 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Numerical Analysis of the Magnetic Dipole Effect on a Radiative Ferromagnetic Liquid Flowing over a Porous Stretched Sheet
1 Department of Mathematics, Narasaraopeta Engineering College, Narasaraopet, India
2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Sciences, University of 20 Août 1955-Skikda, Skikda, Algeria
3 Department of Mathematics, RVR & JC College of Engineering, Guntur, India
4 Department of Mathematics, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Vaddeswaram, India
* Corresponding Author: F. Mebarek-Oudina. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(2), 293-310. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.030325
Received 31 March 2023; Accepted 05 May 2023; Issue published 14 December 2023
Abstract
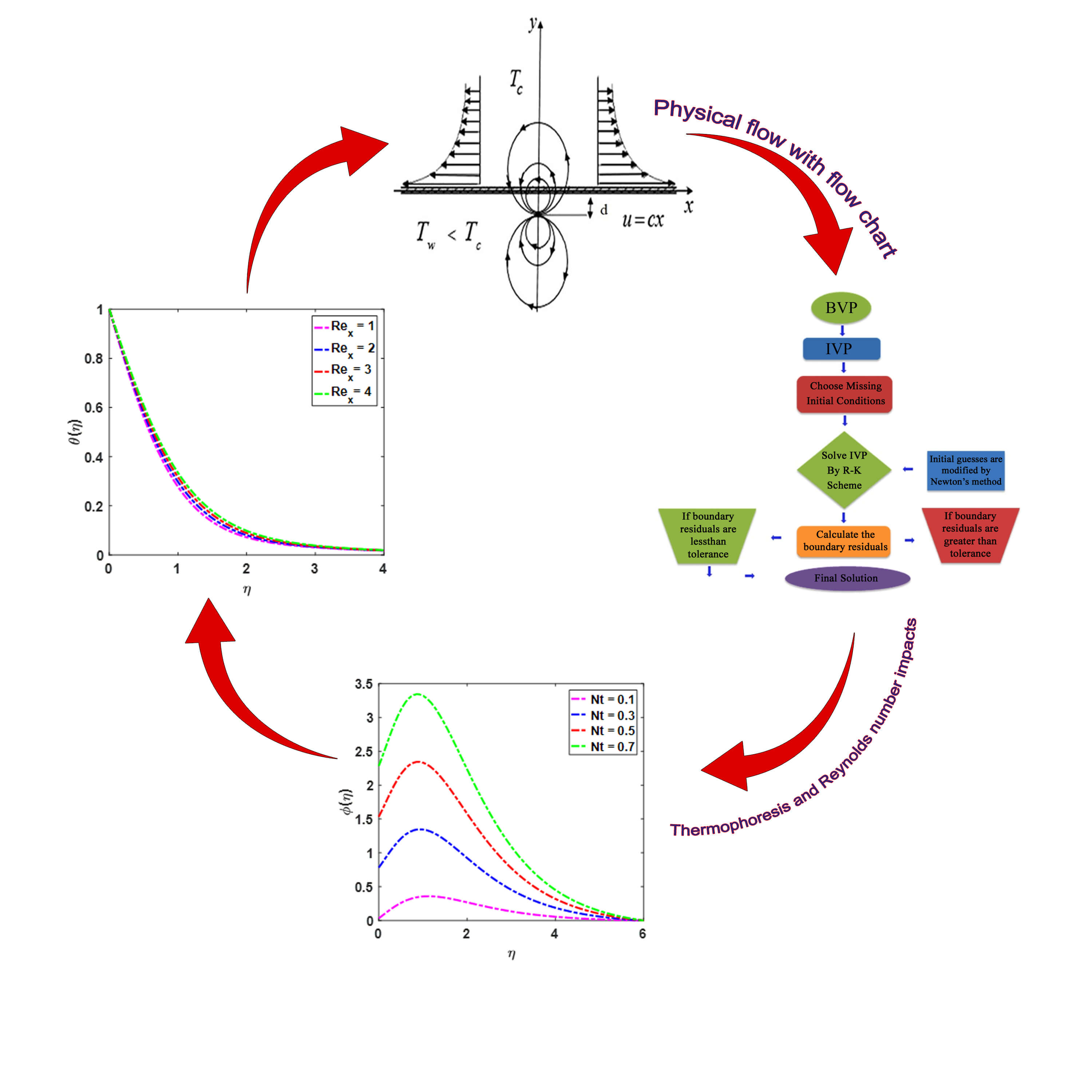
The effects of a magnetic dipole on a nonlinear thermally radiative ferromagnetic liquid flowing over a stretched surface in the presence of Brownian motion and thermophoresis are investigated. By means of a similarity transformation, ordinary differential equations are derived and solved afterwards using a numerical (the BVP4C) method. The impact of various parameters, namely the velocity, temperature, concentration, is presented graphically. It is shown that the nanoparticles properties, in conjunction with the magnetic dipole effect, can increase the thermal conductivity of the engineered nanofluid and, consequently, the heat transfer. Comparison with earlier studies indicates high accuracy and effectiveness of the numerical approach. An increase in the Brownian motion parameter and thermophoresis parameter enhances the concentration and the related boundary layer. The skin-friction rises when the viscosity parameter is increased. A larger value of the ferromagnetic parameter results in a higher skin-friction and, vice versa, in a smaller Nusselt number.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools