 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Evaluation of Well Spacing for Primary Development of Fractured Horizontal Wells in Tight Sandstone Gas Reservoirs
1 Exploration and Development Research Institute, PetroChina Southwest Oil & Gas Field Company, Chengdu, 610041, China
2 Oil and Gas Resources Department, PetroChina Southwest Oil & Gas Field Company, Chengdu, 610000, China
* Corresponding Author: Fang Li. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Solid, Fluid, and Thermal Dynamics in the Development of Unconventional Resources )
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(5), 1015-1030. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.043256
Received 27 June 2023; Accepted 21 November 2023; Issue published 07 June 2024
Abstract
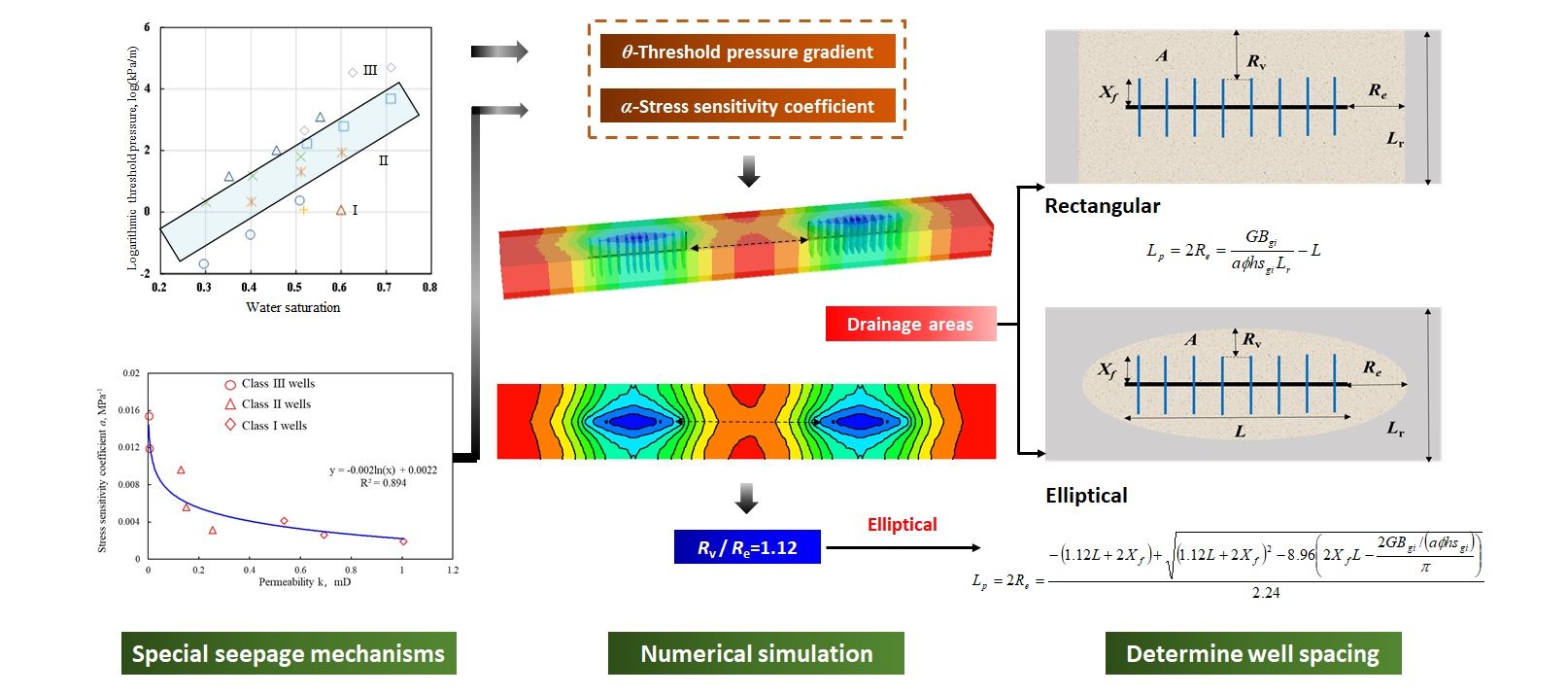
Methods for horizontal well spacing calculation in tight gas reservoirs are still adversely affected by the complexity of related control factors, such as strong reservoir heterogeneity and seepage mechanisms. In this study, the stress sensitivity and threshold pressure gradient of various types of reservoirs are quantitatively evaluated through reservoir seepage experiments. On the basis of these experiments, a numerical simulation model (based on the special seepage mechanism) and an inverse dynamic reserve algorithm (with different equivalent drainage areas) were developed. The well spacing ranges of Classes I, II, and III wells in the Q gas field are determined to be 802–1,000, 600–662, and 285–400 m, respectively, with their average ranges as 901, 631, and 342.5 m, respectively. By considering both the pairs of parallel well groups and series well groups as examples, the reliability of the calculation results is verified. It is shown that the combination of the two models can reduce errors and provide accurate results.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools