 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Numerical Simulation of Asphaltene Precipitation and Deposition during Natural Gas and CO2 Injection
Nanhai East Petroleum Research Institute, Shenzhen Branch of CNOOC Ltd., Shenzhen, 518000, China
* Corresponding Author: Shasha Feng. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(2), 275-292. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.041825
Received 08 May 2023; Accepted 22 September 2023; Issue published 14 December 2023
Abstract
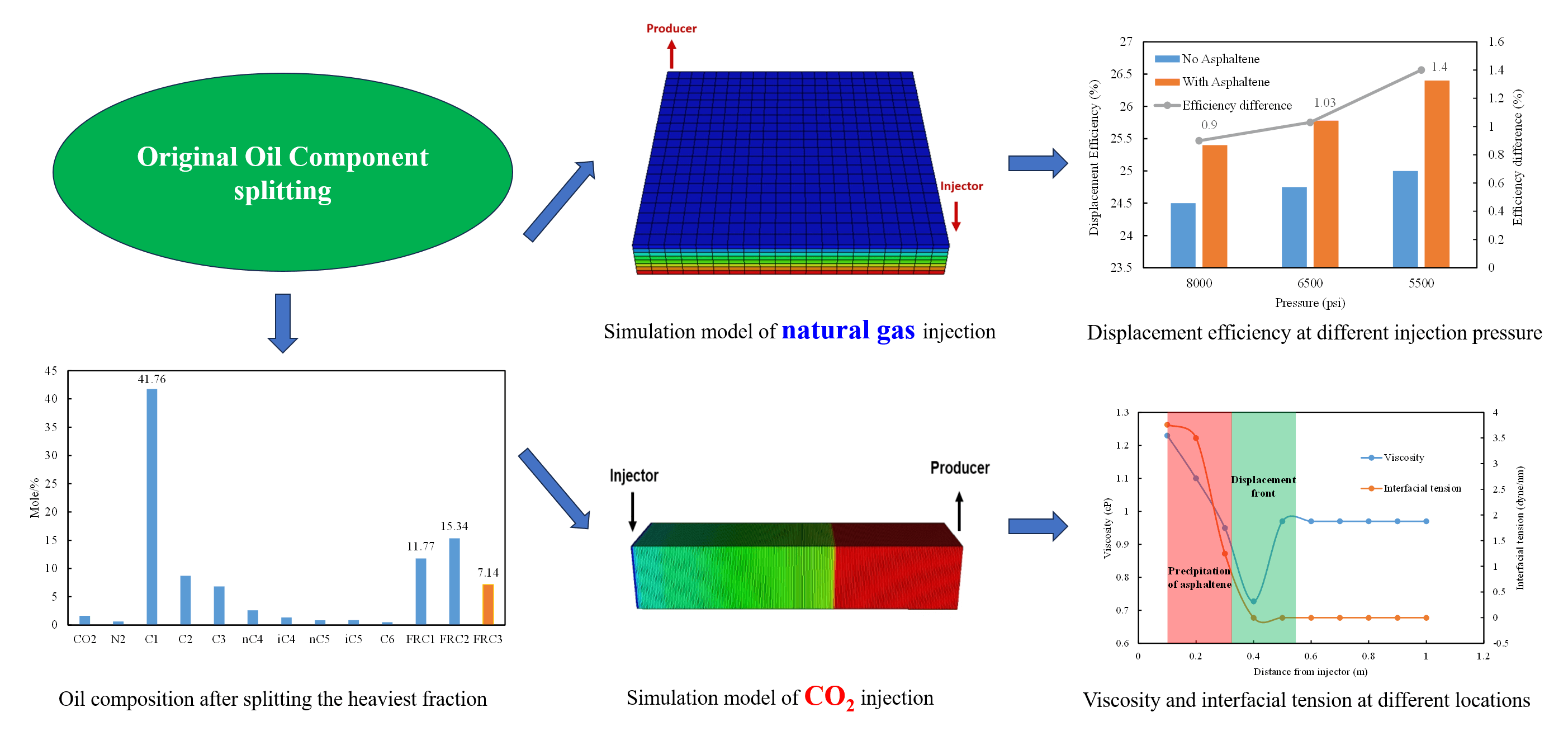
Asphaltene deposition is a significant problem during gas injection processes, as it can block the porous medium, the wellbore, and the involved facilities, significantly impacting reservoir productivity and ultimate oil recovery. Only a few studies have investigated the numerical modeling of this potential effect in porous media. This study focuses on asphaltene deposition due to natural gas and CO2 injection. Predictions of the effect of gas injection on asphaltene deposition behavior have been made using a 3D numerical simulation model. The results indicate that the injection of natural gas exacerbates asphaltene deposition, leading to a significant reduction in permeability near the injection well and throughout the reservoir. This reduction in permeability strongly affects the ability of gas to flow through the reservoir, resulting in an improvement of the displacement front. The displacement efficiency of the injection gas process increases by up to 1.40% when gas is injected at 5500 psi, compared to the scenario where the asphaltene model is not considered. CO2 injection leads to a miscible process with crude oil, extracting light and intermediate components, which intensifies asphaltene precipitation and increases the viscosity of the remaining crude oil, ultimately reducing the recovery rate.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools