 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cross-Diffusion Effects on an MHD Williamson Nanofluid Flow Past a Nonlinear Stretching Sheet Immersed in a Permeable Medium
1 Department of Mathematics, RGUKT, R.K. Valley, Kadapa (D), Andhra Pradesh, 516329, India
2 Department of Mathematics, Gitam University, Hyderabad, 502329, India
3 Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, University of 20 Août 1955-Skikda, Road El-Hadaeik, B.P. 26, Skikda, 21000, Algeria
4 Department of Mathematics, Anurag University, Hyderabad, Telangana, 500088, India
* Corresponding Author: F. Mebarek-Oudina. Email:
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer 2024, 22(1), 15-34. https://doi.org/10.32604/fhmt.2024.048045
Received 26 November 2023; Accepted 23 January 2024; Issue published 21 March 2024
Abstract
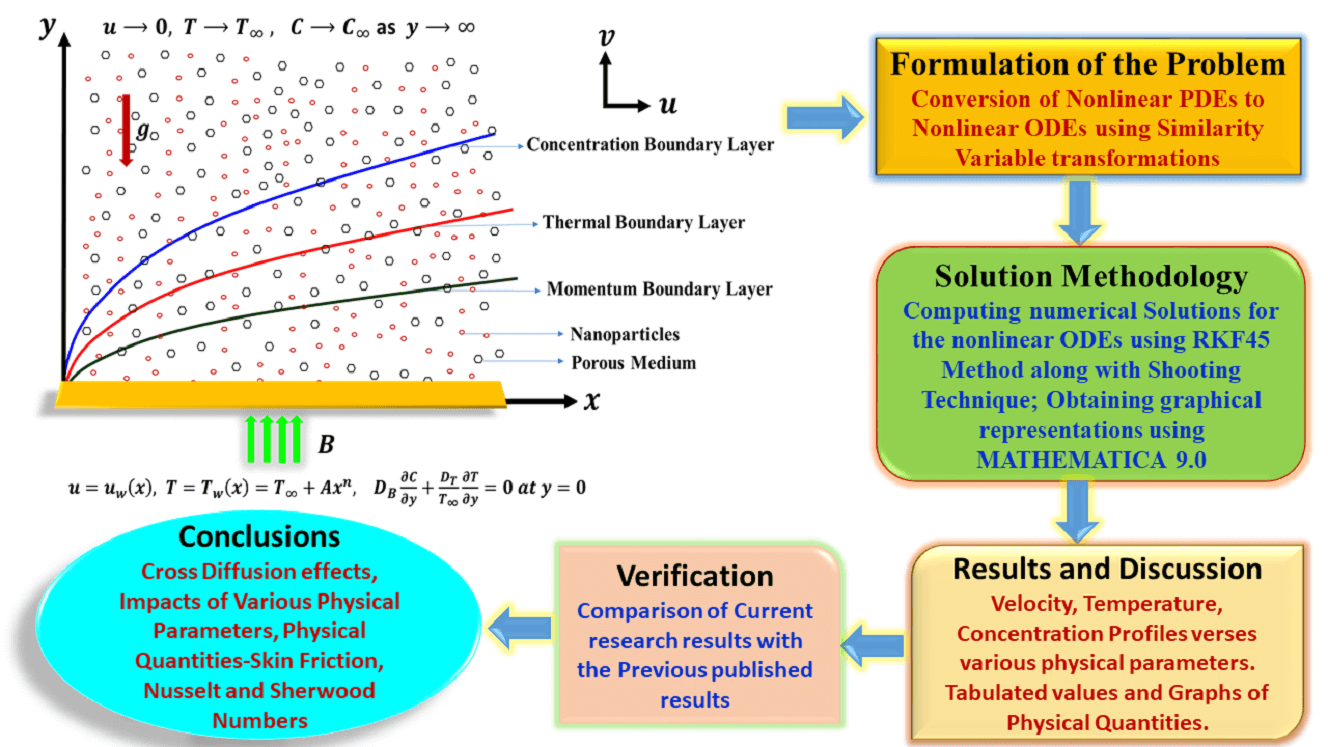
The primary aim of this research endeavor is to examine the characteristics of magnetohydrodynamic Williamson nanofluid flow past a nonlinear stretching surface that is immersed in a permeable medium. In the current analysis, the impacts of Soret and Dufour (cross-diffusion effects) have been attentively taken into consideration. Using appropriate similarity variable transformations, the governing nonlinear partial differential equations were altered into nonlinear ordinary differential equations and then solved numerically using the Runge Kutta Fehlberg-45 method along with the shooting technique. Numerical simulations were then perceived to show the consequence of various physical parameters on the plots of velocity, temperature, and concentration of the nanofluid flow. Boosting the magnetic, Williamson, porosity, and stretching sheet index parameters, the velocity of the fluid flow decreases. The temperature is enhanced as the Williamson and Brownian motion parameters upsurge, but it decreases as the Prandtl, thermophoresis, stretching sheet index, and Dufour parameters escalate. The concentration distribution decreases as the thermophoresis and magnetic parameters upsurge, but it escalates as the Soret, Schmidt, Brownian motion, and stretching sheet index parameters increase. Skin friction coefficient boosted as the stretching sheet index and magnetic parameters enhanced against the Williamson parameter. The findings from this study have been contrasted with earlier findings on local Nusselt numbers, which show substantial support and endorse the existing approach’s validity. The numerical values of the local Sherwood number gradually increase as the Schmidt, Soret, stretching sheet index, and thermophoresis parameters are upsurged.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools