 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Numerical Simulation of Wet Particles Motion in a Vertical Powder Dryer
School of Petrochemical Engineering, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, 730050, China
* Corresponding Author: Dongdong Pang. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(8), 1823-1846. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.048093
Received 27 November 2023; Accepted 01 March 2024; Issue published 06 August 2024
Abstract
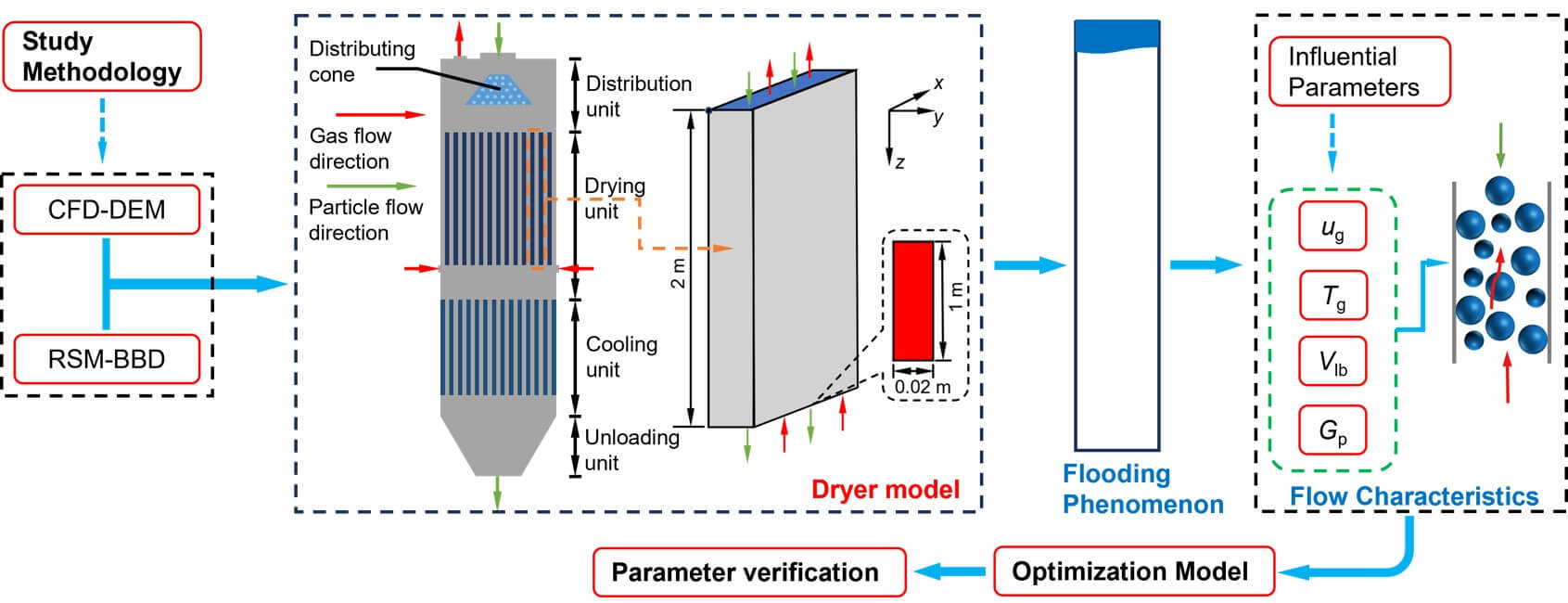
In this study, the motion of wet particles in the drying unit of a vertical powder dryer is investigated by using a Discrete element method (DEM) coupled with a liquid bridge force. In particular, by varying parameters such as the particle mass flow rates, the superficial gas velocities, and superficial gas temperatures, the influence of the moisture content on the flow behavior is examined. The results show that when the moisture content increases, the mean particle velocity decreases while the bed mean solid “holdup” and the mean residence time (MRT) of particles grow. It is also found that the local solid holdup is relatively higher in the near-wall region and decreases towards the near-fluid region. Two regression models are introduced accordingly for the mean particle velocity and the bed mean solid holdup by means of the RSM-BBD (Response surface methodology-Box-Behnken design) method to obtain the optimal combination of parameters for flooding prevention. Finally, the optimal results are compared with numerical observations. As the relative error is less than 10%, this demonstrates that the proposed methodology can accurately describe the particle flow dynamics in the drying unit.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools