 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Influence of Recycled Concrete Fine Powder on Durability of Cement Mortar
1
School of Architectural and Civil Engineering, Zhongyuan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, 450007, China
2
School of Civil Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University & Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai),
Zhuhai, 519082, China
* Corresponding Author: Jihui Zhao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Solid Waste Processing and Recycling Technologies for Civil Engineering Materials)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2024, 20(1), 45-58. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.029299
Received 11 February 2023; Accepted 05 May 2023; Issue published 08 November 2023
Abstract
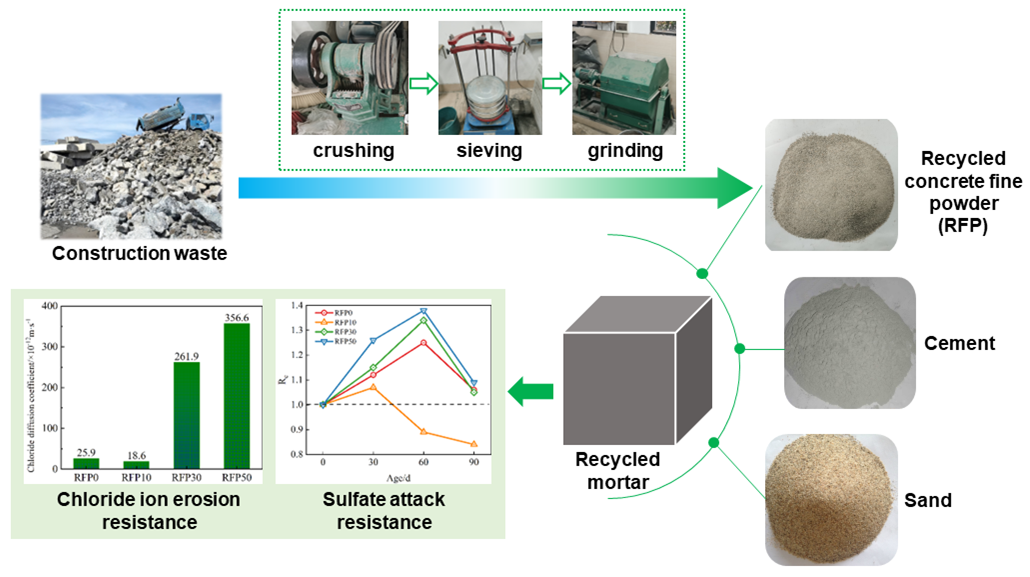
In this paper, the durability of cement mortar prepared with a recycled-concrete fine powder (RFP) was examined; including the analysis of a variety of aspects, such as the carbonization, sulfate attack and chloride ion erosion resistance. The results indicate that the influence of RFP on these three aspects is different. The carbonization depth after 30 days and the chloride diffusion coefficient of mortar containing 10% RFP decreased by 13.3% and 28.19%. With a further increase in the RFP content, interconnected pores formed between the RFP particles, leading to an acceleration of the penetration rate of CO2 and Cl− . When the RFP content was less than 50%, the corrosion resistance coefficient of the compressive strength of the mortar was 0.84–1.05 after 90 days of sulfate attack. But the expansion and cracking of the mortar was effectively alleviated due to decrease of the gypsum production. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis has confirmed that 10% RFP contributes to the formation of a dense microstructure in the cement mortar.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools