 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Progress in the Understanding and Modeling of Cavitation and Related Applications
1 Key Laboratory of Advanced Manufacturing Intelligent Technology, Ministry of Education, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, 150080, China
2 School of Mechanica and Power Engineering, Harbin University of Science and Technology, Harbin, 150080, China
* Corresponding Author: Jianying Li. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2025, 21(3), 445-470. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2025.062337
Received 16 December 2024; Accepted 26 February 2025; Issue published 01 April 2025
Abstract
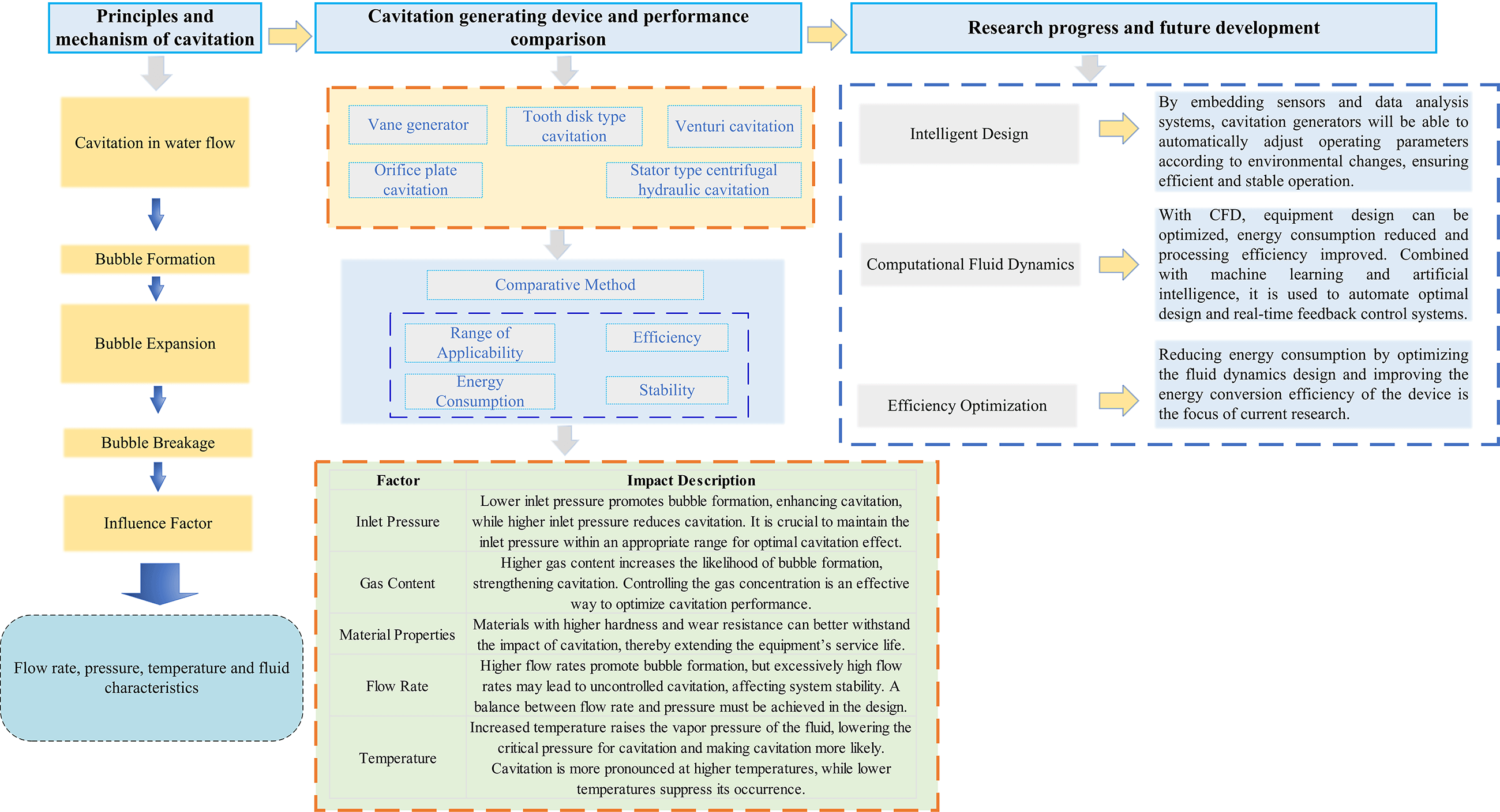
Hydrodynamic cavitation, as an efficient technique applied in many physical and chemical treatment methods, has been widely used by various industries and in several technological fields. Relevant generators, designed with specific structures and parameters, can produce cavitation effects, thereby enabling effective treatment and reasonable transformation of substances. This paper reviews the design principles, performance, and practical applications associated with different types of cavitation generators, aiming to provide theoretical support for the optimization of these systems. It systematically analyzes the underpinning mechanisms and the various factors influencing the cavitation phenomena, also conducting a comparative analysis of the performance of different types of generators. Specific applications dealing with wastewater treatment, chemical reaction acceleration, and other fields are discussed together with the advantages, disadvantages, and applicability of each type of cavitation generator. We also explore research progress in areas such as cavitation stability, energy efficiency, and equipment design upgrades. The study concludes by forecasting the application prospects of intelligent design and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) in optimizing and advancing cavitation generators. It proposes new ideas for the further development of cavitation technology and highlights directions for its widespread future application.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools