 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Management of Networked Smart Railway Stations Considering Regenerative Braking, Energy Storage System, and Photovoltaic Units
1 School of Railway Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology, Tehran, 13114-16846, Iran
2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Kashan, Kashan, 8731753153, Iran
3 Research and Innovational Center for Electrical Engineering (RICE), Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of West Bohemia (UWB), Pilsen, 30100, Czech Republic
* Corresponding Author: Seyed Saeed Fazel. Email:
Energy Engineering 2023, 120(1), 69-86. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2022.024121
Received 24 May 2022; Accepted 10 August 2022; Issue published 27 October 2022
Abstract
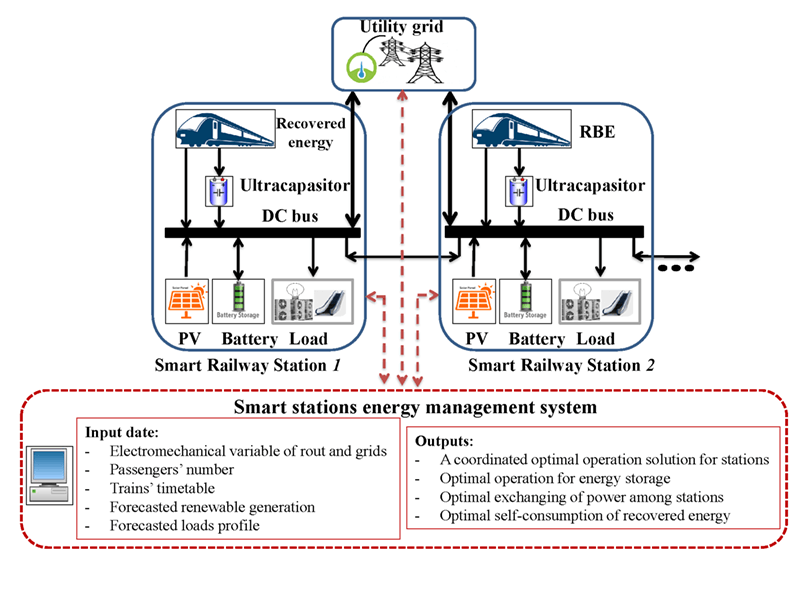
The networking of microgrids has received significant attention in the form of a smart grid. In this paper, a set of smart railway stations, which is assumed as microgrids, is connected together. It has been tried to manage the energy exchanged between the networked microgrids to reduce received energy from the utility grid. Also, the operational costs of stations under various conditions decrease by applying the proposed method. The smart railway stations are studied in the presence of photovoltaic (PV) units, energy storage systems (ESSs), and regenerative braking strategies. Studying regenerative braking is one of the essential contributions. Moreover, the stochastic behaviors of the ESS’s initial state of energy and the uncertainty of PV power generation are taken into account through a scenario-based method. The networked microgrid scheme of railway stations (based on coordinated operation and scheduling) and independent operation of railway stations are studied. The proposed method is applied to realistic case studies, including three stations of Line 3 of Tehran Urban and Suburban Railway Operation Company (TUSROC). The rolling stock is simulated in the MATLAB environment. Thus, the coordinated operation of networked microgrids and independent operation of railway stations are optimized in the GAMS environment utilizing mixed-integer linear programming (MILP).Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools