 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Impact of Radiation and Slip on Newtonian Liquid Flow Past a Porous Stretching/Shrinking Sheet in the Presence of Carbon Nanotubes
1 Department of Mathematics, Davangere University, Shivagangothri, Davangere, 577007, India
2 Institut universitaire de Technologie de Longwy, Université de Lorraine186 rue de Lorraine, Cosnes et Romain, 54400, France
3 LMT/ENS-Cachan/CNRS/Université Paris Saclay, Cachan, 94235, France
* Corresponding Author: T. Anusha. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Materials and Energy an Updated Image for 2021)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2023, 19(4), 929-939. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2022.021996
Received 16 February 2022; Accepted 29 March 2022; Issue published 02 November 2022
Abstract
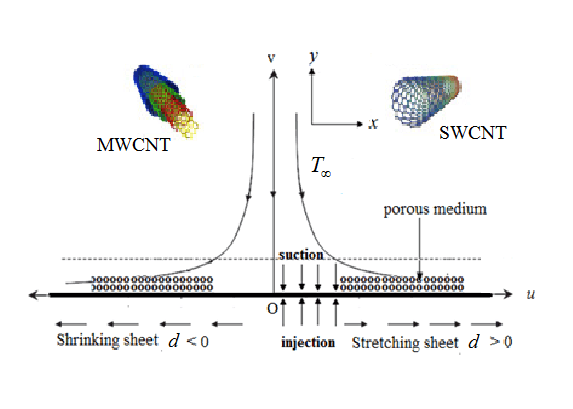
The impacts of radiation, mass transpiration, and volume fraction of carbon nanotubes on the flow of a Newtonian fluid past a porous stretching/shrinking sheet are investigated. For this purpose, three types of base liquids are considered, namely, water, ethylene glycol and engine oil. Moreover, single and multi-wall carbon nanotubes are examined in the analysis. The overall physical problem is modeled using a system of highly nonlinear partial differential equations, which are then converted into highly nonlinear third order ordinary differential equations via a suitable similarity transformation. These equations are solved analytically along with the corresponding boundary conditions. It is found that the carbon nanotubes can significantly improve the heat transfer process. Their potential application in cutting-edge areas is also discussed to a certain extent.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools