 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation of Polymer Flooding
1
Xinjiang Oilfield Company, PetroChina (Experimental Testing Research Institute), Karamay, 834000, China
2
Xinjiang Conglomerate Reservoir Laboratory, Karamay, 834000, China
3
School of Petroleum Engineering, Yangtze University, Wuhan, 430100, China
* Corresponding Author: Kai Li. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Meshless, Mesh-Based and Mesh-Reduction Methods Based Analysis of Fluid Flow in Porous Media)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2022, 18(6), 1815-1826. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2022.020271
Received 14 December 2021; Accepted 08 March 2022; Issue published 27 June 2022
Abstract
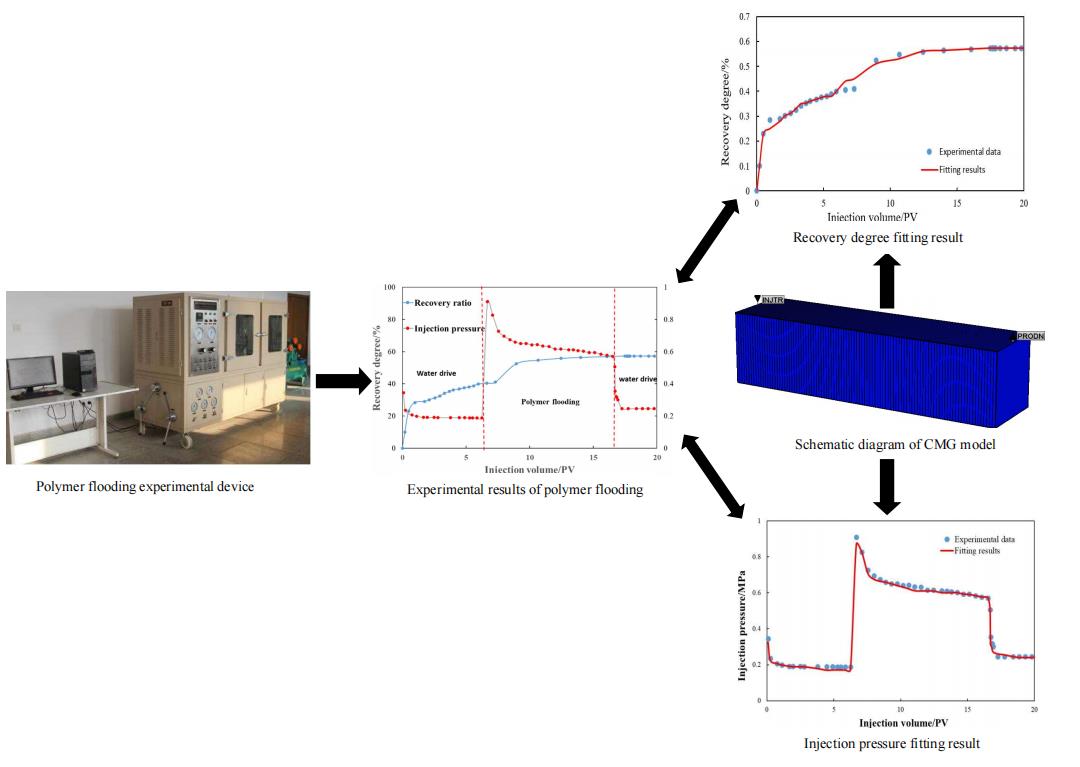
The numerical simulation of polymer flooding is a complex task as this process involves complex physical and chemical reactions, and multiple sets of characteristic parameters are required to properly set the simulation. At present, such characteristic parameters are mainly obtained by empirical methods, which typically result in relatively large errors. By analyzing experimentally polymer adsorption, permeability decline, inaccessible pore volume, viscosity-concentration relationship, and rheology, in this study, a conversion equation is provided to convert the experimental data into the parameters needed for the numerical simulation. Some examples are provided to demonstrate the reliability of the proposed approach.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools