 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Simulation Study on the Heat Transfer Characteristics of a Spray-Cooled Single-Pipe Cooling Tower
1 Tianjin Key Lab of Refrigeration Technology, Department of Refrigeration and Low Temperature Engineering, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, 300134, China
2 Jiangsu Yongzhiyu Technology Development Co., Ltd., Xuzhou, 221700, China
3 Shandong Onar Refrigeration Technology Co., Ltd., Binzhou, 256600, China
* Corresponding Author: Kaiyong Hu. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(9), 2109-2126. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.050773
Received 17 February 2024; Accepted 27 May 2024; Issue published 23 August 2024
Abstract
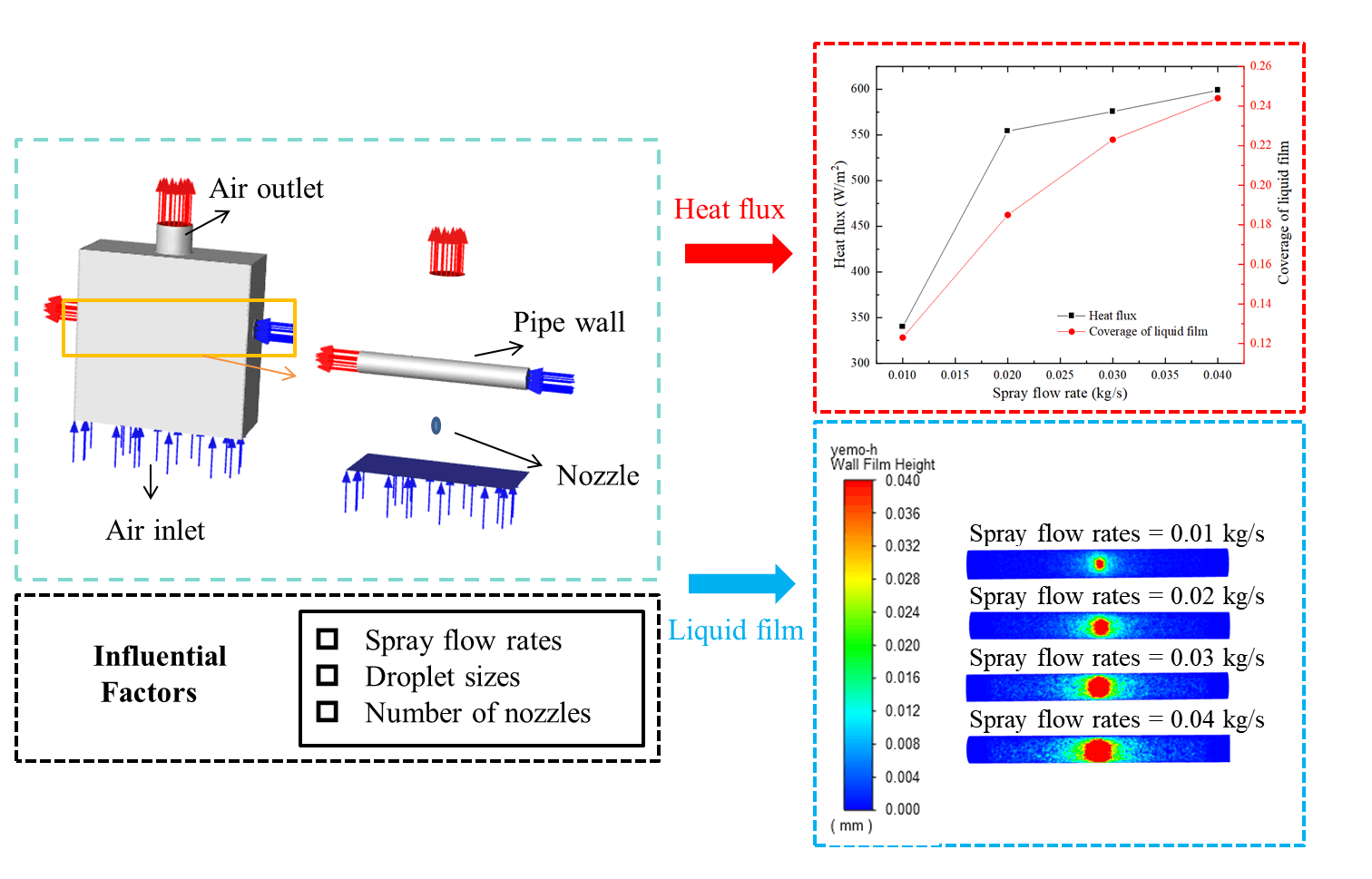
The current study focuses on spray cooling applied to the heat exchange components of a cooling tower. An optimization of such processes is attempted by assessing different spray flow rates and droplet sizes. For simplicity, the heat exchanger of the cooling tower is modeled as a horizontal round tube and a cooling tower spray cooling model is developed accordingly using a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software. The study examines the influence of varying spray flow rates and droplet sizes on the heat flow intensity between the liquid layer on the surface of the cylindrical tube and the surrounding air, taking into account the number of nozzles. It is observed that on increasing the spray flow strength, the heat flow intensity and extent of the liquid film in the system are enhanced accordingly. Moreover, the magnitude of droplet size significantly impacts heat transfer. A larger droplet size decreases evaporation in the air and enhances the deposition of droplets on the round tube. This facilitates the creation of the liquid film and enhances the passage of heat between the liquid film and air. Increasing the number of nozzles, while maintaining a constant spray flow rate, results in a decrease in the flow rate of each individual nozzle. This decrease is not favorable in terms of heat transfer.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools