 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effect of Surface Wettability on the Flow and Heat Transfer Performance of Pulsating Heat Pipe
School of Environment & Energy Engineering, Beijing University of Civil Engineering & Architecture, Beijing, 100044, China
* Corresponding Author: Wei Zhang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Loop Heat Pipe)
Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer 2025, 23(1), 361-381. https://doi.org/10.32604/fhmt.2025.059837
Received 17 October 2024; Accepted 03 December 2024; Issue published 26 February 2025
Abstract
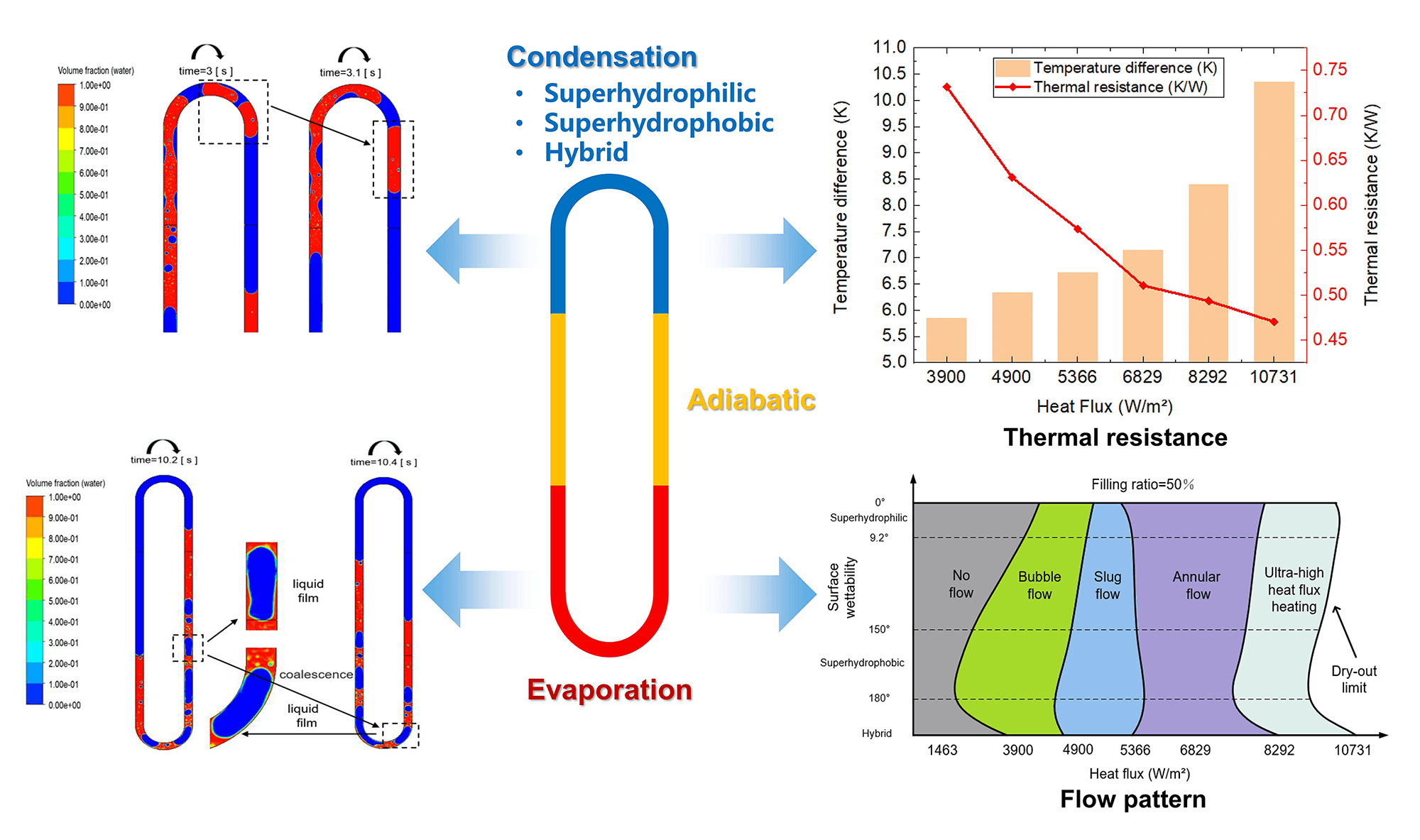
The present work deals with the numerical study of the two-phase flow pattern and heat transfer characteristics of single-loop pulsating heat pipes (PHPs) under three modified surfaces (superhydrophilic evaporation section paired with superhydrophilic, superhydrophobic, and hybrid condensation section). The Volume of Fluid (VOF) model was utilized to capture the phase-change process within the PHPs. The study also evaluated the influence of surface wettability on fluid patterns and thermo-dynamic heat transfer performance under various heat fluxes. The results indicated that the effective nucleation and detachment of droplets are critical factors influencing the thermal performance of the PHPs. The overall heat transfer performance of the superhydrophobic surface was significantly improved at low heat flux. Under medium to high heat flux, the superhydrophilic condensation section exhibits a strong oscillation effect and leads to the thickening of the liquid film. In addition, the hybrid surface possesses the heat transfer characteristics of both superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic walls. The hybrid condensation section exhibited the lowest thermal resistance by 0.45 K/W at the heat flux of 10731 W/m2. The thermal resistance is reduced by 13.1% and 5.4%, respectively, compared to the superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic conditions. The proposed surface-modification method for achieving highly efficient condensation heat transfer is helpful for the design and operation of device-cooling components.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools