 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Physical-Rheological Properties and Performances of Rejuvenated (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) Asphalt with Polymerized-MDI and Aromatic Oil
1 Hubei Regional Management Headquarters, CCCC Asset Management Co., Ltd., Beijing, 101399, China
2 School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan, 430073, China
3 Hubei Provincial Engineering Research Center for Green Civil Engineering Materials and Structures, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan, 430073, China
* Corresponding Author: Xiong Xu. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(7), 1633-1646. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.051010
Received 25 February 2024; Accepted 27 May 2024; Issue published 23 July 2024
Abstract
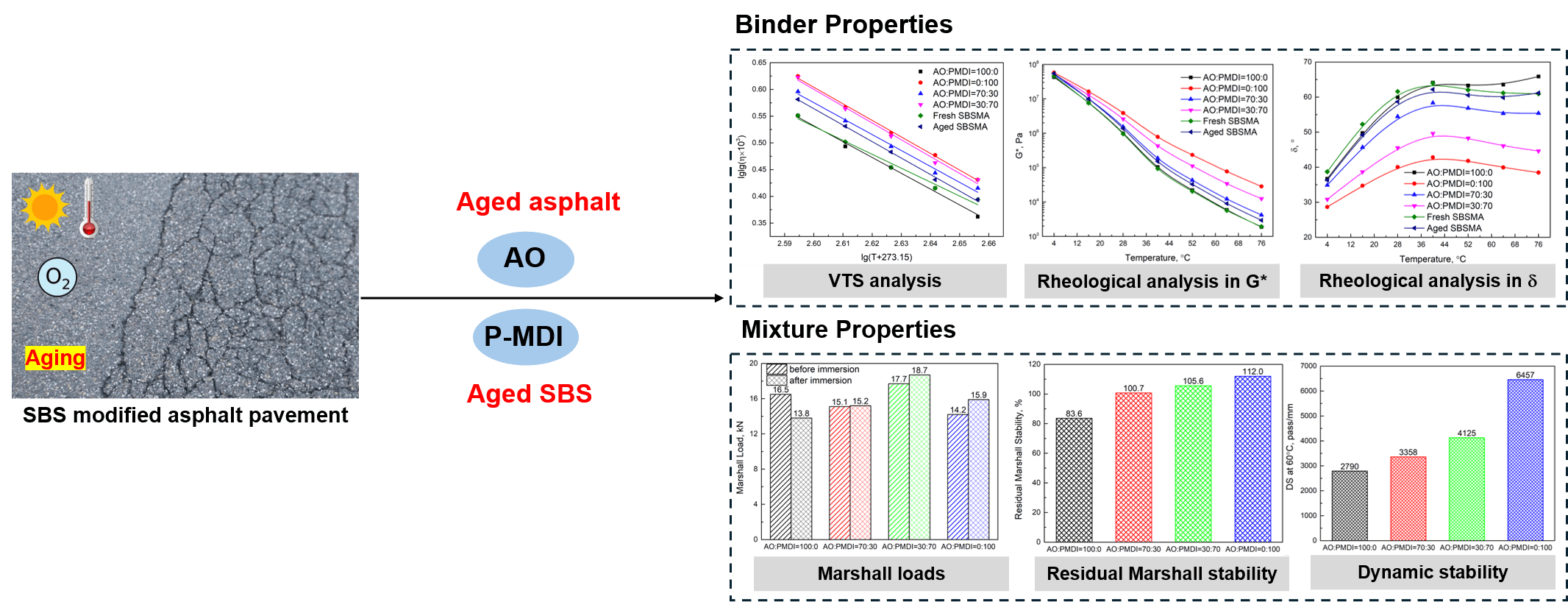
Traditional asphalt rejuvenators, like aromatic oil (AO), are known to be effective in improving the low-temperature properties and fatigue performances of aged SBS (styrene-butadiene-styrene) modified asphalt (SBSMA) binders and mixtures. However, these rejuvenators inevitably compromise their high-temperature properties and deformation resistances because they dilute asphalt binder but do not fix the damaged structures of aged SBS. In this study, a highly-active chemical called polymerized 4,4-diphenylmethane diisocyanate (PMDI) was used to assist the traditional AO asphalt rejuvenator. The physical and rheological characteristics of rejuvenated SBSMA binders and the moisture-induced damage and rut deformation performances of corresponding mixtures were comparatively evaluated. The results showed that the increasing proportion of AO compromises the high-temperature property and hardness of aged SBSMA binder, and an appropriate amount of PMDI works to compensate such losses; 3% rejuvenator at mass ratio of AO:PMDI = 70:30 can have a rejuvenated SBSMA binder with a high-temperature performance similar to that of fresh binder, approximately at 71.4°C; the use of AO can help reduce the viscosity of PMDI rejuvenated SBSMA binder for improving its workability; PMDI can help improve the resistance of AO rejuvenated SBSMA binder to deformation, especially at elevated temperatures, through its chemical reactions with aged SBS; moisture induction can enhance the resistance to damage of rejuvenated mixtures containing AO/PMDI or only PMDI; and the rejuvenator with a mass ratio of AO:PMDI = 70:30 can lead the rejuvenated mixture to meet the application requirement, with a rut depth of only 2.973 mm, although more PMDI can result in a higher resistance of rejuvenated mixtures to high-temperature deformation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools