 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Numerical Simulation of Dust Removal in the Cyclone Collector of a Straw Crusher Based on a Discrete Phase Model
1 State Key Laboratory of Mining Response and Disaster Prevention and Control in Deep Coal Mine, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, 232001, China
2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, 232001, China
* Corresponding Author: Chang Su. Email:
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2023, 19(5), 1143-1157. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2022.022496
Received 13 March 2022; Accepted 13 July 2022; Issue published 30 November 2022
Abstract
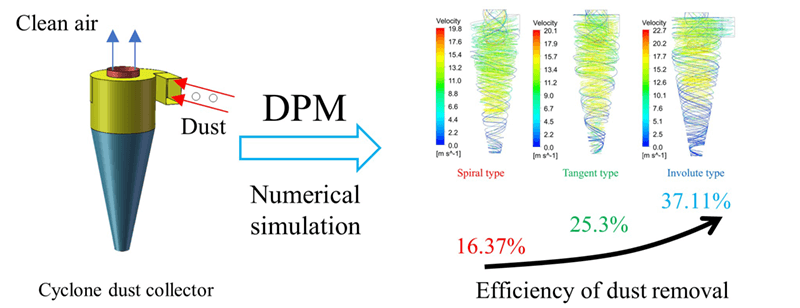
The cyclone dust collector is an important subsystem of straw crushers used in agriculture. In the present study, a new type of dust collector with involute morphology is proposed to obtain better dust removal efficiency with respect to that of classical tangential and spiral dust collectors. A discrete phase model (DPM) method is used in synergy with a turbulence model, and the SIMPLE algorithm to simulate the flow field inside the dust collector and the related particle dynamics. It is shown that the internal flow field features a primary swirl, a secondary swirl and blockage effects. Moreover, for the involute dust collector, the tangential velocity in the initial stage and the pressure in the high-pressure area are larger than those obtained for the classical types. The dust removal efficiency is 37.11%, 25.3%, and 16.37% for the involute type dust collector, the tangential type and the spiral type, respectively.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools