 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Location and Capacity Determination Method of Electric Vehicle Charging Station Based on Simulated Annealing Immune Particle Swarm Optimization
1 Key Laboratory of Smart Grid of Education Ministry, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, China
2 Tianjin Electric Power Company, State Grid, Tianjin, 300010, China
* Corresponding Author: Yanbo Che. Email:
Energy Engineering 2023, 120(2), 367-384. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2023.023661
Received 07 May 2022; Accepted 11 June 2022; Issue published 29 November 2022
Abstract
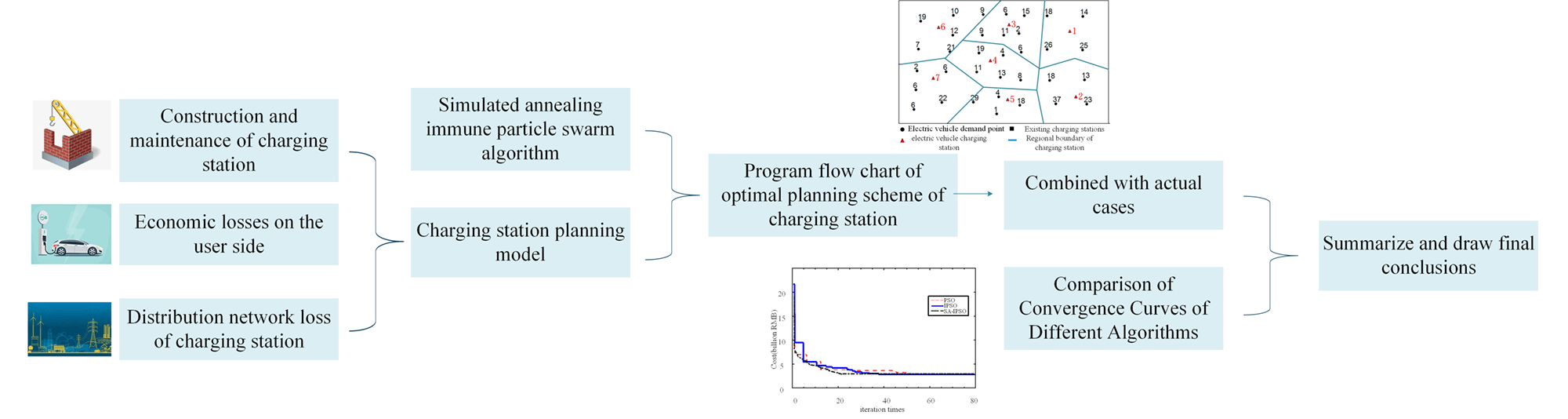
As the number of electric vehicles (EVs) continues to grow and the demand for charging infrastructure is also increasing, how to improve the charging infrastructure has become a bottleneck restricting the development of EVs. In other words, reasonably planning the location and capacity of charging stations is important for development of the EV industry and the safe and stable operation of the power system. Considering the construction and maintenance of the charging station, the distribution network loss of the charging station, and the economic loss on the user side of the EV, this paper takes the node and capacity of charging station planning as control variables and the minimum cost of system comprehensive planning as objective function, and thus proposes a location and capacity planning model for the EV charging station. Based on the problems of low efficiency and insufficient global optimization ability of the current algorithm, the simulated annealing immune particle swarm optimization algorithm (SA-IPSO) is adopted in this paper. The simulated annealing algorithm is used in the global update of the particle swarm optimization (PSO), and the immune mechanism is introduced to participate in the iterative update of the particles, so as to improve the speed and efficiency of PSO. Voronoi diagram is used to divide service area of the charging station, and a joint solution process of Voronoi diagram and SA-IPSO is proposed. By example analysis, the results show that the optimal solution corresponding to the optimisation method proposed in this paper has a low overall cost, while the average charging waiting time is only 1.8 min and the charging pile utilisation rate is 75.5%. The simulation comparison verifies that the improved algorithm improves the operational efficiency by 18.1% and basically does not fall into local convergence.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools