 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A Model for Predicting the Erosion Rate Induced by the Use of a Selective Catalytic Reduction Denitrification Technology in Cement Kilns Flue Gas
1 School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, 243032, China
2 School of Energy and Environment, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, 243002, China
3 Anhui Weida Environment Protection Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei, 230041, China
* Corresponding Author: Fuping Qian. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2023, 19(8), 1997-2011. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2023.026373
Received 01 September 2022; Accepted 30 January 2023; Issue published 04 April 2023
Abstract
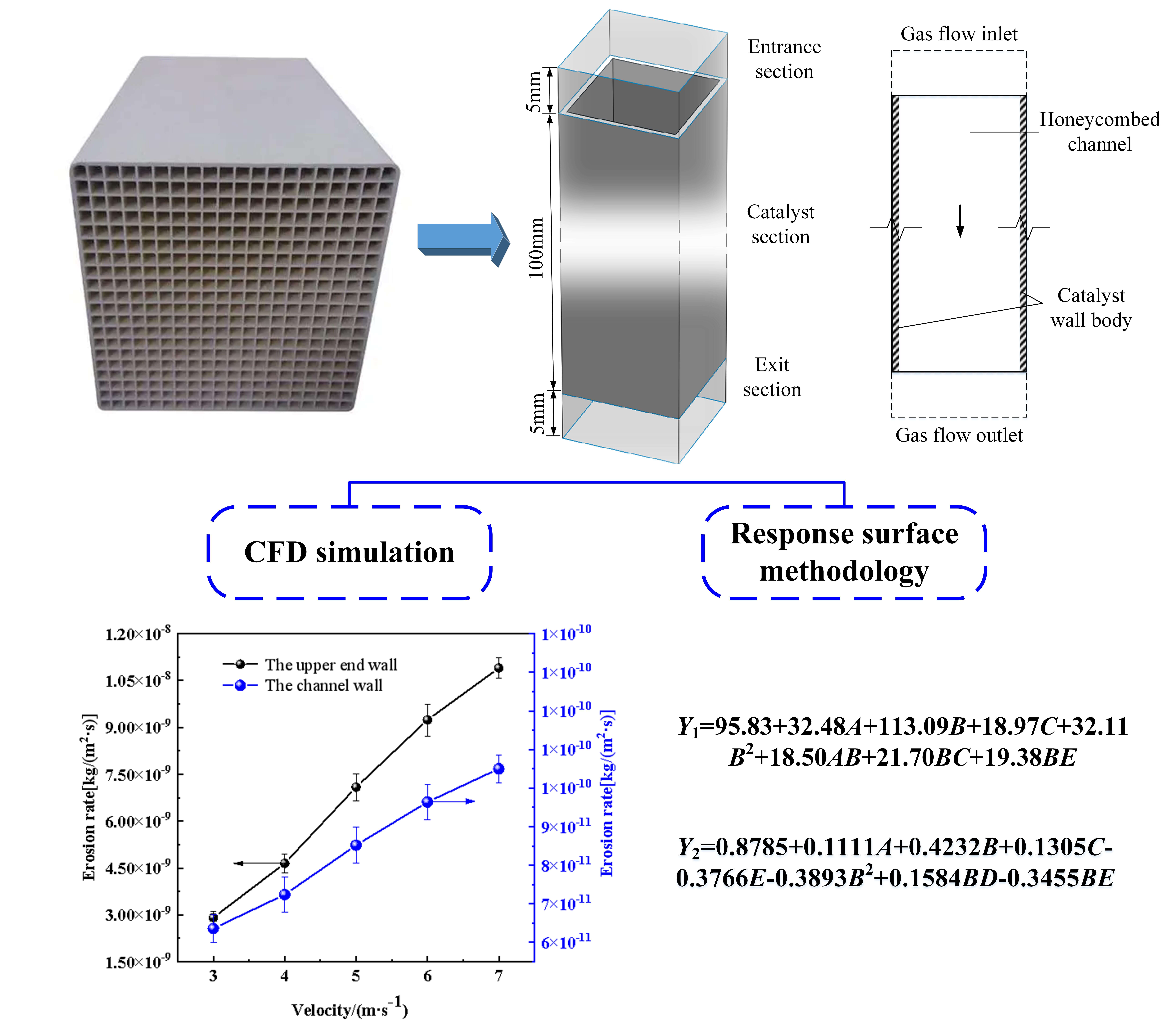
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is a technology by which nitrogen oxides are converted with the aid of a catalyst into diatomic nitrogen and water. It is known that the catalyst can be easily eroded if a cement kiln with a high-dust content is considered. To understand this process, numerical simulations have been carried out considering a single catalyst channel in order to study the collision and erosion of fly ash and catalysts at meso scale. Based on a response surface methodology, the effects of five factors on the erosion rate have been studied, namely, the catalyst particle velocity, the particle size, the particle concentration, the incidence angle and the catalyst porosity. The results show that the influence of particle velocity, particle size and particle concentration is statistically significant and the particle size and incidence angle have a significant effect on the erosion rate. A quadratic polynomial prediction model for the erosion rate of honeycomb catalysts in cement kiln SCR reactors is finally proposed to support the future optimization of these systems.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools