 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Experimental Study on the Effect of a Nanofluid on Oil-Water Relative Permeability
1 Baikouquan Oil Production Plant, PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company, Karamay, 834000, China
2 Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration Development, PetroChina Liaohe Oilfield, Panjin, 124010, China
3 Petroleum Engineering School, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, 610500, China
4 Oil and Gas Development, Haosheng Xincheng Energy Technology, Ltd. of Sicuan, Chengdu, 610213, China
* Corresponding Author: Yannan Wu. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(6), 1265-1277. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.044833
Received 09 August 2023; Accepted 18 December 2023; Issue published 27 June 2024
Abstract
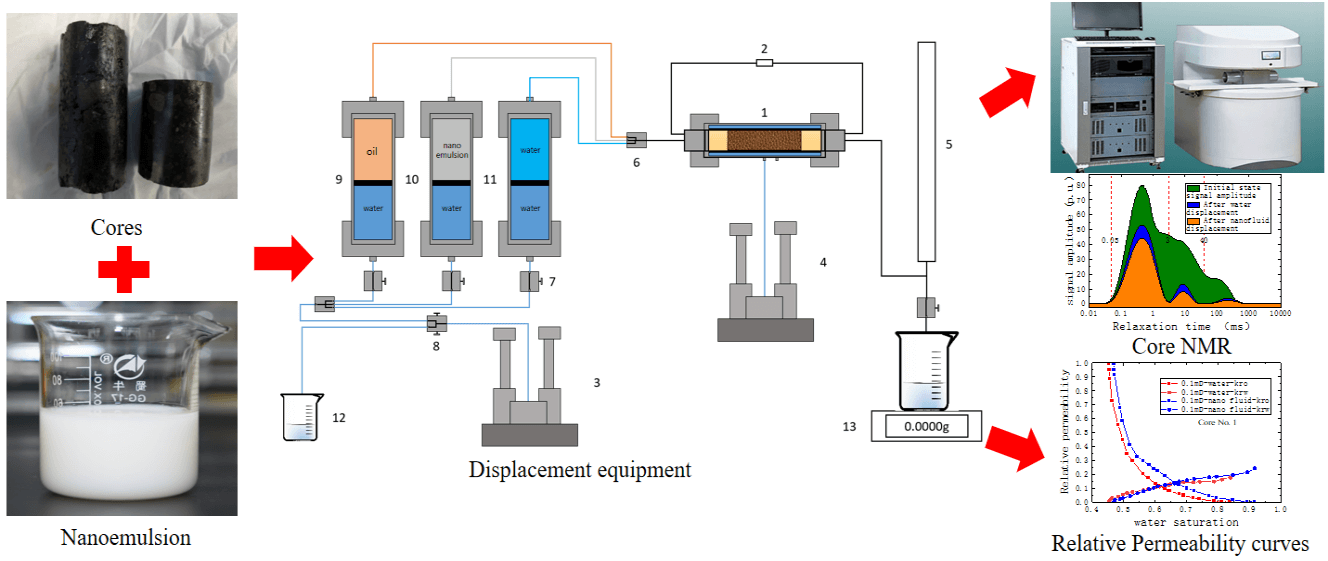
The low porosity and low permeability of tight oil reservoirs call for improvements in the current technologies for oil recovery. Traditional chemical solutions with large molecular size cannot effectively flow through the nano-pores of the reservoir. In this study, the feasibility of Nanofluids has been investigated using a high pressure high temperature core-holder and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The results of the experiments indicate that the specified Nanofluids can enhance the tight oil recovery significantly. The water and oil relative permeability curve shifts to the high water saturation side after Nanofluid flooding, thereby demonstrating an increase in the water wettability of the core. In the Nanofluid flooding process the oil recovery was enhanced by 15.1%, compared to waterflooding stage. The T2 spectra using the NMR show that after Nanofluid flooding, a 7.18% increment in oil recovery factor was gained in the small pores, a 4.9% increase in the middle pores, and a 0.29% increase in the large pores. These results confirm that the Nanofluids can improve the flow state in micro-sized pores inside the core and increase the ultimate oil recovery factor.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools