 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Evaluation and Application of Flowback Effect in Deep Shale Gas Wells
Shale Gas Research Institute, PetroChina Southwest Oil & Gas field Company, Chengdu, 610051, China
* Corresponding Author: Sha Liu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Fluid and Thermal Dynamics in the Development of Unconventional Resources II)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(10), 2301-2321. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2024.052454
Received 02 April 2024; Accepted 06 June 2024; Issue published 23 September 2024
Abstract
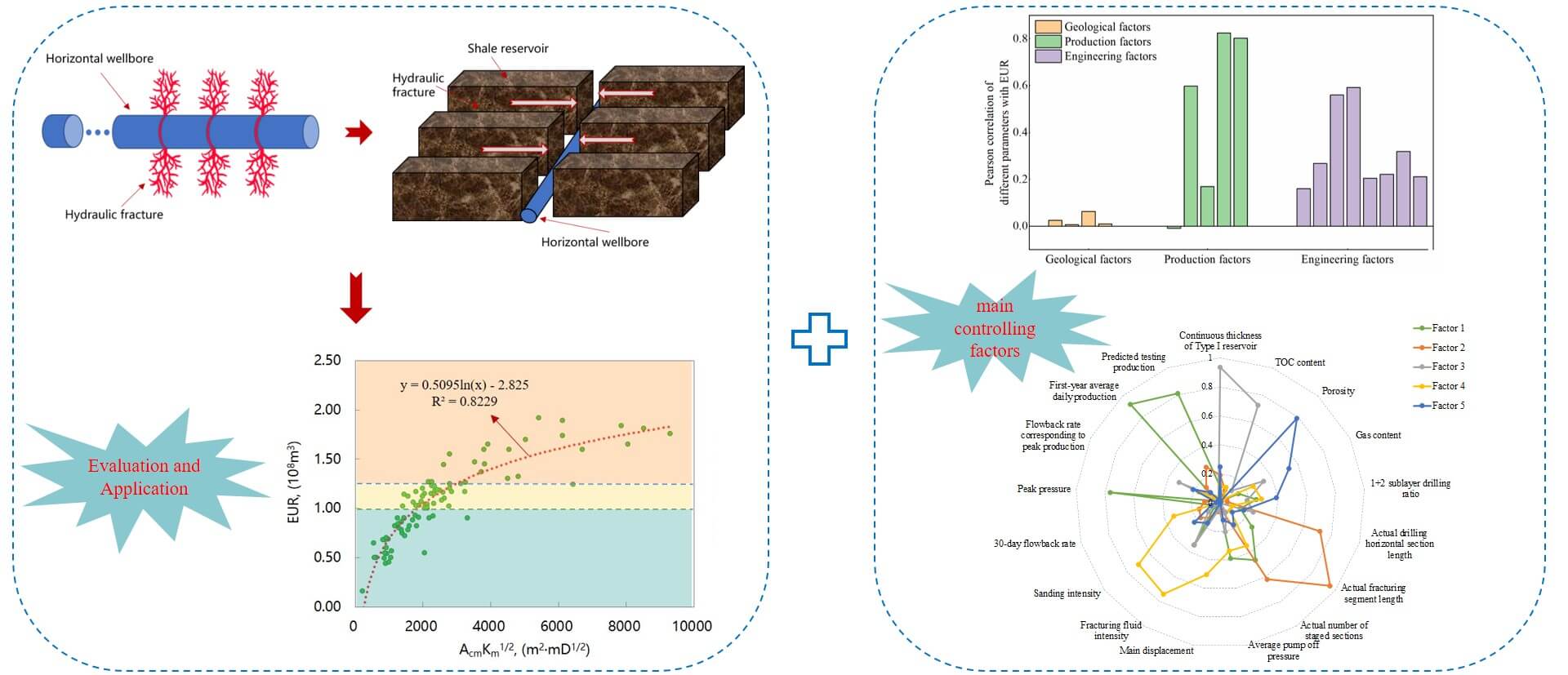
The pivotal areas for the extensive and effective exploitation of shale gas in the Southern Sichuan Basin have recently transitioned from mid-deep layers to deep layers. Given challenges such as intricate data analysis, absence of effective assessment methodologies, real-time control strategies, and scarce knowledge of the factors influencing deep gas wells in the so-called flowback stage, a comprehensive study was undertaken on over 160 deep gas wells in Luzhou block utilizing linear flow models and advanced big data analytics techniques. The research results show that: (1) The flowback stage of a deep gas well presents the characteristics of late gas channeling, high flowback rate after gas channeling, low 30-day flowback rate, and high flowback rate corresponding to peak production; (2) The comprehensive parameter AcmKm1/2 in the flowback stage exhibits a strong correlation with the Estimated Ultimate Recovery (EUR), allowing for the establishment of a standardized chart to evaluate EUR classification in typical shale gas wells during this stage. This enables quantitative assessment of gas well EUR, providing valuable insights into production potential and performance; (3) The spacing range and the initial productivity of gas wells have a significant impact on the overall effectiveness of gas wells. Therefore, it is crucial to further explore rational well patterns and spacing, as well as optimize initial drainage and production technical strategies in order to improve their performance.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools