 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Three-Dimensional Printing Conformal Cooling with Structural Lattices for Plastic Injection Molding
1 Singapore Centre for 3D Printing, Nanyang Technological University, 639798, Singapore
2 School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 639798, Singapore
* Corresponding Author: Fei Duan. Email:
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer 2024, 22(2), 397-415. https://doi.org/10.32604/fhmt.2024.048984
Received 23 December 2023; Accepted 11 March 2024; Issue published 20 May 2024
Abstract
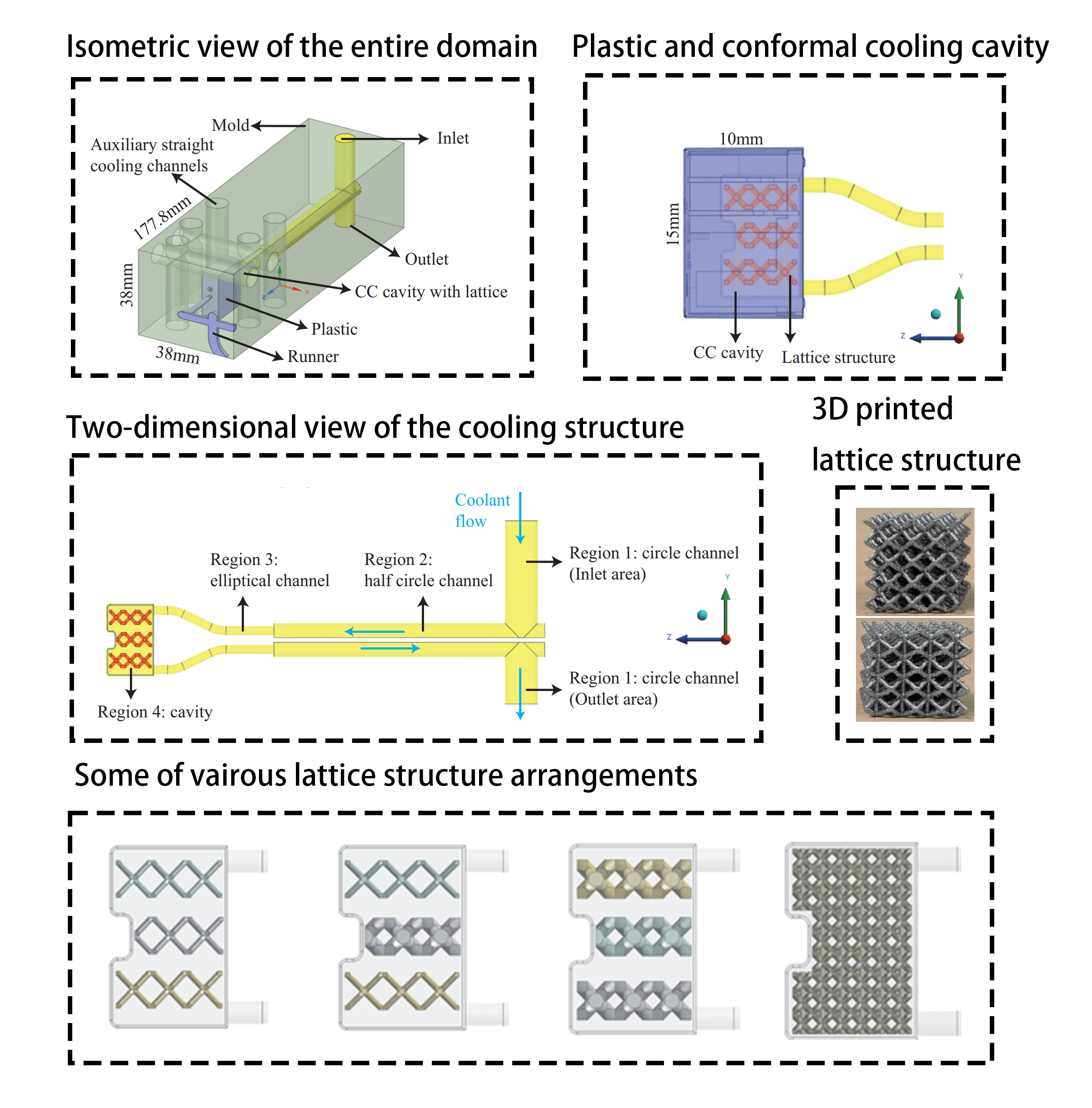
The design of three-dimensional printing based conformal cooling channels (CCCs) in injection molding holds great significance. Compared to CCCs, conformal cooling (CC) cavity solutions show promise in delivering enhanced cooling performance for plastic products, although they have been underexplored. In this research, CC cavity is designed within the mold geometry, reinforced by body-centered cubic (BCC) lattice structures to enhance mechanical strength. Three distinct BCC lattice variations have been integrated into the CC cavity: the BCC structure, BCC with cubes, and BCC with pillars. The thermal performances of the BCC lattice-added CC cavity are assessed numerically after experimental validation. To provide feasible solutions from viewpoints of thermal performances, various BCC lattice structure thicknesses are analyzed in the range of 0.8–1.2 mm. Thermal simulation outcomes reveal that thicker lattice structures enhance mechanical strength but simultaneously lead to an increase in cooling time. Upon examining all the proposed CC cavity solutions supported by BCC, the cooling times range from 2.2 to 4 s, resulting in a reduction of 38.6% to 66.1% when compared to conventional straight-drilled channels. In contrast to CCCs, CC cavities have the potential to decrease the maximum temperature non-uniformity from 8.5 to 6 K. Nevertheless, the presence of lattice structures in CC cavity solutions results in an elevated pressure drop, reaching 2.8 MPa, whereas the results for CCCs remain below 2.1 MPa.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools