 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Optimal Operation Strategy of Electricity-Hydrogen Regional Energy System under Carbon-Electricity Market Trading
1 Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Electrical Energy Conversion Transmission and Control, Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot, 010080, China
2 School of Electric Power, Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot, 010080, China
3 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, 102206, China
* Corresponding Author: Mushui Wang. Email:
Energy Engineering 2024, 121(3), 619-641. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2023.044862
Received 10 August 2023; Accepted 19 October 2023; Issue published 27 February 2024
Abstract
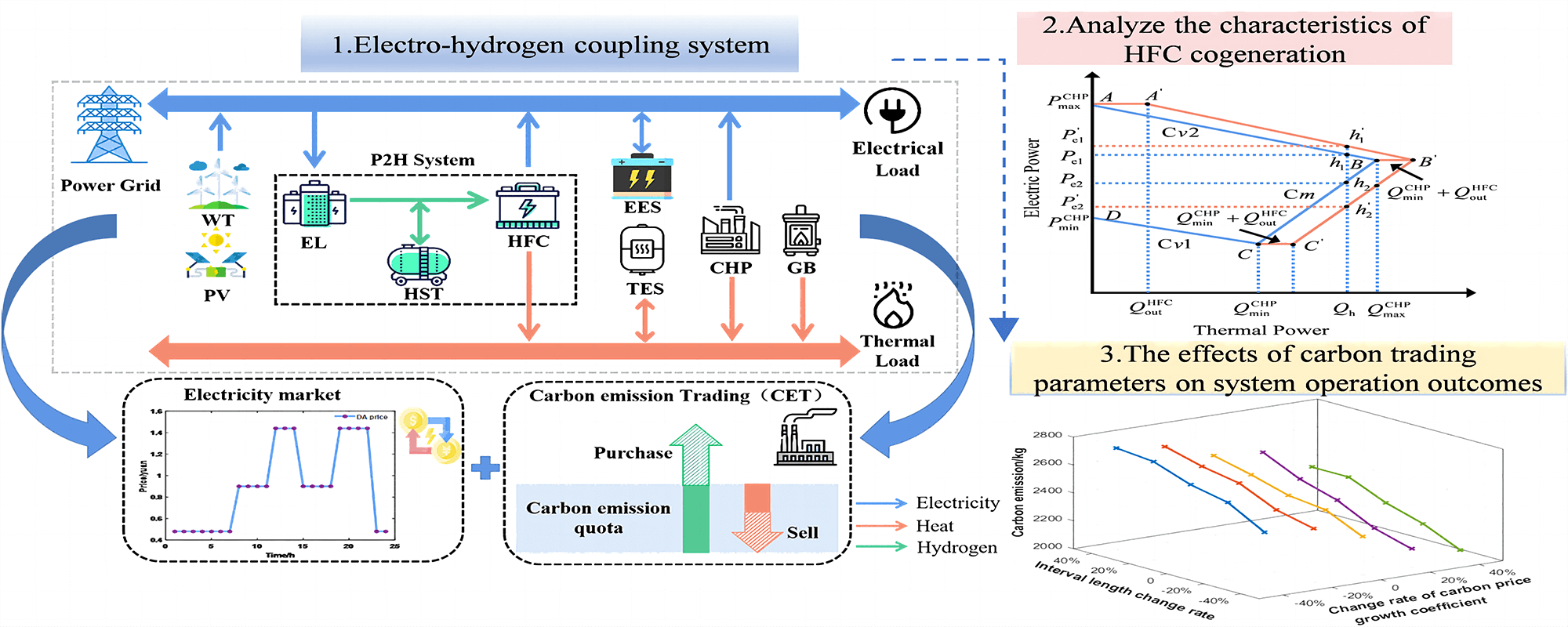
Given the “double carbon” objective and the drive toward low-carbon power, investigating the integration and interaction within the carbon-electricity market can enhance renewable energy utilization and facilitate energy conservation and emission reduction endeavors. However, further research is necessary to explore operational optimization methods for establishing a regional energy system using Power-to-Hydrogen (P2H) technology, focusing on participating in combined carbon-electricity market transactions. This study introduces an innovative Electro-Hydrogen Regional Energy System (EHRES) in this context. This system integrates renewable energy sources, a P2H system, cogeneration units, and energy storage devices. The core purpose of this integration is to optimize renewable energy utilization and minimize carbon emissions. This study aims to formulate an optimal operational strategy for EHRES, enabling its dynamic engagement in carbon-electricity market transactions. The initial phase entails establishing the technological framework of the electricity-hydrogen coupling system integrated with P2H. Subsequently, an analysis is conducted to examine the operational mode of EHRES as it participates in carbon-electricity market transactions. Additionally, the system scheduling model includes a stepped carbon trading price mechanism, considering the combined heat and power generation characteristics of the Hydrogen Fuel Cell (HFC). This facilitates the establishment of an optimal operational model for EHRES, aiming to minimize the overall operating cost. The simulation example illustrates that the coordinated operation of EHRES in carbon-electricity market transactions holds the potential to improve renewable energy utilization and reduce the overall system cost. This result carries significant implications for attaining advantages in both low-carbon and economic aspects.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools