 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effects of Different Concentrations of Sulfate Ions on Carbonate Crude Oil Desorption: Experimental Analysis and Molecular Simulation
School of Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou, 213164, China
* Corresponding Author: Nannan Liu. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(8), 1731-1741. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.048354
Received 05 December 2023; Accepted 31 January 2024; Issue published 06 August 2024
Abstract
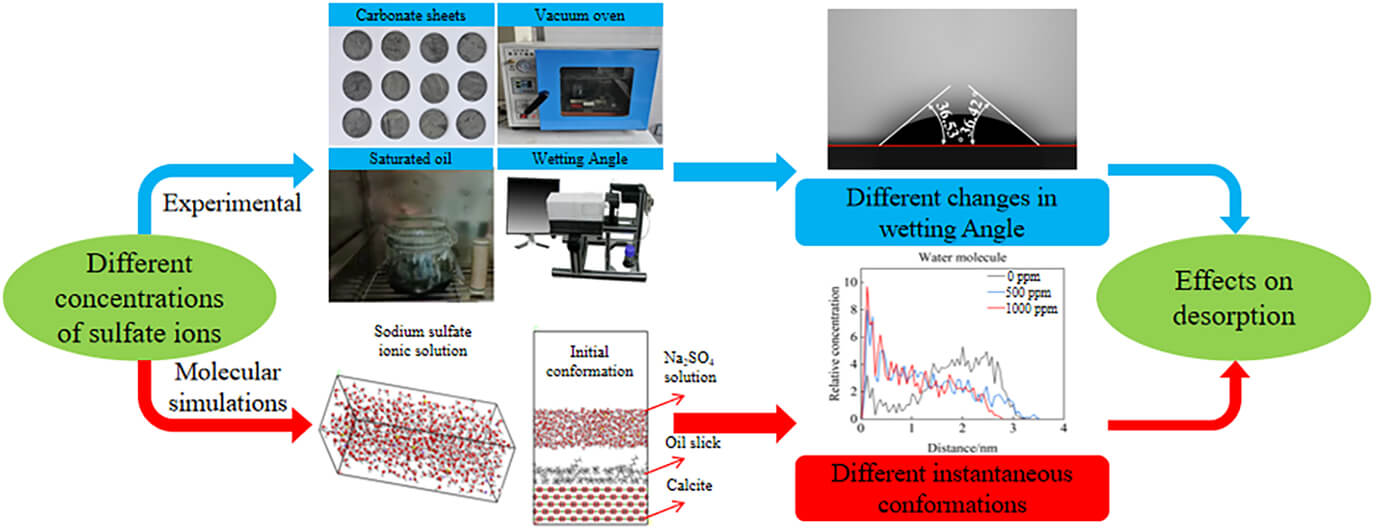
Low salinity water containing sulfate ions can significantly alter the surface wettability of carbonate rocks. Nevertheless, the impact of sulfate concentration on the desorption of oil film on the surface of carbonate rock is still unknown. This study examines the variations in the wettability of the surface of carbonate rocks in solutions containing varying amounts of sodium sulfate and pure water. The problem is addressed in the framework of molecular dynamics simulation (Material Studio software) and experiments. The experiment’s findings demonstrate that sodium sulfate can increase the rate at which oil moisture is turned into water moisture. The final contact angle is smaller than that of pure water. The results of the simulations show that many water molecules travel down the water channel under the influence of several powerful forces, including the electrostatic force, the van der Waals force and hydrogen bond, crowding out the oil molecules on the calcite’s surface and causing the oil film to separate. The relative concentration curve of water and oil molecules indicates that the separation rate of the oil film on the surface of calcite increases with the number of sulfate ions.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools