 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A Numerical Investigation of the Effect of Boundary Conditions on Acoustic Pressure Distribution in a Sonochemical Reactor Chamber
1 UEC-Aviadvigatel, 93 Komsomolsky Prospect, Perm, 614990, Russia
2 Laboratory of Computing Hydrodynamic, Institute of Continuous Media Mechanics UB RAS, Perm, 614013, Russia
3 Laboratory of Interfacial Hydrodynamic, Perm State University, Perm, 614068, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Ivan Sboev. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Problems in Fluid Mechanics)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(6), 1425-1439. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.051341
Received 03 March 2024; Accepted 14 May 2024; Issue published 27 June 2024
Abstract
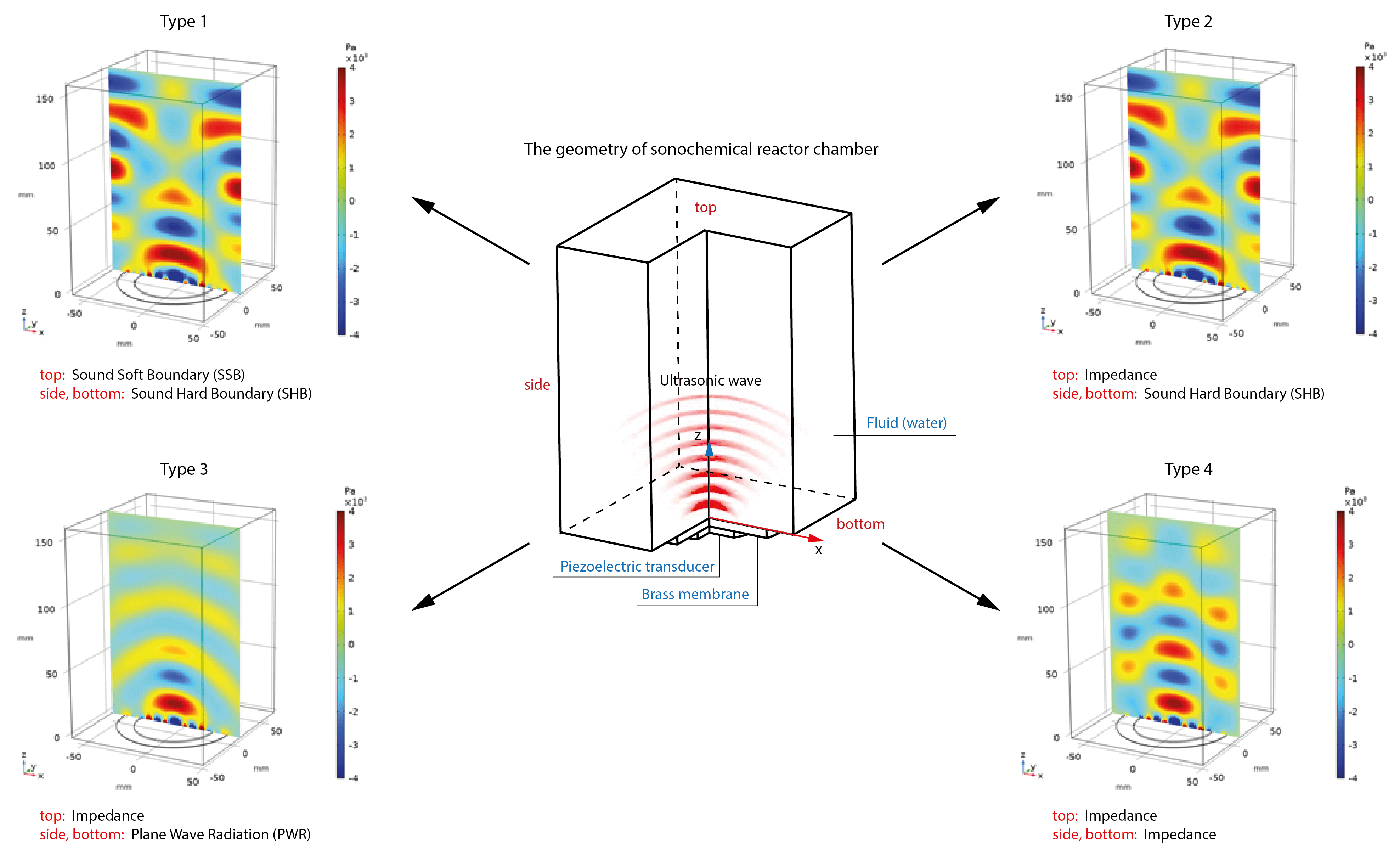
The intensification of physicochemical processes in the sonochemical reactor chamber is widely used in problems of synthesis, extraction and separation. One of the most important mechanisms at play in such processes is the acoustic cavitation due to the non-uniform distribution of acoustic pressure in the chamber. Cavitation has a strong impact on the surface degradation mechanisms. In this work, a numerical calculation of the acoustic pressure distribution inside the reactor chamber was performed using COMSOL Multiphysics. The numerical results have revealed the dependence of the structure of the acoustic pressure field on the boundary conditions for various thicknesses of the piezoelectric transducer. In particular, the amplitude of the acoustic pressure is minimal in the case of absorbing boundaries, and the attenuation becomes more significant as the thickness of the piezoelectric transducer increases. In addition, reflective boundaries play a significant role in the formation and distribution of zones of maximum cavitation activity.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools