentation mask with… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 259-286, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2025.060387 - 21 February 2025
Abstract Precisely forecasting the performance of Deep Learning (DL) models, particularly in critical areas such as Uniform Resource Locator (URL)-based threat detection, aids in improving systems developed for difficult tasks. In cybersecurity, recognizing harmful URLs is vital to lowering risks associated with phishing, malware, and other online-based attacks. Since it directly affects the model’s capacity to differentiate between benign and harmful URLs, finding the optimum mix of hyperparameters in DL models is a significant difficulty. Two commonly used architectures for sequential and spatial data processing, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)/Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and Convolutional Neural Network… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 239-258, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.056582 - 10 January 2025
Abstract Vehicle overtaking poses significant risks and leads to injuries and losses on Malaysia’s roads. In most scenarios, insufficient and untimely information available to drivers for accessing road conditions and their surrounding environment is the primary factor that causes these incidents. To address these issues, a comprehensive system is required to provide real-time assistance to drivers. Building upon our previous research on a LoRa-based lane change decision-aid system, this study proposes an enhanced Vehicle Overtaking System (VOS). This system utilizes long-range (LoRa) communication for reliable real-time data exchange between vehicles (V2V) and the cloud (V2C). By More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 213-238, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.059491 - 10 January 2025
Abstract Globally, liver cancer ranks as the sixth most frequent malignancy cancer. The importance of early detection is undeniable, as liver cancer is the fifth most common disease in men and the ninth most common cancer in women. Recent advances in imaging, biomarker discovery, and genetic profiling have greatly enhanced the ability to diagnose liver cancer. Early identification is vital since liver cancer is often asymptomatic, making diagnosis difficult. Imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT), and ultrasonography can be used to identify liver cancer once a sample of liver tissue is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 185-212, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.056535 - 10 January 2025
Abstract This study presents an energy-efficient Internet of Things (IoT)-based wireless sensor network (WSN) framework for autonomous data validation in remote environmental monitoring. We address two critical challenges in WSNs: ensuring data reliability and optimizing energy consumption. Our novel approach integrates an artificial neural network (ANN)-based multi-fault detection algorithm with an energy-efficient IoT-WSN architecture. The proposed ANN model is designed to simultaneously detect multiple fault types, including spike faults, stuck-at faults, outliers, and out-of-range faults. We collected sensor data at 5-minute intervals over three months, using temperature and humidity sensors. The ANN was trained on 70%… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 159-183, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.058741 - 03 January 2025
Abstract Accurate non-line of sight (NLOS) identification technique in ultra-wideband (UWB) location-based services is critical for applications like drone communication and autonomous navigation. However, current methods using binary classification (LOS/NLOS) oversimplify real-world complexities, with limited generalisation and adaptability to varying indoor environments, thereby reducing the accuracy of positioning. This study proposes an extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model to identify multi-class NLOS conditions. We optimise the model using grid search and genetic algorithms. Initially, the grid search approach is used to identify the most favourable values for integer hyperparameters. In order to achieve an optimised model configuration,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 123-157, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.058314 - 03 January 2025
Abstract This review article provides a comprehensive analysis of the latest advancements and persistent challenges in Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WANs), with a particular emphasis on the multi-objective Controller Placement Problem (CPP). As SD-WAN technology continues to gain prominence for its capacity to offer flexible and efficient network management, the task of 36optimally placing controllers—responsible for orchestrating and managing network traffic—remains a critical yet complex challenge. This review delves into recent innovations in multi-objective controller placement strategies, including clustering techniques, heuristic-based approaches, and the integration of machine learning and deep learning models. Each methodology is critically More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 99-122, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.057754 - 03 January 2025
Abstract The rapid growth of the automotive industry has raised significant concerns about the security of connected vehicles and their integrated supply chains, which are increasingly vulnerable to advanced cyber threats. Traditional authentication methods have proven insufficient, exposing systems to risks such as Sybil, Denial of Service (DoS), and Eclipse attacks. This study critically examines the limitations of current security protocols, focusing on authentication and data exchange vulnerabilities, and explores blockchain technology as a potential solution. Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographically secure framework can significantly enhance Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communication, ensure data integrity, and enable transparent, immutable transactions More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 79-98, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.057439 - 03 January 2025
Abstract Authentication is the most crucial aspect of security and a predominant measure employed in cybersecurity. Cloud computing provides a shared electronic device resource for users via the internet, and the authentication techniques used must protect data from attacks. Previous approaches failed to resolve the challenge of making passwords secure, memorable, usable, and time-saving. Graphical Password (GP) is still not widely utilized in reality because consumers suffer from multiple login stages. This paper proposes an Indexed Choice-Based Graphical Password (ICGP) scheme for improving the authentication part. ICGP consists of two stages: registration and authentication. At the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 49-77, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.057702 - 03 January 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security)
Abstract Intrusion detection (ID) is a cyber security practice that encompasses the process of monitoring network activities to identify unauthorized or malicious actions. This includes problems like the difficulties of existing intrusion detection models to identify emerging attacks, generating many false alarms, and their inability and difficulty to adapt themselves with time when it comes to threats, hence to overcome all those existing challenges in this research develop a Prairie Araneida optimization based fused Convolutional Neural Network model (PAO-CNN) for intrusion detection. The fused CNN (Convolutional Neural Netowrk) is a remarkable development since it combines statistical… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 19-48, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.058327 - 03 January 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security)
Abstract The network security knowledge base standardizes and integrates network security data, providing a reliable foundation for real-time network security protection solutions. However, current research on network security knowledge bases mainly focuses on their construction, while the potential to optimize intelligent security services for real-time network security protection requires further exploration. Therefore, how to effectively utilize the vast amount of historical knowledge in the field of network security and establish a feedback mechanism to update it in real time, thereby enhancing the detection capability of security services against malicious traffic, has become an important issue. Our… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Computer Systems Science and Engineering, Vol.49, pp. 1-17, 2025, DOI:10.32604/csse.2024.056979 - 03 January 2025
Abstract In recent years, automation has become a key focus in software development as organizations seek to improve efficiency and reduce time-to-market. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools, particularly those using natural language processing (NLP) like ChatGPT, has opened new possibilities for automating various stages of the development lifecycle. The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of ChatGPT in automating various phases of software development. An artificial intelligence (AI) tool was developed using the OpenAI—Application Programming Interface (API), incorporating two key functionalities: 1) generating user stories based on case or process… More >