 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Investigation of Cavitation in NaCl Solutions in a Sonochemical Reactor Using the Foil Test Method
1 Institute of Continuous Media Mechanics UB RAS, Perm, 614013, Russia
2 Faculty of Physics, Perm State University, Perm, 614068, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Michael Kuchinskiy. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Problems in Fluid Mechanics)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(5), 1093-1102. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.050059
Received 26 January 2024; Accepted 21 March 2024; Issue published 07 June 2024
Abstract
Ultrasonic baths and sonochemical reactors are widely used in industrial applications dealing with surface cleaning and chemical synthesis. The processes of erosion, cleaning and structuring of the surface can be typically controlled by changing relevant influential parameters. In particular, in this work, we experimentally investigate the effect of NaCl concentration (0–5.5 mol/L) on the erosion of an aluminum foil under ultrasonic exposure at a frequency of 28 kHz. Special attention is paid to the determination of cavitation zones and their visualization using heat maps. It is found that at low NaCl concentration (0.3 mol/L), the foil destruction rate is higher than in distilled water. At higher concentrations of salt, cavitation takes place mainly in the upper part of the container.Graphic Abstract
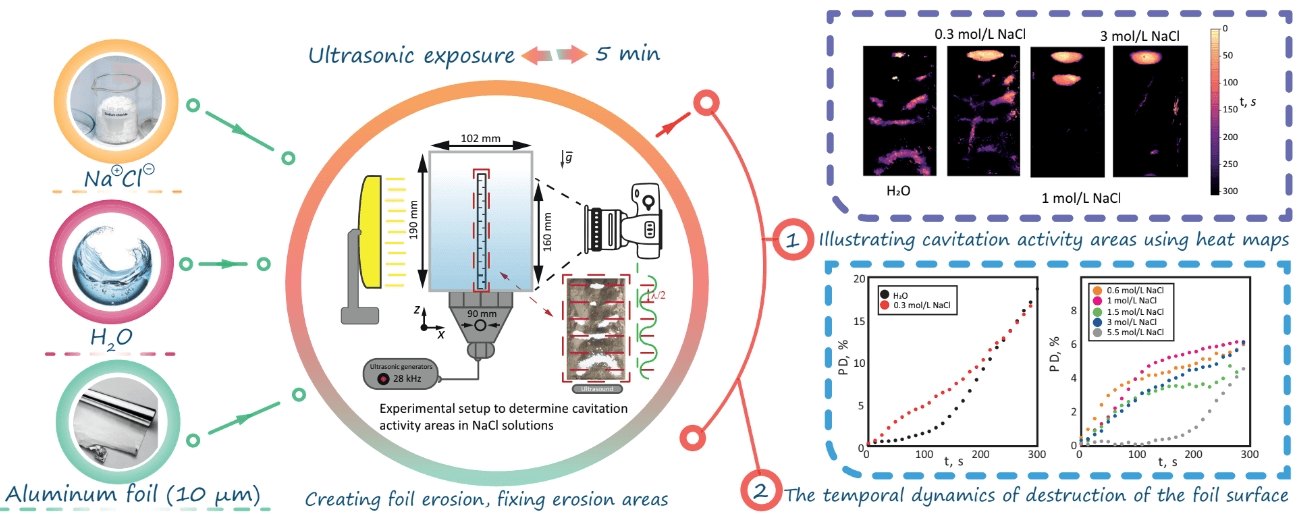
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools