 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Investigate the Impact of Dimple Size and Distribution on the Hydrothermal Performance of Dimpled Heat Exchanger Tubes
Mechanical Engineering Department, College of Engineering, Mustansiriyah University, Baghdad, Iraq
* Corresponding Author: Abeer H. Falih. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Passive Heat Transfer Enhancement for Single Phase and Multi-Phase Flows)
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer 2024, 22(2), 597-613. https://doi.org/10.32604/fhmt.2024.049812
Received 18 January 2024; Accepted 20 February 2024; Issue published 20 May 2024
Abstract
In this study, the primary objective was to enhance the hydrothermal performance of a dimpled tube by addressing areas with low heat transfer compared to other regions. To accomplish this, a comprehensive numerical investigation was conducted using ANSYS Fluent 2022 R1 software, focusing on different diameters of dimples along the pipe’s length and the distribution of dimples in both in-line and staggered arrangements. The simulations utilized the finite element method to address turbulent flow within the tube by solving partial differential equations, encompassing Re numbers spanning from 3000 to 8000. The study specifically examined single-phase flow conditions, with water utilized as the cooling fluid. The results of the investigation indicated that increasing the Reynolds number resulted in higher average Nusselt numbers, pressure drops, the overall performance criterion, and a reduction in average thermal resistance across all models analyzed. Notably, both proposed models demonstrated improved heat transfer when compared to the conventional model. Out of all the models evaluated, the tube featuring staggered dimples (Model B) demonstrated the most notable improvement in the Nu number. It exhibited an enhancement of approximately twice the value compared to the conventional model. The mean thermal resistance for the tube with dimples in the staggered arrangement (Model B) is 0.0057 k/W, compared to 0.0118 k/W for the traditional model. The maximum overall performance criterion for Model -A- and Model -B- is 1.22 and 1.33, respectively.Graphic Abstract
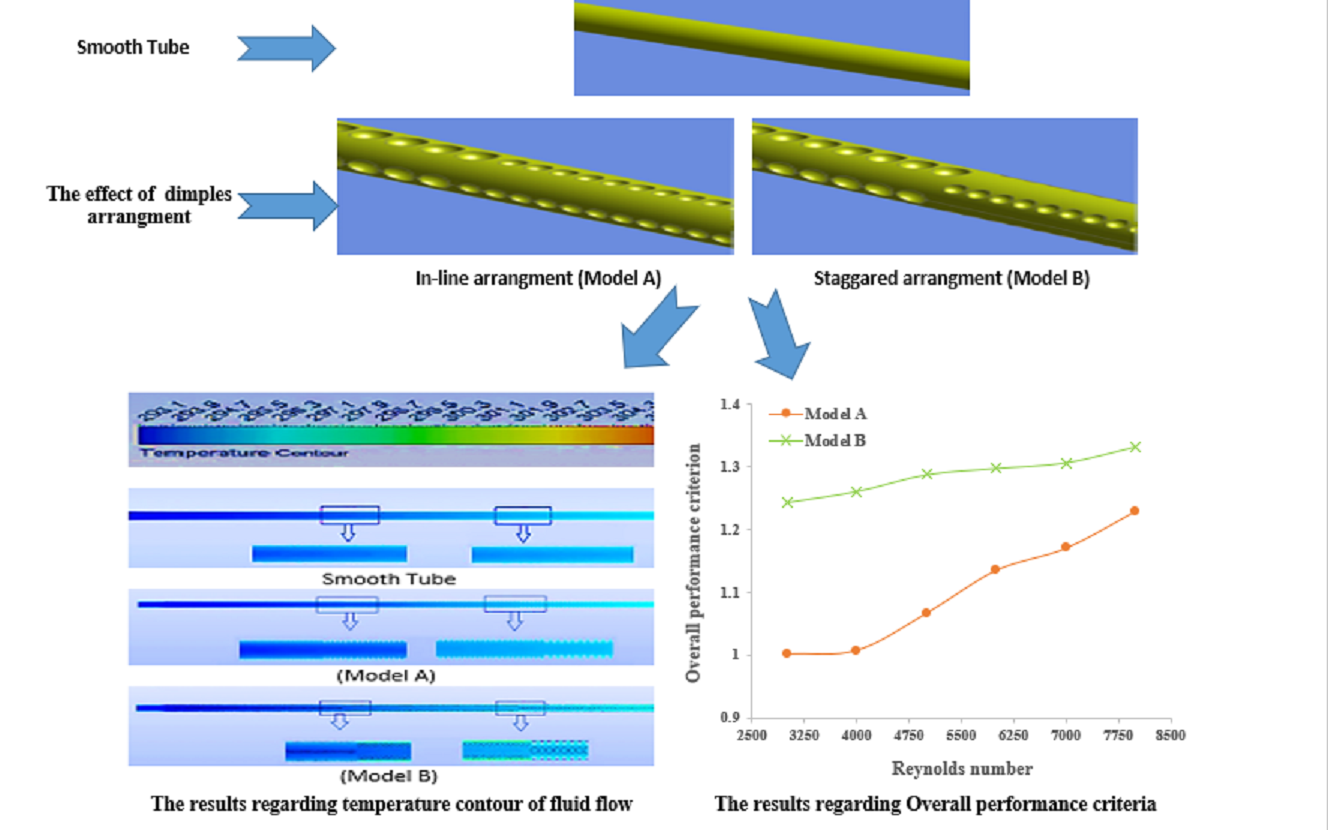
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools